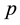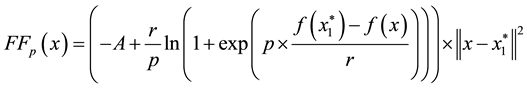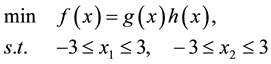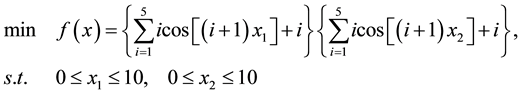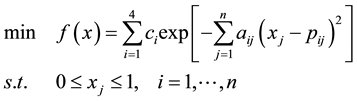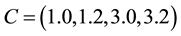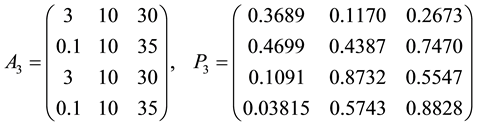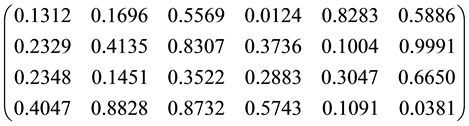Open Journal of Optimization
Vol.04 No.01(2015), Article ID:54745,10 pages
10.4236/ojop.2015.41002
A New Filled Function with One Parameter to Solve Global Optimization
Hongwei Lin1, Huirong Li2
1Department of Basic Courses, Jinling Institute of Technology, Nanjing, China
2Department of Mathematic and Computation Application, Shangluo University, Shangluo, China
Email: linhongwei_jt@hotmail.com, lihuirong417@163.com
Copyright © 2015 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 26 February 2015; accepted 16 March 2015; published 18 March 2015
ABSTRACT
In this paper, a new filled function with only one parameter is proposed. The main advantages of the new filled function are that it not only can be analyzed easily, but also can be approximated uniformly by a continuously differentiable function. Thus, a minimizer of the proposed filled function can be obtained easily by using a local optimization algorithm. The obtained minimizer is taken as the initial point to minimize the objective function and a better minimizer will be found. By repeating the above processes, we will find a global minimizer at last. The results of numerical experiments show that the new proposed filled function method is effective.
Keywords:
Global Optimization, Filled Function Method, Smoothing Technique, Global Minimize, Local Minimizer

1. Introduction
Global optimization methods have wide applications in many fields, such as engineering, finance, management, decision science and so on. The task of global optimization is to find a solution with the smallest or largest objective function value. In this paper, we mainly discuss the method to find the global minimizer of the objective function. For some problems with only one minimizer, there are many local optimization methods available, for instance, the steepest decent method, the Newton method, the trust region method and so on. However, many problems include multiple local minimizers, and most of the existing methods will not be applicable to these problems.
The difficulty for global optimization is to escape from the current local minimizer to a better one. One of the most efficient methods to deal with this issue is the filled function method which was proposed by Ge [1] [2] . The generic framework of the filled function method can be described as follows:
1) An arbitrary point is taken as an initial point to minimize the objective function by using a local optimi- zation method, and a minimizer of the objective function is obtained.
2) Based on the current minimizer of the objective function, a filled function is designed and a point near the current minimizer is used as an initial point to further minimize the filled function. As a result, a minimizer of the filled function will be found. This minimizer falls into a better region (called basin) of the original objective function.
3) The minimizer of the filled function obtained in 2 is taken as an initial point to minimize the objective function and a better minimizer of the objective function will be found.
4) By repeating steps 2 and 3, the number of the local minimizers will be gradually reduced, and a global minimizer will be found at last.
Although the filled function method is an efficient global optimization method and different filled functions have been proposed, there are some drawbacks for the existing filled functions, such as more than one para- meters to be controlled, being sensitive to the parameters and ill-condition. For example, the filled functions proposed in [1] [2] contain exponent term or logarithm term which will cause ill-condition problem; the filled functions proposed in [3] [4] are non-smooth functions to which the usual classical local optimization methods can not be used; the filled functions proposed in [1] [5] [6] have more than one parameter which is difficult to adjust. To overcome these shortcomings, a new filled function with only one parameter is presented. Although it is not a smooth function, it can be approximated uniformly by a continuously differentiable function. Thus its minimizer can be easily obtained. Based on this new filled function, a new filled function method is proposed.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Related concepts of the filled function method are given in Section 2. In Section 3, a new filled function is proposed and its properties are analyzed. Furthermore, an ap- proximate function of the proposed filled function is given. Finally, the method for avoiding numerical difficulty is presented. In Section 4, a new filled function method is proposed and the numerical experiments on several test problems are made. Finally, some concluding remarks are drawn in Section 5.
2. The Related Concepts
Consider the following global optimization problem with a box constraint:
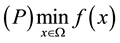
where 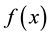 is a twice continuously differentiable function on
is a twice continuously differentiable function on 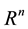 and
and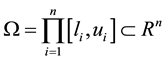 . Generally, we
. Generally, we
assume that 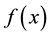 has only a finite number of minimizers and the set of the minimizers is denoted as
has only a finite number of minimizers and the set of the minimizers is denoted as
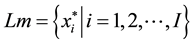 in
in 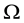 (
(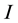 is the number of minimizers of
is the number of minimizers of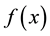 ).
).
Some useful concepts and notations are introduced as follows:
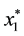 : A local minimizer of
: A local minimizer of 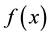 on
on  found so far;
found so far;
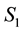 : Set;
: Set;
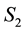 : Set;
: Set;
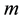 : A constant satisfying
: A constant satisfying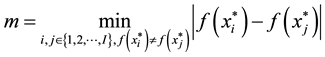 ;
;
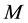

Assumption. All of the local minimizers of 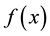
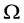
Definition 1 The basin [7] of 
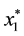
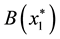
contains
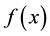

verge to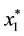
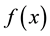
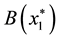

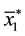
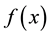
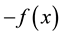
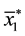


It is obvious that if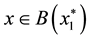



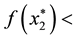

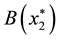




The first concept of the filled function was introduced by Ge [1] [2] . Since the concept of the filled function was introduced, different filled functions are given (e.g., [8] [9] ). A new concept of the filled function was presented which is easier to understand in [8] . It can be described as follows:
The first concept of the filled function was introduced in [1] .
Definition 2 A function 


1) 
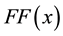
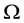
2) 
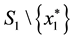
3) if the set 
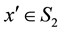

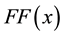
Based on definition 2, we present a new filled function with only one parameter in Section 3.
3. A New Filled Function and Its Properties
Assume that a local minimizer 

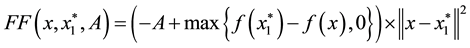
where 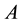
The following theorems will show that the formula (1) is a filled function which satisfies definition 2.
Theorem 1 Suppose 
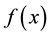
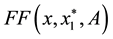
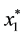
strict local maximizer of 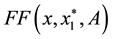

Proof. Since 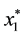

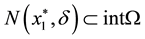
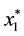


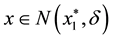


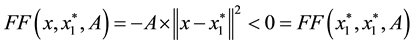
Thus, 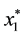

Theorem 2 Suppose 

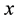
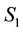
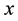
point of 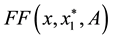

Proof. Due to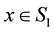
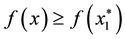

Namely 
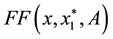
Theorem 3 Suppose 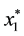

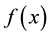


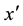
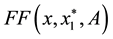
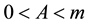
Proof. Since 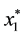
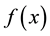
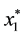
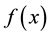
another local minimizer 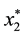
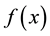

By the definition of 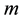




So
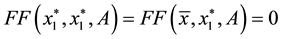
By 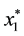
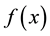

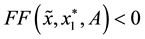
Then, there exists a point 
minimizer of
Furthermore, by the Theorem 2, one has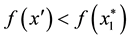
From Theorem 1, 2 and 3, we know that if there is a better local minimizer 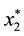
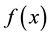
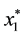
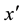
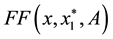
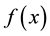

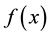
We can find that if 


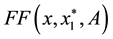

Let
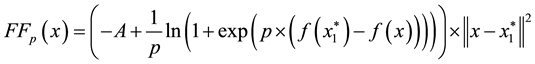
where 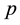
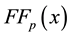
and
we have that the inequality
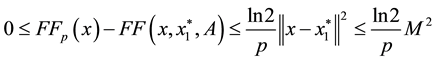
holds. From above discussion, we can see that 
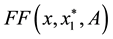

to infinity. Therefore, by selecting a sufficiently large


In order to obtain a more precise minimizer of 


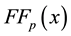
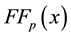
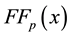
First of all, it is necessary to estimate 
(e.g., take it as
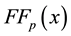

Then, in order to prevent the difficulty of numerical computation, a large 
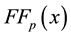

By doing so, the existing shortcomings can be overcome.
4. A New Filled Function Algorithm and Numerical Experiments
4.1. A New Filled Function Algorithm
Based on the theorems and discussions in the previous section, a new filled function algorithm for finding a global minimizer of 
Step 1 (Initialization). Choose the initial values 




are also given in advance, where 



the dimension of the optimization problems. Set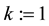
Step 2 Minimize 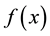



Step 3 Construct
Set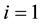
Step 4 If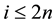

Step 5 Use 
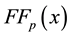

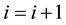
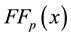
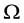



Step 6 If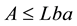
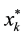

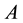
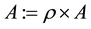
Before we go to the experiments, we have to give some explanations on the above filled function algorithm.
1) In minimization of 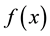

2) In Step 4, the smaller 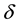



3) Step 5 means that if a local minimizer 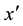

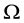

better local minimizer of 
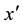
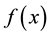
4.2. Numerical Experiment
In this section, the proposed algorithm is tested on some benchmark problems taken from some literatures.
Problem 1. (Two-dimensional function)
where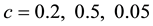
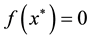

Problem 2. (Three-hump back camel function)
The global minimum solution is 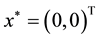
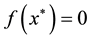
Problem 3. (Six-hump back camel function)
The global minimum solution is 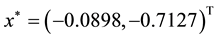

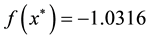
Problem 4. (Treccani function)
The global minimum solution are 


Problem 5. (Goldstein and Price function function)
where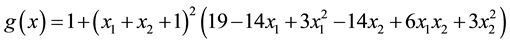
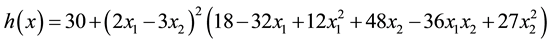
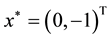
Problem 6. (Two-dimensional Shubert function)
This function has 760 minimizers in total. The global minimum value is
Problem 7. (Hartman function)
where 




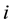
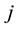


for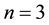
The known global minimizer is 
For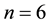
The known global minimizer is 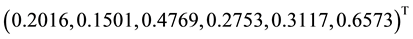
Enerally, in order to illustrate the performance of the filled function method, it is necessary to record the total number of function evaluations of 
Additionally, the proposed algorithm is compared with the algorithm presented in [11] . A series of minimizers obtained by the above two algorithms are recorded in Tables 2-14 for all testing problems.
Some symbols used in the following tables are given firstly.



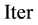

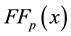
The initial value of 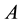
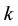


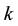
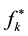
Table 1. Numerical results of all testing problems.
Table 2. Computational results for problem 1 with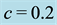
Table 3. Computational results for problem 1 with
Table 4. Computational results for problem 1 with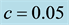
Table 5. Computational results for problem 2 with initial point
Table 6. Computational results for problem 2 with initial point
Table 7. Computational results for problem 3 with initial point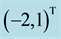

According to the Tables 2-13, we will find that our algorithm is effective, and it is affected by the initial va- lue of 
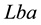
Table 8. Computational results for problem 3 with initial point
Table 9. Computational results for problem 3 with initial point
Table 10. Computational results for problem 4.
Table 11. Computational results for problem 5.
Table 12. Computational results for problem 6.
Table 13. Computational results for problem 7.
Table 14. Computational results for problem 7 with
also the lower computation cost will be; meanwhile, if the function value of the current local minimizer is closed to that of the global minimizer, then the sufficiently small 
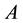
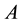


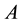
5. Concluding Remarks
The filled function method is a kind of efficient approaches for the global optimization. The existing filled func- tions have some drawbacks, for example, some are non-differentiable functions, some contain more than one adjust parameter and some contain ill-condition terms and so on. These drawbacks may result in failure or diff- iculty of the algorithm in searching global optimal solution. In order to overcome these shortcomings, a new filled function with only one parameter is proposed in this paper. Although the proposed filled function is non- differentiable at some points, it can be approximated uniformly by a continuous differentiable function. The inherent shortcomings of the approximate function can be eliminated by simple treatment. The effectiveness of the new filled function method is demonstrated by numerical experiments on some testing optimization pro- blems.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 11161001, No. 61203372, No. 61402350, No. 61375121), The Research Foundation of Jinling Institute of Technology (No. jit-b-201314 and No. jit-n-201309) and Ningxia Foundation for key disciplines of Computational Mathematics.
References
- Ge, R.P. (1990) A Filled Function Method for Finding a Global Minimizer of a Function of Several Variables. Mathematical Programming, 46, 191-204. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF01585737
- Ge, R.P. (1987) The Theory of Filled Function Method for Finding Global Minimizers of Nonlinearly Constrained Minimization Problems. Journal of Computational Mathematics, 5, 1-9.
- Wang, X.L. and Zhou, G.B. (2006) A New Filled Function for Unconstrained Global Optimization. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 174, 419-429. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2005.05.009
- Wang, Y.-J. and Zhang, J.-S. (2008) A New Constructing Auxiliary Function Method for Global Optimization. Mathematical Computer Modeling, 47, 1396-1410. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2007.08.007
- Liu, X. and Xu, W. (2004) A New Filled Function Applied to Global Optimization. Computer and Operation Research, 31, 61-80. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0305-0548(02)00154-5
- Liu, X. (2004) The Barrier Attribute of Filled Functions. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 149, 641-649. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0096-3003(03)00168-1
- Dixon, L.C.W., Gomulka, J. and Herson, S.E. (1976) Reflections on Global Optimization Problem, Optimization in Action. Academic Press, New York, 398-435.
- Liang, Y.M., Zhang, L.S., Li, M.M. and Han, B.S. (2007) A Filled Function Method for Global Optimization. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 205, 16-31. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2006.04.038
- Ling, A.-F., Xu, C.-X. and Xua, F.-M. (2008) A Discrete Filled Function Algorithm for Approximate Global Solutions of Max-Cut Problems. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 220, 643-660. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2007.09.012
- Polak, E., Royset, J.O. and Womersley, R.S. (2003) Algorithms with Adaptive Smoothing for Finite Minimax Problems. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 119, 459-484. http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/B:JOTA.0000006685.60019.3e
- Zhang, L.-S., Ng, C.-K., Li, D. and Tian, W.-W. (2004) A New Filled Function Method for Global Optimization. Journal of Global Optimization, 28, 17-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/B:JOGO.0000006653.60256.f6