Intelligent Information Management
Vol.4 No.2(2012), Article ID:18215,7 pages DOI:10.4236/iim.2012.42005
The Effect of Applying Human Resources Information System in Corporate Performance in the Banking Sector in Jordanian Firms
Computer Information System, Karak University College, Albalqa Applied University, Salt, Jordan
Email: {Moh_8877, haroontarawneh}@yahoo.com
Received November 22, 2011; revised December 19, 2011; accepted December 28, 2011
Keywords: Human Resources (HR); Human Resources Information System (HRIS); Corporate; Motives; Organizational Performance
ABSTRACT
This paper aimed to demonstrate the impact of the effectiveness of the Application of human Resources Management System in Corporate Performance which perspective of workers in the Banking Sector in Jordanian Firm, and to achieve the purpose of the study questionnaire was developed to measure the impact of the effectiveness of the Application of human Resources Management System in Corporate Performance, and the sample consists of the study (500) employees in the banking sector, and used statistical methods appropriate to answer the study questions and test hypotheses. The study found asset of results, including: 1) There is a significant effect between the quality of the output of human resources information system and institutional performance in banking sector in the Jordanian firm; 2) There is a statistically significant effect between motives and corporate performance in the banking sector in the Jordanian firm; 3) There is a significant effect between training and organizational performance in the banking sector in the Jordanian firm. The study was presented a set of recommendations, including: activating the role of human resources information system, where still the information system performs the function of traditional supply the decision maker authorized one to read the outputs historical information when they want, either directly or after completing a series of routine procedures that enable it, without that, this applies to access information system to avoid problems that many occur later. Must go beyond human resources information system (HRIS) traditional role in the process of selection and appointment of the new human resource to work in the organization, which is merely providing information to decision makers about the people who stepped forward to fill a job order that differentiation among those application. That the ambitious goal of that system to provide a base for data (data bank) includes all of the details of the employment available in the market.
1. Introduction
The human resources information system is one of the sub-systems within the information systems that concerns of providing all the historical, present and future information related to human resources, presenting them to the parties interested in these resources whether they are internal or external ones, to identify the value of human resources which are considered the sources that have the greater value in the economic units particularly in the service and industrial projects.
The design of the human resources information systems assists in measuring the value of the human resources in a fiscal way and contributes to plan these resources on the economic unit, as well as the national one through the contribution in drawing the labor and employment policies and the other linked polices as migration, payments, promotions, and motives in a scientific way. The importance of human resources spurs out in the industrial and service projects through affecting the market valve of these economic units in the bank and commercial projects, as to their contribution to the economic processes used by these units and what these resources could form and occupy of the tangible and intangible that could affect in a way or another on the performance continuation of these corporations, as a result, it is necessary to concern all the data related to human resources to be possible to get their benefit in all domains that need more improvement in performance.
This study came out to identify the effect of applying the human resources information systems in the institutional performance in banks sector in Jordan.
2. Background
Using of Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) has been addressed as an opportunity for human resource (HR) professionals to in order to become strategic partners with top management. Human resource information system (HRIS) would help by allowing human resource function to become more efficient and by providing better information for decision-making. But the question remains if HRIS has fulfilled its promise?
The most basic form of HRIS is a system used for gaining, storing, manipulate, analyzing, retrieving and distributing pertinent information about an organization’s human resources. It is often regarded as a service provided to an organization in the form of information [1]. For that, the promise for using of those systems becomes more widespread, so there need to evolve higher level of HRIS. According to Lengnick-Hall and Moritz [2] implementation of HRIS will be at three levels which is: information publishing; transactions automation; and, changing human resource management which conducted in the organization through transforming HR to strategic partner the business. HR as promoted by HRIS start from evolves from information to automation and from information to then transformation. Although HRIS has been deployed widely, but its use in HR management has accord in few numbers of organizations.
According to Walker [3], the evolution of HRIS give more efficient information and save the cost, so HR department will give their attention to analyze current data and its uses, so these data which is more accurate help in strategic decisions making. Similarly, Haines and Petit write [4], “Thus, relieved from many routine paper handling tasks, the human resource professional can hopefully develop a service orientation and participative more fully in strategic decision making”. This paper provides some initial answers to the question of whether HRIS has evolved into the higher forms that Lengnick-Hall and Moritz suggest.
3. Potential Benefits of HRIS
In 1992 Overman [5] done a survey about the advantage of HRIS using, that was HRIS are faster in information processing, information more accurate, improve planning and program development, last thing improve communication of employee. But all these benefits come administrative efficiency didn’t explore the possible strategic advantage as most studies at the time of research. Today many studies recognize the possibility of strategic benefits existence. But these studies failed to explain the way of those benefits to release within an organization, also it failed in gaining the measure about whether those benefits have occurred.
Some authors like [6] explained that the HRIS usage in HR would reduce costs by automation information and number of employees will reduce; through helping of employees to control their own personal information; also HRIS allow to mangers to reach relevant information and data easily, conduct analysis, make decisions, and communicate with others without need to consult an HR professsional. In ideal case the perfect use of HRIS, fewer employees should be needed for performing administrative tasks like record keeping which would give more time to managers to assist through providing data on strategic level. Some of these researchers think that the future is brighter for HRIS by creating new paths for human resources and for the organizations that use HRIS in effective manner. One study even goes as far as to suggest that there is evidence that HRIS can improve shareholder value [7]. A significant problem with deciding whether HRIS benefits the organization is that of measuring the effect of HR and more particularly HRIS on the bottom line. There are few clear cut ways to measure the value of HRIS. While there are measurements for administrative HRIS such as cost reductions in HR departments, it is difficult to measure precisely the return on investment and specific improvements in productivity within the HR departments [8]. Indeed, while the ideal assessment of HRIS success might include hard measures such as ROI, the control of extraneous variables makes this type of measurement of success difficult if not impossible. This is why user satisfaction and perception of the system has often be used as a proxy measure for the effectiveness of the system [4].
4. Administrative and Strategic Implementation of HRIS
In examining the benefits of HRIS there are two extremes, the pure administrative use of HRIS and its strategic use. Ultimately the goal of both is to increase organizational value. HRIS efficiency and administrative effectiveness can be described by studies of administrative HRIS, but the overall efficiency and effectiveness of an organization can only be reached through strategic deployment of the information provided by an HRIS. Administrative HRIS is used in day-to-day operations and it is usually in the form of records that hold employee information. Administrative HR is much more efficient when it is used with IT because HR professionals are better able to handle large amounts of information efficiently. For instance, Watson Wyatt’s survey report [9] concluded that it does not take a high progression of e-HR to reach high HRIS performance on the administrative side. The results showed that a properly integrated e-HR system is the key to the evolution of the system. The survey covered all organization sizes, and the measures used included productivity improvements within the HR Organization, cost reductions, return on investment, and enhanced employee communications. They concluded that by properly implementing an e-HR system an organization should be able to reduce the amount of work for which the HR department is responsible which would then leave HR professionals free to concentrate on performing more strategic roles for the organization. In contrast to administrative HRIS, strategic HRIS is much more difficult to explain and measure because there is no way to be sure that the benefits are a direct result of strategic deployment of an HRIS system. Strategic HRIS consists of tools that assist in decision making. For example strategic decisions may include those associated with recruitment and retaining employees. Much, if not all, of the administrative information held by HRIS can be used to analyze an organization and formulate strategies to increase the value of an HRIS. Some experts also believe that easy access to vital information will become an integrated part of many strategic decision-making processes [10]. But, the possibilities of strategic deployment still remain useless without a way of getting there. The use of Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) has been advocated as an opportunity for human resource (HR).
5. Study Problem
The study problem is included in that companies and economic organizing do not give the sufficient importance for contexts, that regard the human resources which they work in, and this leads to shortage in information systems as providing information related to these resources from the accurate aspect which could contribute to increase their employees performance and lead to serve the economic unit more effectively. Therefore, the study problem came through the following question: what is the effect of the efficiency in applying the systems of human resources administration on the institutional performance in the banks sector in Jordan.
6. Study Importance
The study problem is included in highlighting the importance of human resources as an information system in the economic corporations which could assist in organizing the data of these resources and use them to be in an information from that could give the benefit of improving performance and make it more efficient for what is related to human resources specially when achieving the complementary between it and the human resources information system in these corporations.
Consequently, the importance of the study is summarized in the following question: What is the effect of applying the systems of human resources administration in the organizational performance in the banks sector in Jordan (See Figure 1).
7. Study Goals
• Identifying the concept of human resources information systems and its importance for economic organizations.
• The effect of applying the systems of human resources administration in the organization of performance in the banks sector in Jordan.
• Presenting some recommendations that in turn lead to increase the concern in the human resources information system and its effective role in improving the workers performance.
8. Study Hypotheses
8.1. The Main Hypothesis
There is no significant statistical effect evidence between the efficiency of applying the human resources information systems and the organizational performance in the banks sector in Jordan.
8.2. The Sub-Hypotheses
From the main hypothesis, the following subdivided hypotheses come out:
•There is no significant statistical effect evidence between the quality of human resources information systems outcomes and the organizational performance in banks sector in Jordan.
• There is no significant statistical effect evidence between motives and the organizational performance in the banks sector in Jordan.
• There is no significant statistical effect evidence between training and the organizational performance in banks sector in Jordan.
9. Study Model
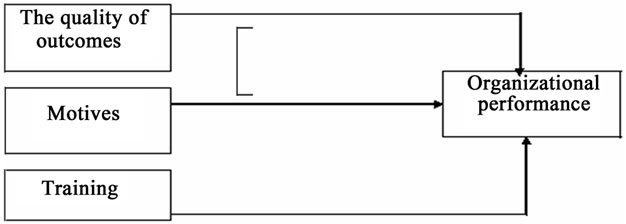
Figure 1. Study model.
10. Procedural Identifications
• The human resources system: it is the system that includes information on the human resources in the organization. It is possible to make use of this information in making various decisions related to human resources as training, development, encouragement and promotion.
• Performance it is bearing the job burdens as responsibilities and duties according to the average that should be performed in the qualified trained work.
• Planning human resources: it is a process that includes the systematic prophecies of the demand or the need for human resources and displays these resources in the organization during a future period.
• to stimulate human resources: on external thing found in the work context which attracts the individual as it is a method to satisfy a desire that the individual feels, or stimuli that mobilize human behavior and assist the performance direction and consequently the performance becomes distinguished.
• Assessment of employee performance: it includes both the competency and the efficiency; the assessment process includes the duty of identifying measuring, and administrating the workers in the organization.
11. Way and Procedures
11.1. Study Approach
This study depended the discretional approach to study the theoretical frame of the previous studies that are related to the topic of human resources administration system through secondary resources of information and the analytical approach to study the relationship between the variables through the fundamental resources.
11.2. Study Population
The study population contains all employees in the commercial banks in Jordan.
11.3. Study Sample
The Study sample was appropriately chosen from the study population, it comprised the employees in the commercial banks in Jordan and (500) questionnaires were distributed.
11.4. Study Method
Primarily, the questionnaire was depended, it was consisting of a group of the study variables and distributed on the study sample.
11.5. Study Reliability
To find the study reliability the study reliability coefficient (Gronbach Alpha) to make sure the questionnaire reliability, its value was 0.81.
11.6. Statistical Treatment
1) The percentages and frequencies of the study sample properties were found.
2) The means and standard deviations of the questionnaire items were found.
3) The multiple regression tests were depended to examine the study hypotheses.
12. Analyzing and Examining the Hypothesis
12.1. Description of Demographical Factors of the Respondents
First: Sex We notice through Table 1 that 75% of the samples are from males category, and 25% are from female code gory.
Second: Qualification We notice from Table 2, that 40% of the sample is of Bachelor holders, 24% are Diploma holders, 21% General Secondary or less, and 15% who are graduates holders.
Three: Experience We notice from Table 3 that 42% of the sample are experienced (6 - 10) years, 26% of the experienced (from 11 - 15) years, and 16% of the experienced are (less than 5 years) and (16 or more).
Fourth: Age We notice from Table 4 that 22% of the sample are of

Table 1. Frequencies and percentages of sex variable.

Table 2. Frequencies and percentages of the academic qualification variable.
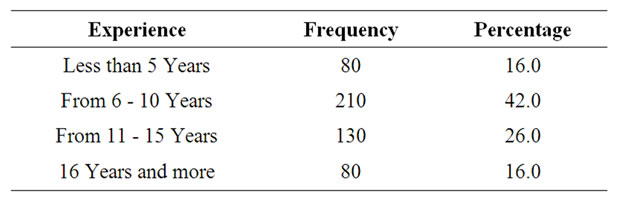
Table 3. Frequencies and percentages of experience variable.
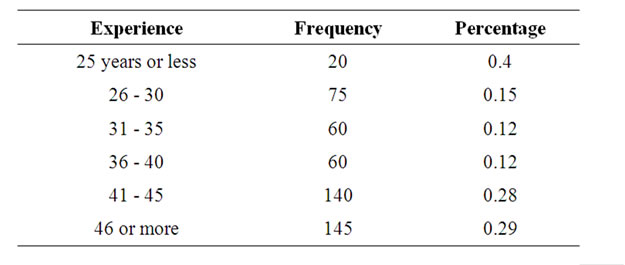
Table 4. Frequencies and percentages of age variable.
the age 16 years or more, 28% are of 41 - 45 years, 15% of the age (26 - 30), 12% are of the age 13 - 35, 36 - 40, and 4% of the age are of 25 or less.
13. Hypotheses Examination
The First Hypothesis:
• There is no significant statistical evidence between the quality of the human resources information systems and the organizational performance in the banks sector in Jordan.
From Tables 5 and 6 it is clear that there is significant statistical effect between the independent variable, the
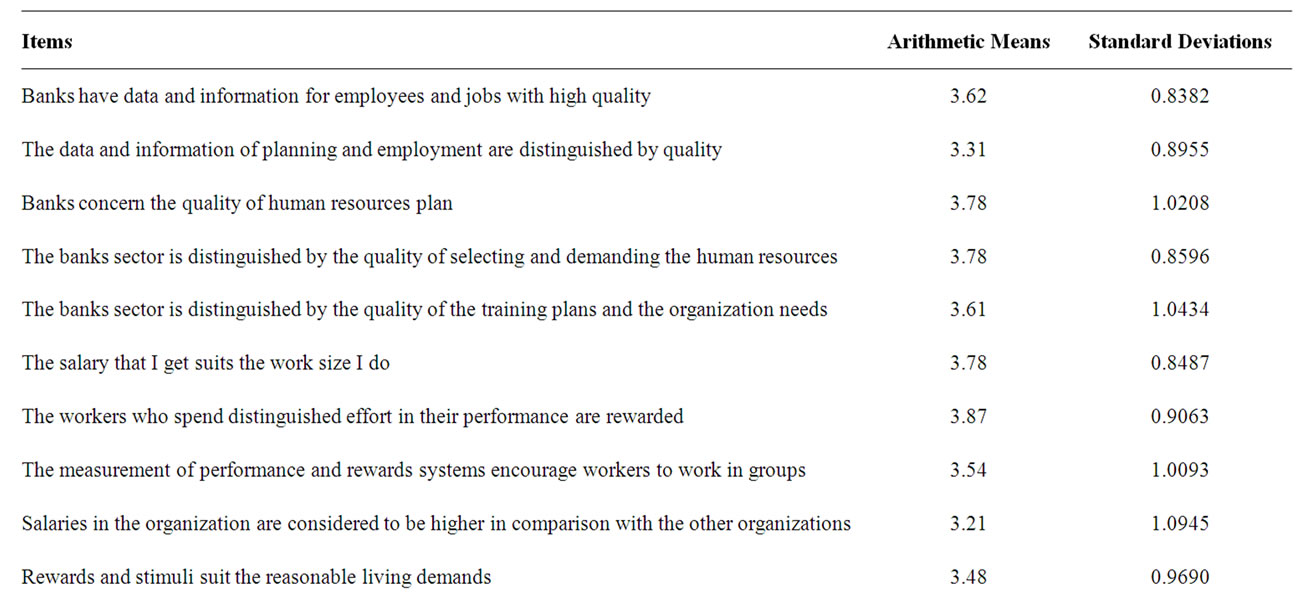


Table 5. The arithmetic means and standard deviations of the study questions.
quality of the systems of the human resources information systems quality and the dependent variable, the organization performance in banks sector in Jordan, depending on that the calculated f value is greater than its scheduled value at the evidence level (0.05 > a), also the quality of the human resources systems outcomes explain 24.2% of the organizational performance in the banks sector in Jordan, depending on the value of the identification coefficient R2 = 0.242 which requires the rejection of the first nihilism hypothesis and substituting it by the alternative hypothesis that assumes no significant statistical effect between the outcomes quality of the human resources information systems and the organization performance in banks sector in Jordan.
The Second Hypothesis:
•There is no significant statistical effect between stimuli and organizational performance in banks sector in Jordan.
From Table 7 there is significant statistical effect between the independent variable of stimuli and the dependent variable, the organization performance in banks sector in Jordan, depending on the calculated f value which is greater in its scheduled value of the evidence level (0.05 > a), also the stimuli explain 30.4% of the organizational performance in the banks sector in Jordan, depending on the value of identification coefficient R2 = 0.304 which requires refusing the first nihilism hypothesis and substituting it with the alternative hypothesis that supposes no significant statistical effect between stimuli and the organization performance in banks sector in Jordan.
The Third Hypothesis:
• There is no significant statistical effect between training and the organizational performance in banks sector in Jordan.
From Table 8 it is clear there is significant statistical effect between the independent variable of training and the dependent variable of the organization performance in banks sector in Jordan, depending on that the calculated f value is greater than its scheduled value at the evidence level (0.05 > a), also training explain 11.7% of the organizational performance in the banks sector in Jordan, depending on the value of identification coefficient R2 = 0.117 which requires rejecting the first nihilism hypothesis and substituting it by the alternative hypothesis that assumes no significant statistical effect between training and organization performance in banks sector in Jordan.
14. Result and Recommendations
14.1. Study Results
• There is significant statistical effect evidence between the quality of the outcomes of the human resources information systems and the organizational performance in bank sector in Jordan.
• There is significant statistical effect evidence between stimuli and the organizational performance in bank sector in Jordan.
• There is significant statistical effect evidence between training and the organizational performance in bank sector in Jordan.
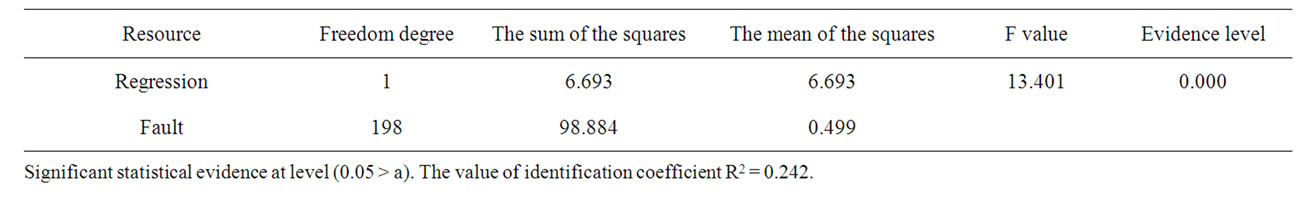
Table 6. The result of multiple regression test of the first hypothesis.
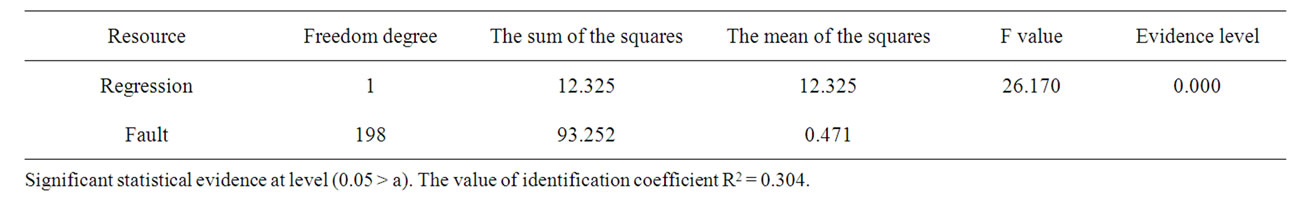
Table 7. The result of multiple regression test of the second hypothesis.
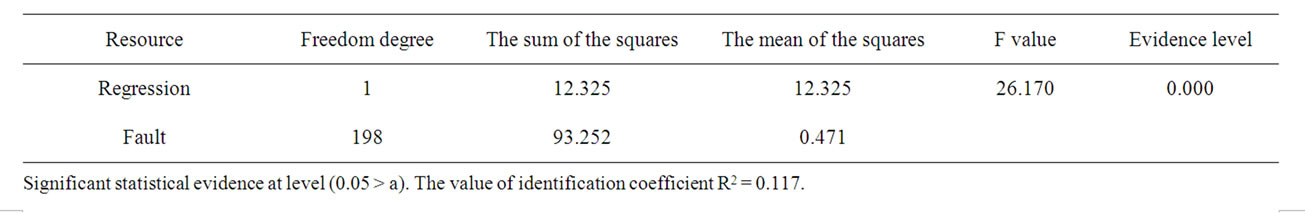
Table 8. The result of multiple regression test of the third hypothesis.
14.2. Recommendations
This research approached the following recommendations:
1) To activate the role of human resource information systems since they still restricted to performing traditional by providing the decision-maker who is authorized to view its outpost with historical information directly when he needs them after the completion of a series of routine procedures that enables him of this, without applying this on the possibility of making use of the information system of human resources in avoiding problems that may occur later on.
2) The human resources information system should exceed its traditional role in the process of selecting and assigning the new human resources to work in the organization, which is represented in just providing the information for the decision-makers about applicants who applied for a specific job to make a comparison among these applicant, but the responsible of human resources information system in the organizations should provide an information base which includes all details about available labor in the market.
3) Assuring the success of human resources information system to present reports about human resources that are expected to deviate them from work in the suitable time to assist the decision maker to take the appropriate decision, and to make the organization avoids any obstacles or confusion in work during the period between leaving the human resource for its work and the replacement of another one in its place, this reduces the looses that way result from this to the minimum possible limit through offering the early opportunities to select and rehabilitate the human resource candidate to occupy that job before assigning him officially, as a result, the human resources information system becomes more effective in achieving the goals and quality and this is reflected on the organization in achieving its goals.
4) The serious treatment with complaints that the human resources provides them in the organization leads to guide the decisions made and consequently, the human resources information systems in the organization should have an experienced system in how to deal with these complaints and consequently provide the decision = makers with the appropriate alternatives to deal with the complaints and the mechanisms of avoiding the occurrence of such complaints.
REFERENCES
- S. I. Tannenbaum, “Human Resource Information Systems: User Group Implications,” Journal of Systems Management, Vol. 41, No. 1, 1990, pp. 27-32.
- M. L. Lengnick-Hall and S. Moritz, “The Impact of e-HR on the Human Resource Management Function,” Journal of Labor Research, Vol. 24, No. 3, 2003, pp. 365-379. doi:10.1007/s12122-003-1001-6
- A. J. Walker, “How the Web and Other Trends Are Changing Human Resources,” In: J. W. Alfred, Ed., WebBased Human Resources, McGraw-Hill, New York, 2001.
- V. Y. Haines and A. Petit, “Conditions for Successful Human Resource Information Systems,” Human Resource Management, Vol. 36, No. 2, 1997, pp. 261-275. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-050X(199722)36:2<261::AID-HRM7>3.0.CO;2-V
- S. Overman, “Reaching for the 21st Century,” HR Magazine, Vol. 37, 1992, pp. 61-63.
- Y. Awazu and K. C. Desouza, “Knowledge Management,” HRMagazine, Vol. 48, No. 11, 2003, p. 107.
- D. Brown, “eHR-Victim of Unrealistic Expectations,” Canadian HR Reporter, Vol. 15, No. 16, 2002, pp. 1-6.
- J. Mayfield, M. Mayfield and S. Lunce, “Human Resource Information Systems: A Review and Model Development,” Advances in Competitiveness Research, Vol. 11, No. 1, 2003, pp. 139-151.
- W. Wyatt, “e-HR: Getting Results along the Journey,” 2002 Survey, 2002. http://www.watsonwyatt.com/research/printable.asp?id=W-524
- K. A. Kovach, A. A. Hughes, P. Fagan and P. Maggitti, “Administrative and Strategic Advantages of HRIS,” Employment Relations Today, Vol. 29, No. 2, 2002, pp. 43- 48. doi:10.1002/ert.10039

