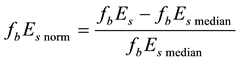International Journal of Geosciences
Vol.06 No.07(2015), Article ID:58085,9 pages
10.4236/ijg.2015.67053
On the Diurnal Dependence of fbEs-Variations Due to Earthquakes
Elena V. Liperovskaya1, Claudia-Veronika Meister2,3, Dieter H. H. Hoffmann2,3, Alexandra S. Silina1, Natalia E. Vasil’eva1
1Institute of Physics of the Earth of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia
2Institut für Kernphysik, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Darmstadt, Germany
3Graduate School of Excellence Energy Science and Engineering, Darmstadt, Germany
Email: liper@ifz.ru, c.v.meister@skmail.ikp.physik.tu-darmstadt.de
Copyright © 2015 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 5 June 2015; accepted 13 July 2015; published 17 July 2015
ABSTRACT
In the present work, disturbances of the half-transparency frequency
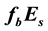 of the ionospheric sporadic E-layer are investigated in connection with earthquakes. The
of the ionospheric sporadic E-layer are investigated in connection with earthquakes. The
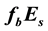 -frequency is propor- tional to the square root of the maximum ionisation density of the sporadic E-layer. In this work, it is shown that in 2/3 of the cases, two days before a seismic shock with magnitude
-frequency is propor- tional to the square root of the maximum ionisation density of the sporadic E-layer. In this work, it is shown that in 2/3 of the cases, two days before a seismic shock with magnitude
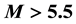 and on the day of the shock, an increase of the
and on the day of the shock, an increase of the
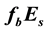 -frequency is obtained at sunset hours at distances from the epicenter
-frequency is obtained at sunset hours at distances from the epicenter
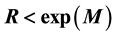 km. In contrast, before sunrise, the
km. In contrast, before sunrise, the
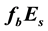 -value decreases. The data analysed are obtained by the three vertical ionospheric sounding stations “Kokubunji”, “Yamagawa”, and “Wakkanai” during some tens of years.
-value decreases. The data analysed are obtained by the three vertical ionospheric sounding stations “Kokubunji”, “Yamagawa”, and “Wakkanai” during some tens of years.
Keywords:
Earthquake Precursors, Ionosphere, Sporadic E-Layer, Half-Transparency Frequency, Earthquake Preparation Region, Solar Influence on E-Layer, Geomagnetic Influence on E-Layer

1. Introduction
Recently, it has been experimentally verified that at different altitudes above the Earth’s surface, and accor- dingly in different ionospheric layers, disturbances are observed, which occur―in comparison with the so-called non-seismic background time―with large probability at a special daytime some days before earthquakes [1] . Of late, in connection with the search for ionospheric precursors of earthquakes, variations of different ionospheric parameters are being discussed. There are regular parameters among them like the frequencies
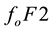 and
and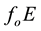 , but it also exists parameters which characterize irregular processes. To them, for instance, the half-transparency frequency
, but it also exists parameters which characterize irregular processes. To them, for instance, the half-transparency frequency
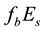 of the sporadic E-layer
of the sporadic E-layer
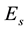 belongs. Many scientific works are devoted to effects of earthquake preparation in
belongs. Many scientific works are devoted to effects of earthquake preparation in
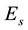 -layers.
-layers.
It is found that earthquake preparatory anomalies of ionospheric parameters are observed most often 1 - 5 days before seismic shocks with magnitudes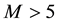 . Besides it is perceived that the anomalies’ occurrence is connected with the magnitude of the earthquakes and with their distances to the epicentres [2] -[6] .
. Besides it is perceived that the anomalies’ occurrence is connected with the magnitude of the earthquakes and with their distances to the epicentres [2] -[6] .
In the work [7] , a statistical analysis of pre-earthquake ionospheric anomalies is performed, which are registered by continuous GPS TEC (Global Positioning System-Total Electron Content) measurements for earthquakes with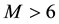 . It is found that anomalies are obtained one-two days before seismic shocks (on the days (−2, −1)) most often. In [8] , seismo-ionospheric effects in the temporary run of the frequency
. It is found that anomalies are obtained one-two days before seismic shocks (on the days (−2, −1)) most often. In [8] , seismo-ionospheric effects in the temporary run of the frequency
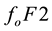 are observed 1-5 days before earthquakes with
are observed 1-5 days before earthquakes with
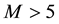 from 12 to 18 h LT. Before very strong earthquakes with
from 12 to 18 h LT. Before very strong earthquakes with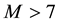 , sometimes anomalies are observed in the
, sometimes anomalies are observed in the
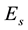
Anomalous
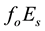
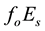
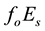
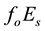
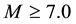
Daytime dependences of the occurrence of pre-earthquake anomalies are investigated in only some works. In the works by Ondoh and Hayakawa [9] and by Ondoh [11] , an anomaly of the
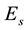
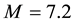
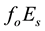
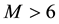
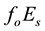
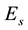
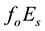
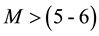
The distance R from the epicentre, at which earthquake precursors are observed in the ionosphere, amounts, as a rule, to some hundreds of kilometres. On the average, it may be estimated by the formula
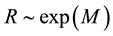
In the present work, an analysis of the
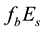
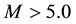
2. Method of Data Analysis
Here, ionospheric effects of earthquakes are investigated by using data recorded by the vertical sounding stations “Kokubunji” (Tokyo) (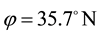
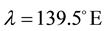
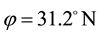
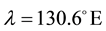
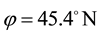
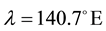
Sporadic
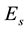
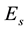
In the order of magnitude, the maximum plasma concentration of the
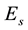
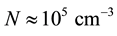
The thickness of the sporadic layers, i.e. their vertical dimensions, varies between a few hundred metres and a few kilometres. One of the main characteristic frequencies which is observed by ionograms of vertical sounding stations is the screening (or half-transparency) frequency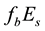
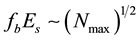
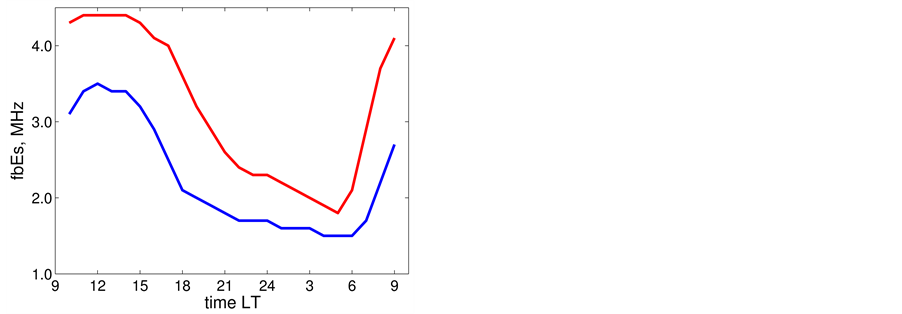
Let us investigate the daytime variations of the
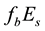
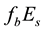
The
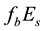
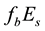
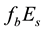
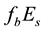
In the daytime dependence of the
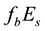
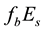
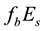
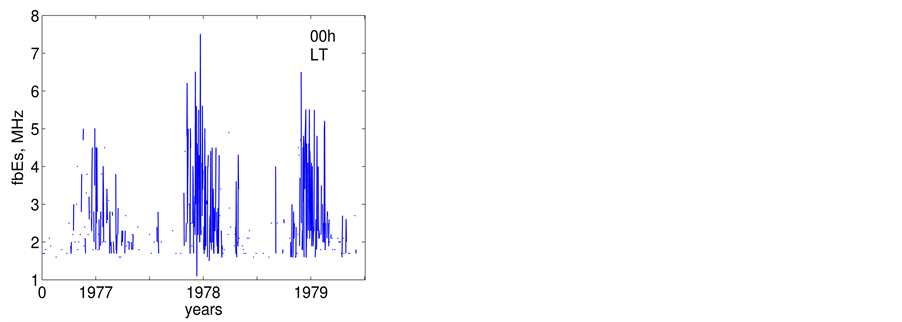
Figure 1. Monthly-mean
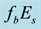
Figure 2. Daytime dependence of the
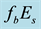
To obtain observable variations of the
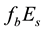
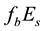
is calculated. The median value of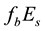
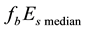
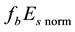
It has to be underlined that the form of the
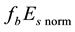
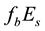
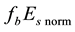
It should be mentioned that the maximum
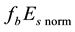
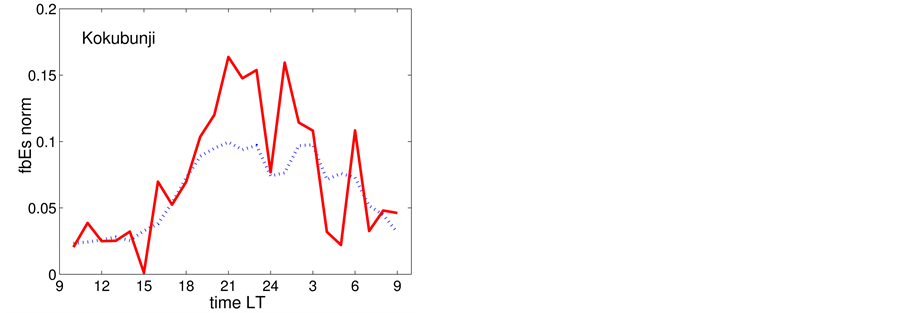
Now the influence of the processes of earthquake preparation on the daytime behaviour of the dimensionless parameter
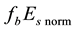
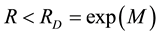
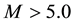
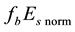
Let us study the dependence of
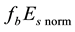
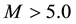
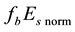
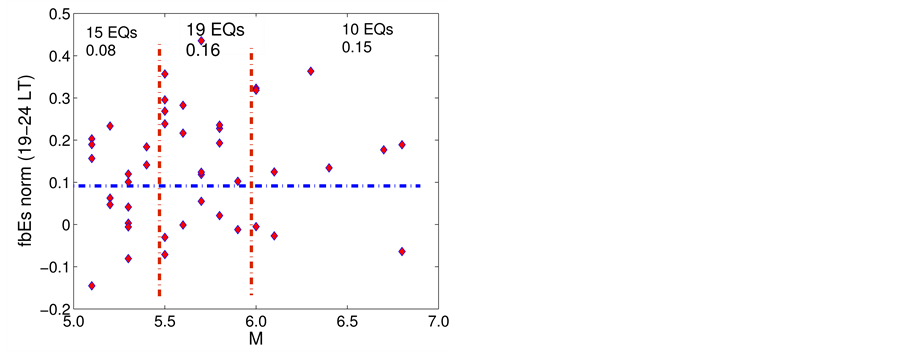
The result of the study is presented in Figure 4. From the analysis follows, that an anomalous increase of
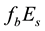
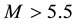
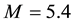
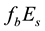
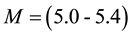
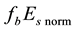
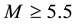
Figure 3. Result of the superposition of epoches. Normalized frequency
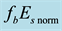

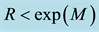

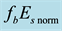
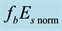
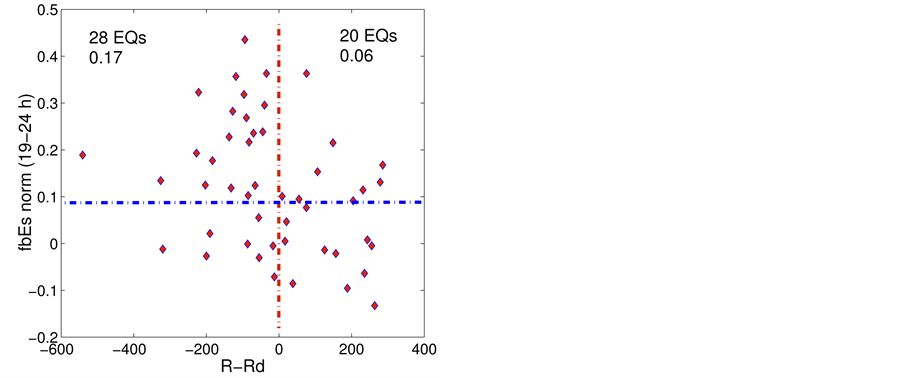
Next, the influence of the distance between the epicentre and the sounding station on
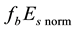
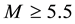
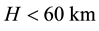
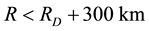
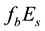
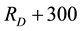
Figure 4.
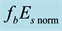

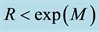

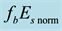
Figure 5.
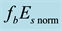
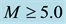
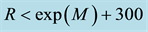

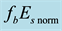
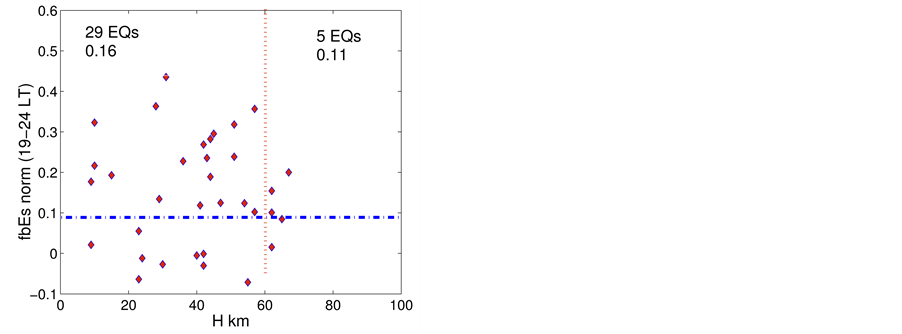
Finally, the anomalous
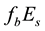
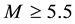
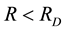
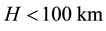
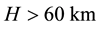
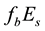
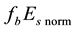
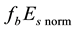
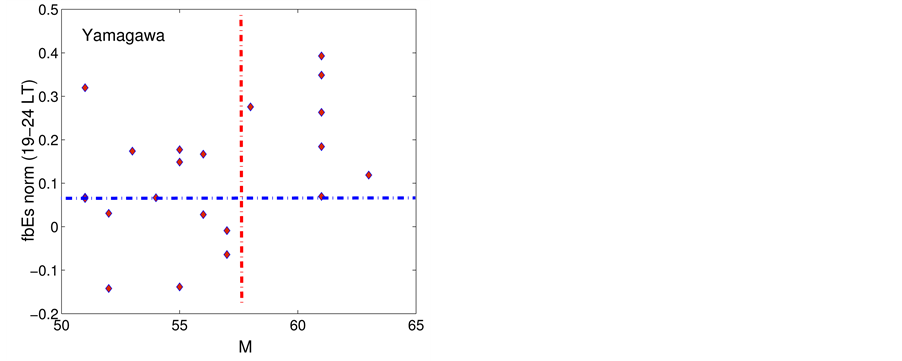
Let us study analogous dependences of pre-earthquake effects on the daytime dependence for other vertical sounding stations. In case of the station “Yamagawa” (Figure 7) it is found, that an increase of
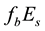
Figure 6.
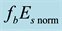
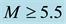
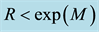

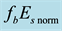
Figure 7.
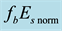
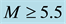
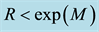

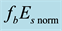
observed for earthquakes with magnitudes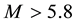
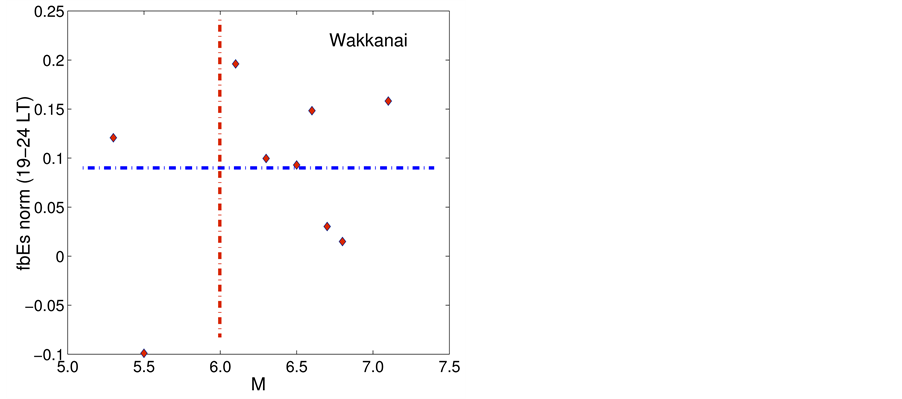
Studying data registered by the vertical sounding station “Wakkanai” (Figure 8), an increase of
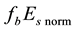
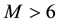
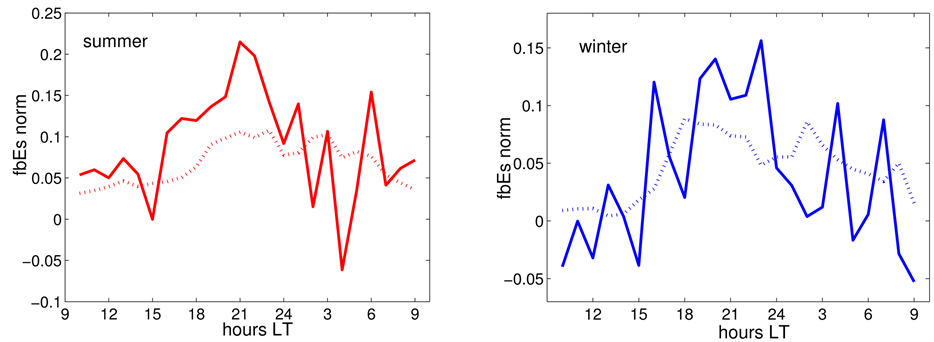
To demonstrate the seasonal dependence of the variations of the normalized frequency
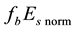
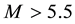
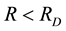
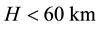
Figure 8.
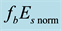
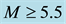
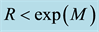

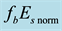
Figure 9. Daytime dependence of
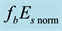
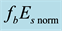
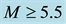
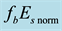
The full lines show the
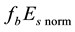
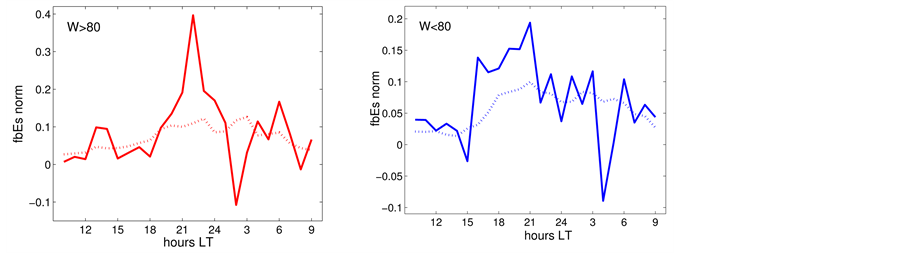
Next, the influence of the solar activity on the diurnal behaviour of
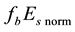
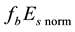
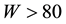
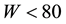
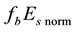
The background values of
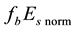
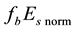
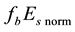
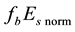
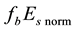
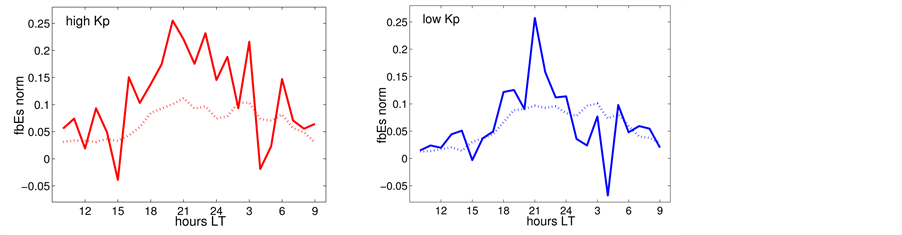
Finally, the influence of geomagnetic disturbances on the diurnal
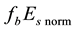
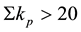
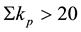
Using the data of the station “Kokubunji”, in Figure 11, the daytime behaviour of
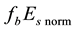
Figure 10. Daytime dependence of
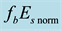
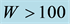
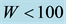
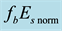
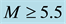
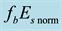
Figure 11. Daytime dependence of
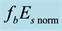
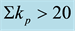
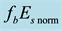
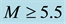
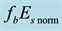
different levels of geomagnetic activity. All data are divided into two parts, into days with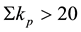
The results of the analysis are presented in Figure 11. It has to be noticed that, considering the data of the station “Kokubunji”, in the time interval from midnight until the morning hour of 05 LT,
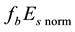
3. Conclusions
Analysing
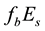
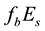
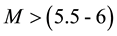
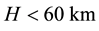
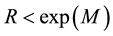
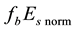
The radius R of the earthquake preparation region may be estimated based on the Dobrovolsky formula
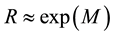
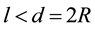
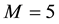
Maximum amplitudes of the disturbances in the ionosphere occur at almost vertical propagation of the disturbance from the Earth’s surface to larger altitudes. Thus the authors suggest that an influence on the lower part of the ionosphere may be observed in connection with earthquakes, the preparation region of which contains the location of the vertical sounding station.
This work was presented at the Spring Conference “Plasma Physics” of the German Physical Society in Bochum, 2-5 March 2015.
Cite this paper
Elena V.Liperovskaya,Claudia-VeronikaMeister,Dieter H. H.Hoffmann,Alexandra S.Silina,Natalia E.Vasil’eva,11, (2015) On the Diurnal Dependence of fbEs-Variations Due to Earthquakes. International Journal of Geosciences,06,656-665. doi: 10.4236/ijg.2015.67053
References
- 1. Pulinets, S.A. and Boyarchuk, K.A. (2004) Ionospheric Precursors of Earthquakes. Springer, Berlin.
- 2. Liperovsky, V.A., Pokhotelov, O.A., Liperovskaya, E.V., Parrot, M., Meister, C.-V. and Alimov, A. (2000) Modification of Sporadic E-Layers Caused by Seismic Activity. Survey in Geophysics, 21, 449-486. http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/A:1006711603561
- 3. Pulinets, S.A. and Davidenko, D. (2014) Ionospheric Precursors of Earthquakes and Global Electric Circuit. Advances in Space Research, 53, 709-723. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2013.12.035
- 4. Liperovskaya, E.V., Meister, C.-V., Pokhotelov, O.A., Parrot, M., Bogdanov, V.V. and Vasilieva, N.E. (2006) On Es-Spread Effects in the Ionosphere Connected to Earthquakes. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 6, 740-744. http://dx.doi.org/10.5194/nhess-6-741-2006
- 5. Liperovskaya, E.V., Silina, A.S., Liperovsky, V.A., Meister, C.-V., Hoffmann, D.H.H. and Biagi, P.-F. (2012) Midnight Variations of Es-Spread of the Ionosphere before Earthquakes. Annales of Geophysics, 55, 119-123.
- 6. Liperovskaya, E.V., Meister, C.-V., Hoffmann, D.H.H. and Silina. A.S. (2015) On Diurnal Dependence and Spatial Scales of Seismo-Ionospheric Effects in the E-Layer. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, in Press. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2015.01.008
- 7. Liu, J.Y., Chuo, Y.J., Shan, S.J., Tsai, Y.B., Chen, Y.I., Pulinets, S.A. and Yu. S.B. (2004) Pre-Earthquake Ionospheric Anomalies Registered by Continuous GPS TEC Measurements. Annales Geophysicae, 22, 1585-1593. http://dx.doi.org/10.5194/angeo-22-1585-2004
- 8. Liu, J.Y. Chen, Y.I. Chuo, Y.J. and Chen. C.S. (2006) A Statistical Investigation of Preearthquake Ionospheric Anomaly. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111, A05354.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2005JA011333 - 9. Ondoh, T. and Hayakawa, M. (1999) Anomalous Occurrence of Sporadic-E Layers before the Hyogoken Nanbu Earthquake, M7.2 of January 17, 1995. In: Hayakawa, M., Ed., Atmospheric and Ionospheric Electromagnetic Phenomena Associated with Earthquakes, TERRAPUB, Tokyo, 629-639.
- 10. Ondoh, T. and Hayakawa, M. (2006) Synthetic Study of Precursory Phenomena of the M7.2 Hyogoken Nanbu Earthquake. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 31, 378-388.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2006.02.017 - 11. Ondoh, T. (2004) Anomalous Sporadic-E Ionization before a Great Earthquake. Advances in Space Research, 34, 1830-1835. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2003.05.044
- 12. Chuo, Y.J., Liu, J.Y., Kamogawa, M. and Chen. Y.I. (2002) The Anomalies in the Prior to Taiwan Earthquakes. Seismo-Electromagnetics: Lithosphere-Atmosphere-Ionosphere Couplings, Hayakawa M., Molchanov O.A. (eds.), TERRAPUB, Tokyo, 309-312.
- 13. Liperovsky, V.A., Meister, C.-V., Liperovskaya, E.V., Vasil’eva, N.E. and Alimov, O.A. (2005) On Es-Spread Effects in the Ionosphere before Earthquakes. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 5, 59-62. http://dx.doi.org/10.5194/nhess-5-59-2005
- 14. Silina, A.S., Liperovskaya, E.V., Vasil'eva, N.E. and Alimov, O.A. (2010) The Influence of the Processes of Earthquakes Preparation on Variations of Parameters of the Ionosphere Sporadic E Layer. 5th International Conference on Solar-Terrestrial Relations and Physics of Earthquake Precursors, Paratunka, 2-7 August 2010, Collection of Reports, eds. Shevtsov B.V., Bogdanov V.V., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky; IKIR FEB RAS, 440-444.
- 15. Dobrovolsky, I.R., Zubkov, S.I. and Myachin, V.I. (1979) Estimation of the Size of Earthquake Preparation Zones. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 117, 1025-1044. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00876083
- 16. Whitehead, J.D. (1989) Recent Work on Mid-Latitude and Equatorial Sporadic E. Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics, 51, 401-424. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0021-9169(89)90122-0