Advances in Pure Mathematics
Vol.06 No.09(2016), Article ID:69714,10 pages
10.4236/apm.2016.69047
Strong Laws of Large Numbers for Fuzzy Set-Valued Random Variables in Gα Space
Lamei Shen, Li Guan
College of Applied Sciences, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing, China
Copyright © 2016 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 7 July 2016; accepted 12 August 2016; published 15 August 2016
ABSTRACT
In this paper, we shall present the strong laws of large numbers for fuzzy set-valued random variables in the sense of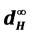 . The results are based on the result of single-valued random variables obtained by Taylor [1] and set-valued random variables obtained by Li Guan [2] .
. The results are based on the result of single-valued random variables obtained by Taylor [1] and set-valued random variables obtained by Li Guan [2] .
Keywords:
Laws of Large Numbers, Fuzzy Set-Valued Random Variable, Hausdorff Metric

1. Introduction
With the development of set-valued stochastic theory, it has become a new branch of probability theory. And limits theory is one of the most important theories in probability and statistics. Many scholars have done a lot of research in this aspect. For example, Artstein and Vitale in [3] had proved the strong law of large numbers for independent and identically distributed random variables by embedding theory. Hiai in [4] had extended it to separable Banach space. Taylor and Inoue had proved the strong law of large numbers for independent random variable in the Banach space in [5] . Many other scholars also had done lots of works in the laws of large numbers for set-valued random variables. In [2] , Li proved the strong laws of large numbers for set-valued random variables in 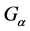 space in the sense of dH metric.
space in the sense of dH metric.
As we know, the fuzzy set is an extension of the set. And the concept of fuzzy set-valued random variables is a natural generalization of that of set-valued random variables, so it is necessary to discuss convergence theorems of fuzzy set-valued random sequence. The limits of theories for fuzzy set-valued random sequences are also been discussed by many researchers. Colubi et al. [6] , Feng [7] and Molchanov [8] proved the strong laws of large numbers for fuzzy set-valued random variables; Puri and Ralescu [9] , Li and Ogura [10] proved convergence theorems for fuzzy set-valued martingales. Li and Ogura [11] proved the SLLN of [12] in the sense of 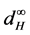 by using the “sandwich” method. Guan and Li [13] proved the SLLN for weighted sums of fuzzy set- valued random variables in the sense of
by using the “sandwich” method. Guan and Li [13] proved the SLLN for weighted sums of fuzzy set- valued random variables in the sense of 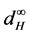 which used the same method. In this paper, what we concerned are the convergence theorems of fuzzy set-valued sequence in
which used the same method. In this paper, what we concerned are the convergence theorems of fuzzy set-valued sequence in 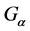 space in the sense of
space in the sense of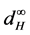 .
.
The purpose of this paper is to prove the strong laws of large numbers for fuzzy set-valued random variables in 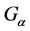 space, which is both the extension of the result in [1] for single-valued random sequence and also the extension in [2] for set-valued random sequence.
space, which is both the extension of the result in [1] for single-valued random sequence and also the extension in [2] for set-valued random sequence.
This paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we shall briefly introduce some concepts and basic results of set-valued and fuzzy set-valued random variables. In Section 3, I shall prove the strong laws of large numbers for fuzzy set-valued random variables in 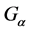 space, which is in the sense of Hausdorff metric
space, which is in the sense of Hausdorff metric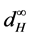 .
.
2. Preliminaries on Set-Valued Random Variables
Throughout this paper, we assume that 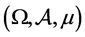 is a complete probability space,
is a complete probability space, 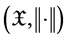 is a real separable
is a real separable
Banach space, 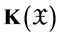 is the family of all nonempty closed subsets of
is the family of all nonempty closed subsets of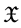 , and
, and 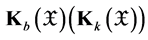 is the family
is the family
of all non-empty bounded closed(compact) subsets of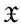 , and
, and 

Let A and B be two nonempty subsets of 

The Hausdorff metric on 
for


The metric space 


Theorems 1.1.2 and 1.1.3). For more general hyperspaces, more topological properties of hyperspaces, readers may refer to the books [15] and [14] .
For each
where 

Let 



as
The following is the equivalent definition of Hausdorff metric.
For each
A set-valued mapping 
function) if, for each open subset O of

For each set-valued random variable F, the expectation of F, denoted by
where 


and
Let 

1) The level set
2) Each v is upper semicontinuous, i.e. for each



3) The support set 
A function v in 
for any
Let 

It is known that v is convex in the above sense if and only if, for any




defined by the relation 

For any two fuzzy sets 
for any
Similarly for a fuzzy set 

for any
The following two metrics in 

Denote



It is well known that


Cauchy sequence 

A fuzzy set-valued random variable (or a fuzzy random set, or a fuzzy random variable in literature) is a mapping


The expectation of any fuzzy set-valued random variable X, denoted by


where the expectation of right hand is Aumann integral. From the existence theorem (cf. [19] ), we can get an equivalent definition: for any
Note that 

3. Main Results
In this section, we will give the limit theorems for fuzzy set-valued random variables in 

Definition 3.1. A Banach space 



1)
2)
3)

Note that Hilbert spaces are 

Lemma 3.2. Let 


random elements in



where A is the positive constant in 3) of definition 3.1.
In order to obtain the main results, we firstly need to prove Lemma 3.5. The following lemma are from [14] (cf. p89, Lemma 3.1.4), which will be used to prove Lemma 3.5.
Lemma 3.3. Let 

for some
Lemma 3.4. (cf. [13] ) For any

Now we prove that the result of Lemma 3.3 is also true for fuzzy sets.
Lemma 3.5. Let 


for some
Proof. By (3.1), we can have
and
for

and
By Lemma 3.4, take an

Then for
Consequently,
Since the first two terms on the right hand converge to 0 in probability one, we have
but 
Theorem 3.6. Let 




where 



Proof. Define
Note that 


fuzzy set-valued random variables. When


And from

Since convergence in the mean implied convergence in probability, Ito and Nisios result in [9] for independent random elements (cf. Section 4.5) provides that
So, for any n, m ≥ 1, m > n, by triangle inequality we have
It means 




Next we shall prove that 


For any fixed n, m, there exists a sequence
That means there exist a sequence
Then by Cr inequality, dominated convergence theorem and Lemma 3.2, we have
for each n and m.
Then, we know 



with probability 1 in the sense of

So, we can prove that
with probability 1 in the sense of




bility 1 in the sense of
From Theorem 3.6, we can easily obtain the following corollary.
Corollary 3.7. Let 



a sequence of independent fuzzy set-valued random variables in





implies that
converges with probability one in the sense of
Proof. Let
If

That is

If

That is

Then as the similar proof of Theorem 3.6, we can prove both 

one in the sense of
Acknowledgements
We thank the Editor and the referee for their comments. Research of Li Guan is funded by the NSFC (11301015, 11571024, 11401016).
Cite this paper
Lamei Shen,Li Guan, (2016) Strong Laws of Large Numbers for Fuzzy Set-Valued Random Variables in G<sub>α</sub> Space. Advances in Pure Mathematics,06,583-592. doi: 10.4236/apm.2016.69047
References
- 1. Taylor, R.L. (1978) Lecture Notes in Mathematics. Springer-Verlag, 672.
- 2. Li, G. (2015) A Strong Law of Large Numbers for Set-Valued Random Variables in Gα Space. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, 3, 797-801.
http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jamp.2015.37097 - 3. Artstein, Z. and Vitale, R.A. (1975) A Strong Law of Large Numbers for Random Compact Sets. Annals of Probability, 3, 879-882.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1214/aop/1176996275 - 4. Hiai, F. (1984) Strong Laws of Large Numbers for Multivalued Random Variables, Multifunctions and Integrands. In: Salinetti, G., Ed., Lecture Notes in Mathematics, Vol. 1091, Springer, Berlin, 160-172.
- 5. Taylor, R.L. and Inoue, H. (1985) A Strong Law of Large Numbers for Random Sets in Banach Spaces. Bulletin of the Institute of Mathematics Academia Sinica, 13, 403-409.
- 6. Colubi, A., López-Díaz, M., Domnguez-Menchero, J.S. and Gil, M.A. (1999) A Generalized Strong Law of Large Numbers. Probability Theory and Related Fields, 114, 401-417.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s004400050229 - 7. Feng, Y. (2004) Strong Law of Large Numbers for Stationary Sequences of Random Upper Semicontinuous Functions. Stochastic Analysis and Applications, 22, 1067-1083.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1081/SAP-120037631 - 8. Molchanov, I. (1999) On Strong Laws of Large Numbers for Random Upper Semicontinuous Functions. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 235, 249-355.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmaa.1999.6403 - 9. Puri, M.L. and Ralescu, D.A. (1991) Convergence Theorem for Fuzzy Martingales. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 160, 107-121.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0022-247X(91)90293-9 - 10. Li, S. and Ogura, Y. (2003) A Convergence Theorem of Fuzzy Valued Martingale in the Extended Hausdorff Metric H∞. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 135, 391-399.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(02)00145-8 - 11. Li, S. and Ogura, Y. (2003) Strong Laws of Numbers for Independent Fuzzy Set-Valued Random Variables. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 157, 2569-2578.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2003.06.011 - 12. Inoue, H. (1991) A Strong Law of Large Numbers for Fuzzy Random Sets. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 41, 285-291.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0165-0114(91)90132-A - 13. Guan, L. and Li, S. (2004) Laws of Large Numbers for Weighted Sums of Fuzzy Set-Valued Random Variables. International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowledge-Based Systems, 12, 811-825.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1142/S0218488504003223 - 14. Li, S., Ogura, Y. and Kreinovich, V. (2002) Limit Theorems and Applications of Set-Valued and Fuzzy Set-Valued Random Variables. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-9932-0 - 15. Beer, G. (1993) Topologies on Closed and Closed Convex Sets. Mathematics and Its Applications. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Holland.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-8149-3 - 16. Chen, Y. (1984) Fuzzy Systems and Mathematics. Huazhong Institute Press of Science and Technology, Wuhan. (In Chinese)
- 17. Klement, E.P., Puri, L.M. and Ralescu, D.A. (1986) Limit Theorems for Fuzzy Random Variables. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A, 407, 171-182.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1986.0091 - 18. Puri, M.L. and Ralescu, D.A. (1986) Fuzzy Random Variables. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 114, 406-422.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0022-247X(86)90093-4 - 19. Li, S. and Ogura, Y. (1996) Fuzzy Random Variables, Conditional Expectations and Fuzzy Martingales. Journal of Fuzzy Mathematics, 4, 905-927.

















































