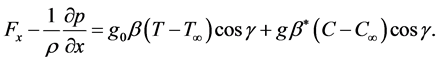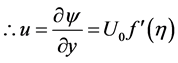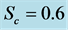Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics
Vol.03 No.12(2015), Article ID:62457,22 pages
10.4236/jamp.2015.312195
Numerical Solution of MHD Convection and Mass Transfer Flow of Viscous Incompressible Fluid about an Inclined Plate with Hall Current and Constant Heat Flux
Mohammad Wahiduzzaman1, Runu Biswas2, Md. Eaqub Ali3, Md. Shakhaoath Khan4, Ifsana Karim4
1Mathematics Discipline, Khulna University, Khulna, Bangladesh
2Mathematics Open School, Bangladesh Open University, Gazipur, Bangladesh
3Department of Civil Engineering, Sonargaon University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
4Discipline of Chemical Engineering, The University of Newcastle, Callaghan, Australia

Copyright © 2015 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 14 November 2015; accepted 27 December 2015; published 30 December 2015
ABSTRACT
The present numerically study investigates the influence of the Hall current and constant heat flux on the Magneto hydrodynamic (MHD) natural convection boundary layer viscous incompressible fluid flow in the manifestation of transverse magnetic field near an inclined vertical permeable flat plate. It is assumed that the induced magnetic field is negligible compared with the imposed magnetic field. The governing boundary layer equations have been transferred into non-similar model by implementing similarity approaches. The physical dimensionless parameter has been set up into the model as Prandtl number, Eckert number, Magnetic parameter, Schmidt number, local Grashof number and local modified Grashof number. The numerical method of Nactsheim- Swigert shooting iteration technique together with Runge-Kutta six order iteration scheme has been used to solve the system of governing non-similar equations. The physical effects of the various parameters on dimensionless primary velocity profile, secondary velocity profile, and temperature and concentration profile are discussed graphically. Moreover, the local skin friction coefficient, the local Nusselt number and Sherwood number are shown in tabular form for various values of the parameters.
Keywords:
MHD, Heat and Mass Transfer, Hall Current, Inclined Plate, Constant Heat Flux

1. Introduction
Hall current has important contribution in the study of MHD viscous flows. It has many applications in problems of the Hall accelerators as well as in the flight MHD. The current trend is on the application of MHD towards a strong magnetic field and a low density of gas. For this reason, the Hall current and ion slip become important. Hydrodynamic flow of a viscous liquid through a straight channel in presence of Hall Effect is examined by Sato [1] , Yamanishi [2] , and Sherman and Sutton [3] . The Hall current effects on the boundary layer flow past a semi-infinite plate are studied by Katagiri [4] . Free convection flow of a conducting fluid permeated by a transverse magnetic field in the presence of the Hall effects and uniform magnetic field is analyzed by Pop and Watanabe [5] . Aboeldahab and Elbarbary [6] studied the effect of the Hall current on the MHD free convection flow in the presence of foreign species over a vertical surface, where the flow is subjected to a strong external magnetic field. Eichhorn [7] investigated the similarity solution by considering the power-law variations in the plate temperature and transpiration velocity. Vedhanayagam et al. [8] worked on the free convection flow along a vertical plate with the arbitrary blowing and wall temperature. Lin and Yu [9] investigated the free convection flow over a horizontal plate. Recently, Hossain et al. [10] investigated the natural convection flow from a vertical permeable flat plate with the variable surface temperature, considering the temperature and transpiration rates to follow the power-law variation. Saha et al. [11] studied the effect of Hall current on the steady laminar natural convection boundary layer flow of MHD viscous and incompressible fluids. Lately, Saha et al. [12] examined the effect of Hall current on MHD natural convection flow from vertical permeable flat plate with uniform surface heat flux. In recent years a number of studies of MHD convective heat and mass transfer boundary layer flow of viscous incompressible fluid were reported in the literature [13] -[25] . However, the effect of hall current and constant heat flux is still not getting promising attraction to the researchers. In this study MHD Free Convection and Mass Transfer Flow of Viscous Incompressible Fluid about an inclined Plate with Hall Current and Constant Heat Flux is investigated.
2. Mathematical Analysis
Steady natural convection boundary layer flow of an electrically conducting and viscous incompressible fluid from a semi-infinite heated permeable inclined flat plate with a uniform surface heat flux and transverse magnetic field with the effect of the Hall current is considered. Here x axis is taken along the vertically upward direction and y axis is normal to it. The leading edge of the permeable surface is taken along z axis. The uniform heat is supplied from the surface of the plate to the fluid, which is maintained uniformly throughout the fluid flow. The temperature and concentration at the wall are 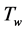 and
and 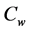 respectively. The temperature and concentration outside the boundary layer are
respectively. The temperature and concentration outside the boundary layer are 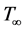 and
and 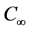 respectively. Uniform magnetic field of magnitude
respectively. Uniform magnetic field of magnitude 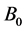 is imposed to perpendicular to the flow along the y axis. Let the angle of inclination of the plate is
is imposed to perpendicular to the flow along the y axis. Let the angle of inclination of the plate is 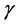 and the plate is semi finite. The x component momentum equation reduces to the boundary layer equation if and only if body force is made by gravity, then the body force per unit mass is
and the plate is semi finite. The x component momentum equation reduces to the boundary layer equation if and only if body force is made by gravity, then the body force per unit mass is 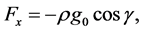 where
where 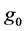 is the accele-
is the accele-
ration due to gravity. Further no body force exists in the direction of y and z, i.e.  and
and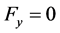 ,
,
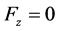 . The x component of pressure gradient at any point in the boundary layer must equal to the pressure gradient in the region outside the boundary layer, in this region
. The x component of pressure gradient at any point in the boundary layer must equal to the pressure gradient in the region outside the boundary layer, in this region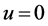 ,
,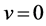 . Hence x component of pressure gra-
. Hence x component of pressure gra-
dient become 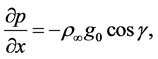 where
where 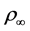 is the density of the surrounding fluid at temperature
is the density of the surrounding fluid at temperature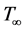
quantity 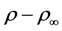

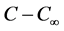
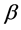
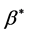

We have the generalized ohm’s law in the absence of electric field to the case of short circuit problem is of the form

where, 
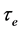
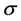
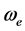
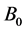
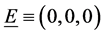
Therefore Equation (1) becomes
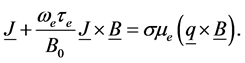
If is assumed that induced magnetic field generated by fluid motion is negligible in comparison to the applied one i.e.
Since the Hall coefficient is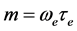
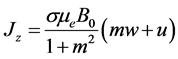

where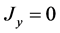
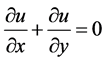
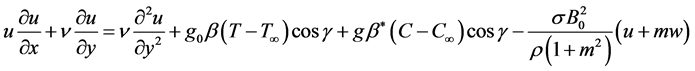
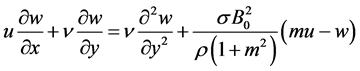
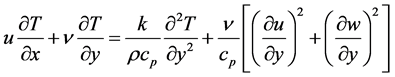

Subjected to the boundary conditions
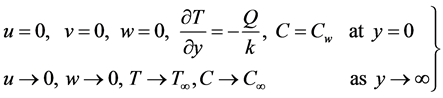
where 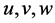
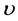

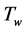
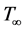
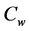
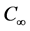
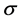
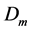
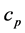
In order to solve the above system (Figure 1) of Equations (6)-(9) with the boundary conditions (10), we
Figure 1. Physical configuration and co-ordinate system.
adopt the well-defined similarity analysis to attain similarity solutions. For this purpose, the following similarity transformations are now introduced;
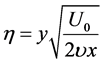
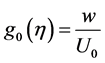
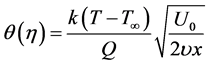
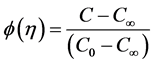
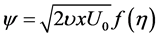
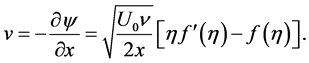
Thus, Equations (6)-(10) becomes;
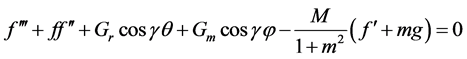
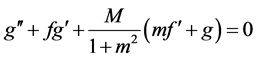
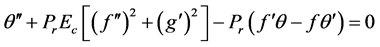
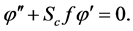
The corresponding boundary conditions are

where 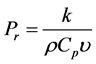
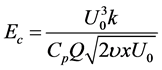
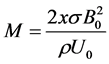
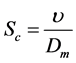
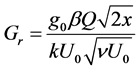

3. Skin-Friction Coefficients, Nusselt Number and Sherwood Number
The quantities of chief physical interest are the skin friction coefficients, the Nusselt number and the Sherwood number. The equation defining the wall skin frictions are 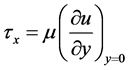


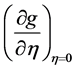
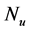

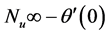
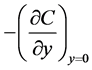
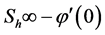
4. Results and Discussions
In this study the MHD Free Convection and Mass Transfer Flow of Viscous Incompressible Fluid about an
Table 1. Numerical values of Skin friction coefficient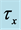

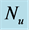
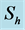
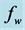

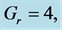
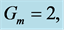
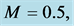

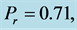
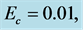
Table 2. Numerical values of Skin friction coefficient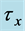



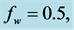

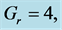

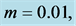


Table 3. Numerical values of Skin friction coefficient


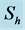
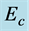
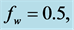
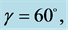
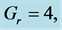
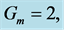

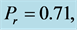
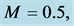
Table 4. Numerical values of Skin friction coefficient

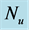
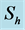
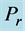
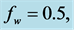
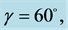

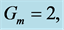

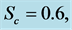
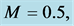
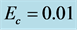
Table 5. Numerical values of Skin friction coefficient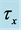

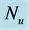
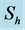

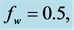


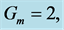
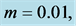
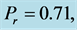
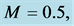
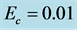
Table 6. Numerical values of Skin friction coefficient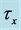

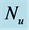
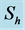
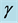
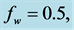
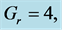
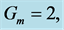
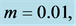
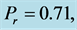

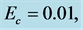
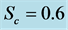
Table 7. Numerical values of Skin friction coefficient

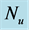
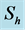
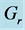
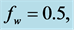
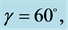
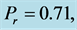
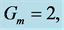


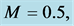

Table 8. Numerical values of Skin friction coefficient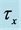

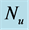

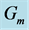

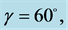
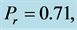

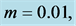

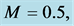
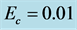
inclined Plate with Hall Current and Constant Heat Flux have been investigated using the Nachtsheim-Swigert shooting iteration technique. To study the physical situation of this problem, we have computed the numerical values of the velocity, temperature, and concentration within the boundary layer and also find the skin friction coefficient, Nusseltnumber, Sherwood number at the plate. It can be seen that the solutions are affected by the parameters, namely suction parameter

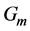
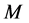
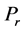
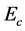

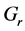
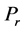
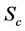
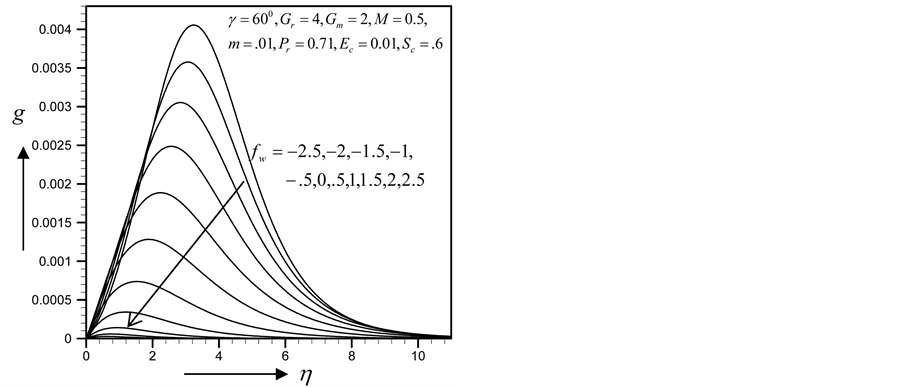
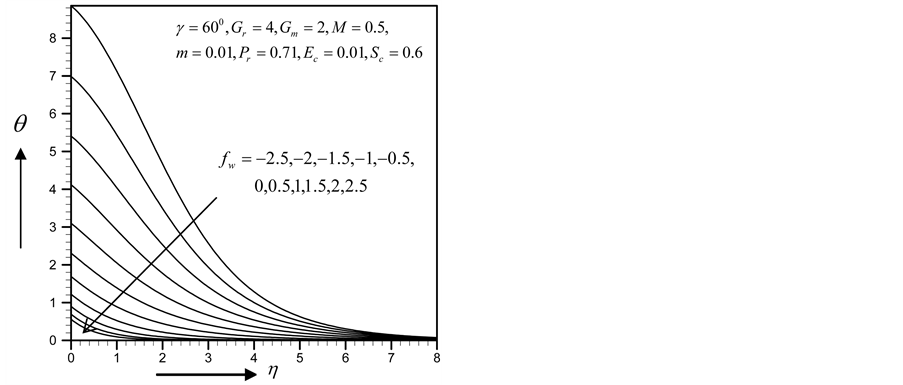
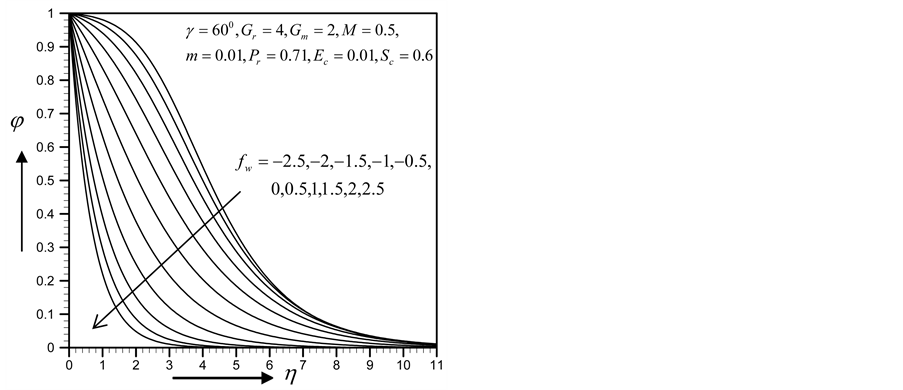
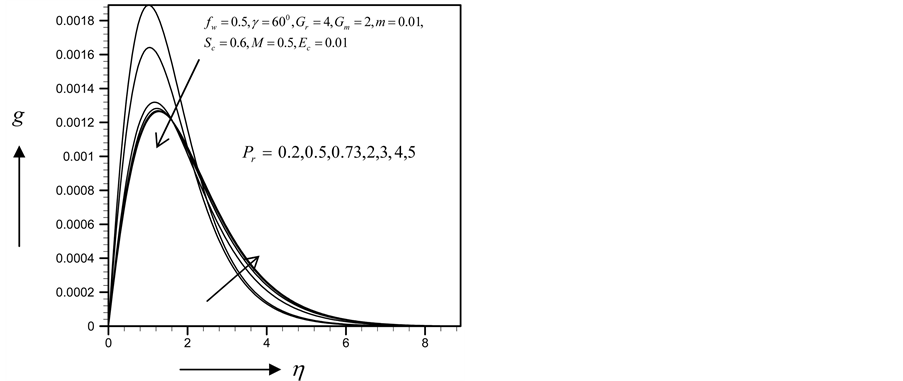
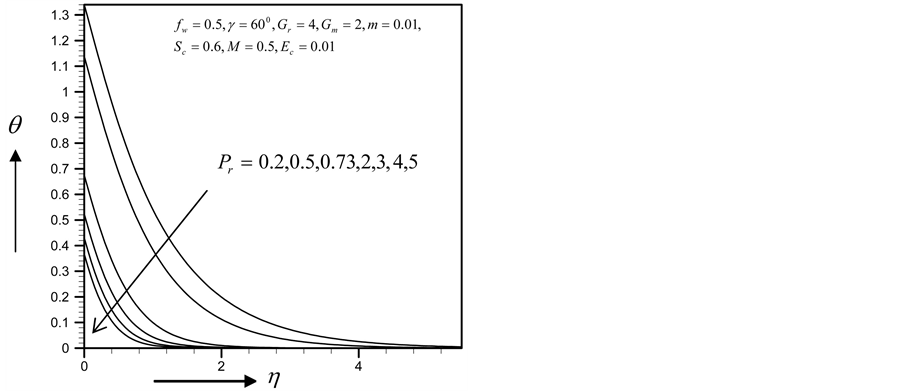
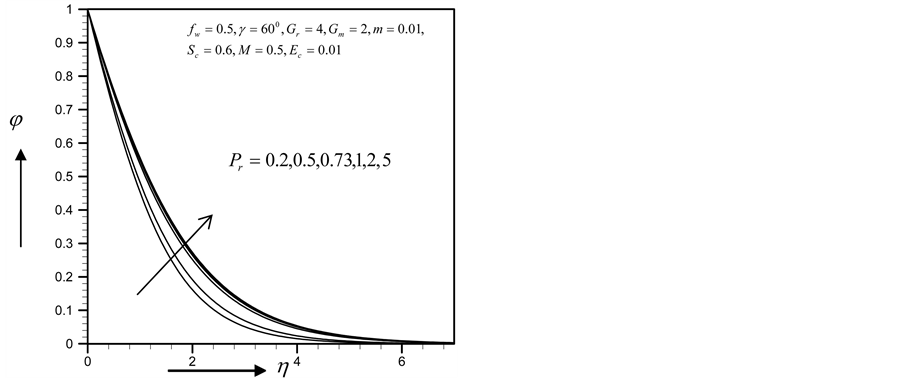
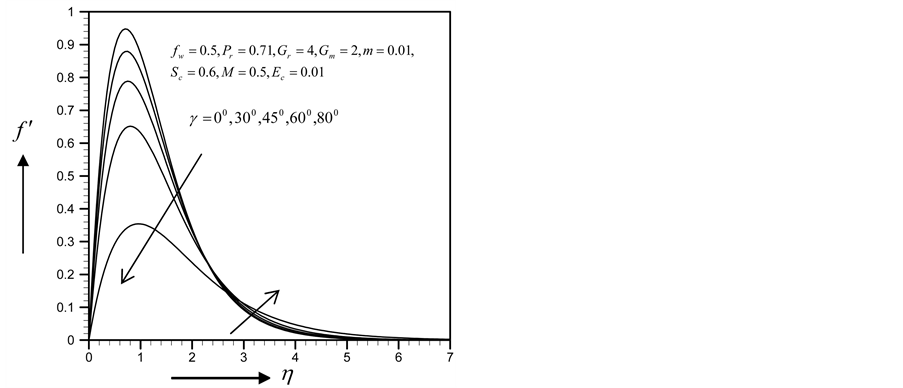
Figures 2-5, respectively, show the primary velocity, secondary velocity, temperature and concentration profiles for different values of suction parameter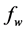
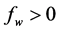
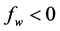

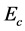
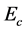
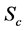
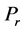
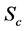

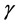
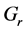

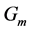
Figure 2. Primary velocity profile for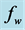
Figure 3. Secondary velocity profile for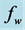
Figure 4. Temperature profile for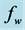
Figure 5. Concentration profile for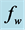
Figure 6. Primary velocity profile for
Figure 7. Secondary velocity profile
Figure 8. Temperature profile for
Figure 9. Concentration profile for
Figure 10. Primary velocity profile for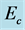
Figure 11. Secondary velocity profile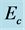
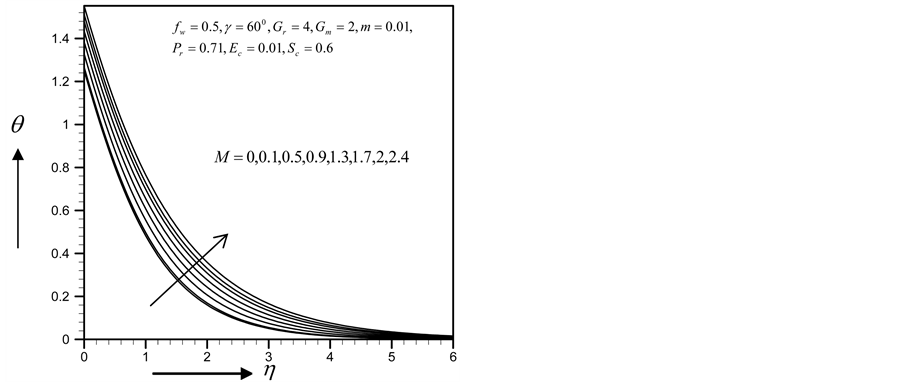
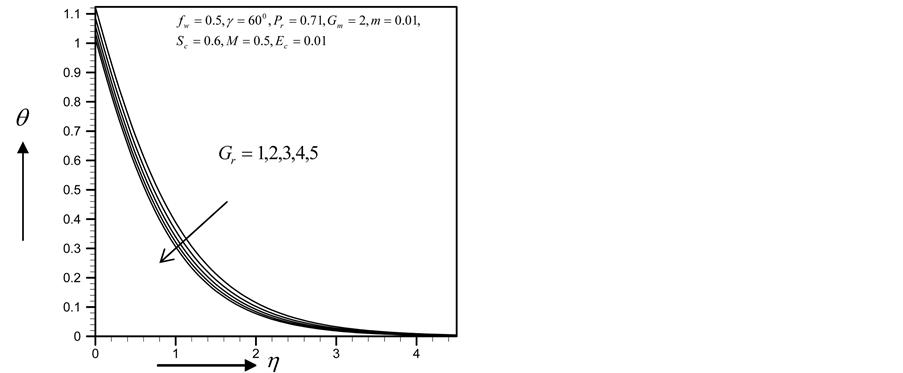
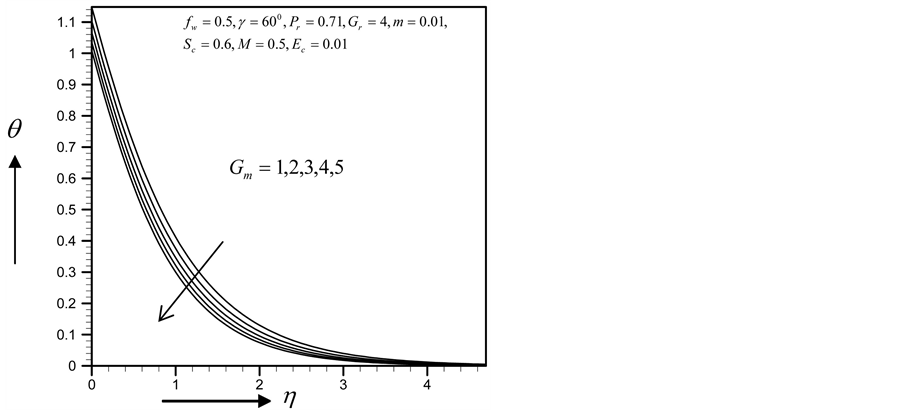
Figure 12. Temperature profile for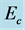
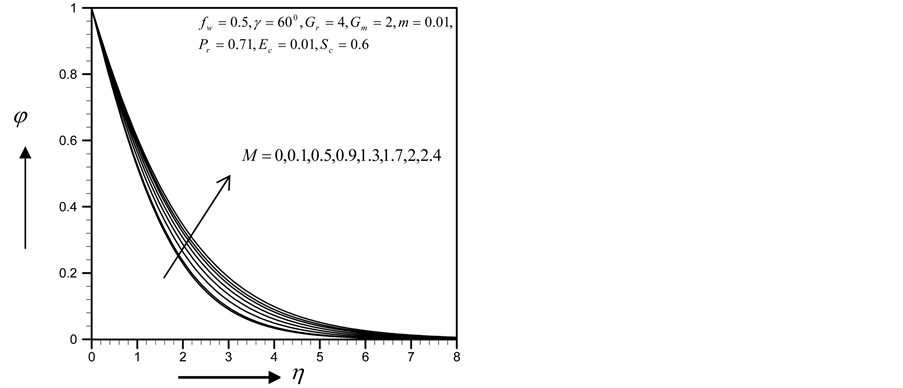
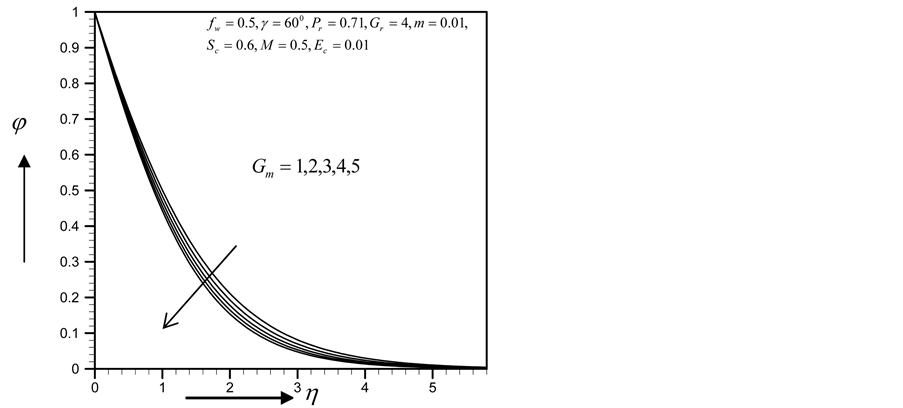
Figure 13. Concentration profile for
Figure 14. Primary velocity profile for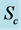
Figure 15. Secondary velocity profile for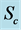
Figure 16. Temperature profile for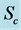
Figure 17. Concentration profile for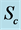
Figure 18. Primary velocity profile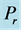
Figure 19. Secondary velocity profile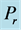
Figure 20. Temperature profile for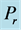
Figure 21. Concentration profile for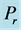
Figure 22. Primary velocity profile for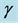
Figure 23. Secondary velocity profile for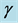
Figure 24. Temperature profile for
Figure 25. Concentration profile for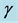
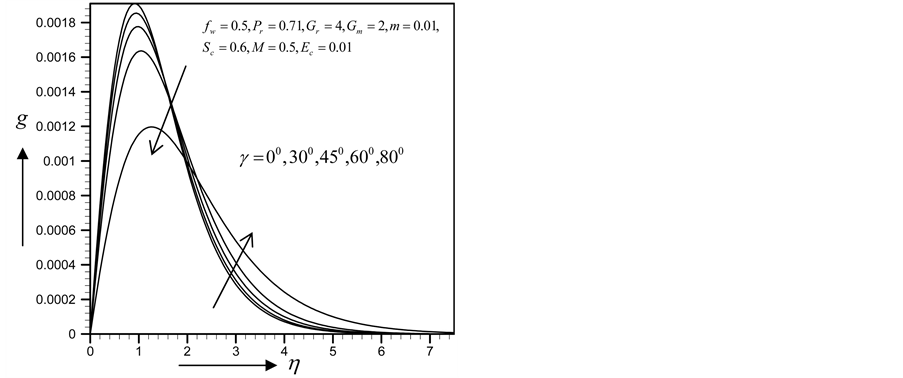
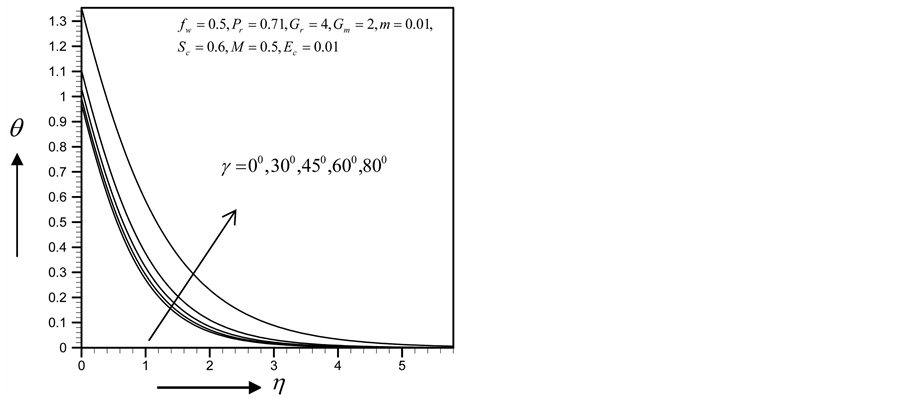
Figure 26. Primary velocity profile for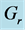
Figure 27. Secondary velocity profile for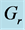
Figure 28. Temperature profile for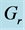
Figure 29. Concentration profile for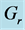
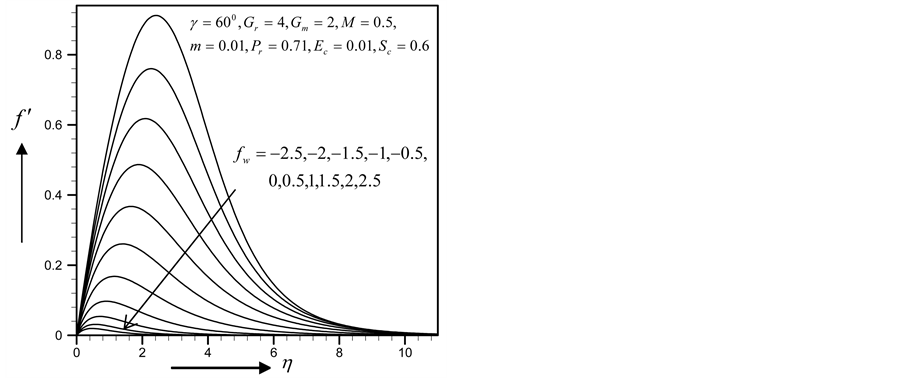
Figure 30. Primary velocity profile for
Figure 31. Secondary velocity profile for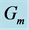
Figure 32. Temperature profile for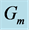
Figure 33. Concentration profile for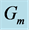
with the increase of
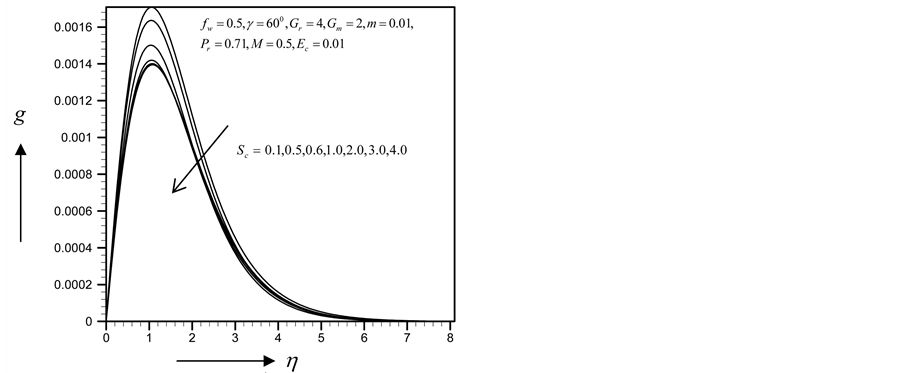
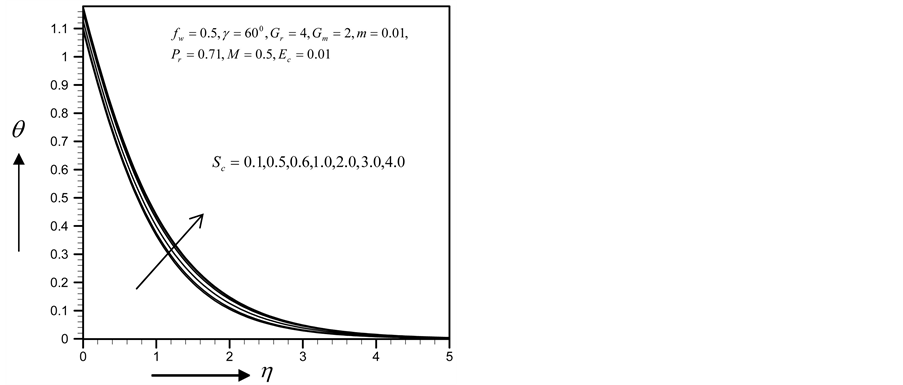
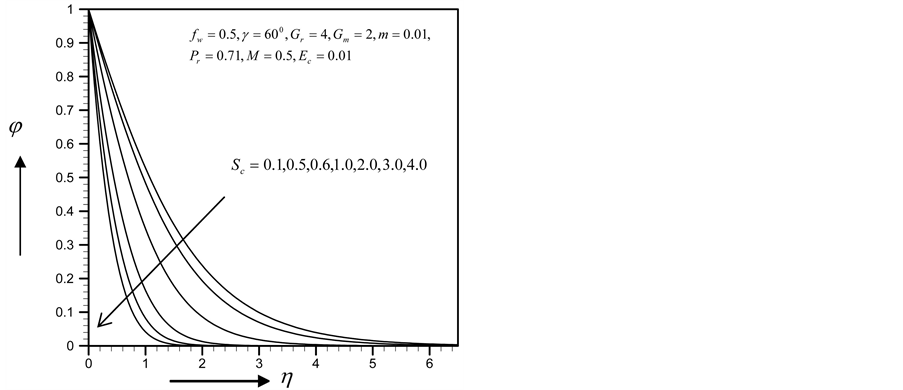
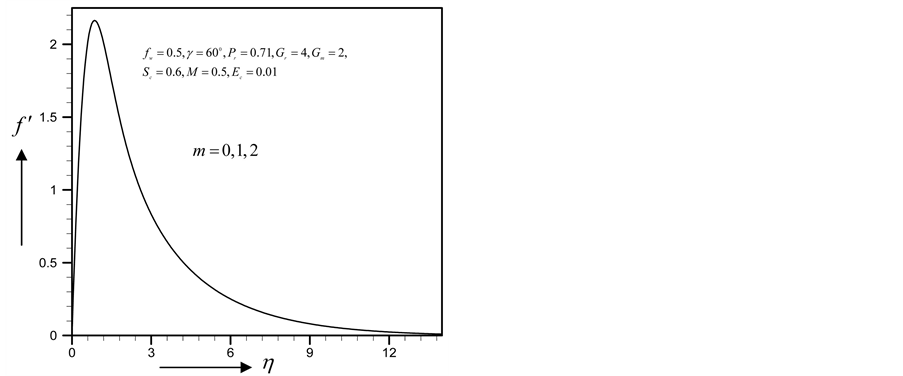
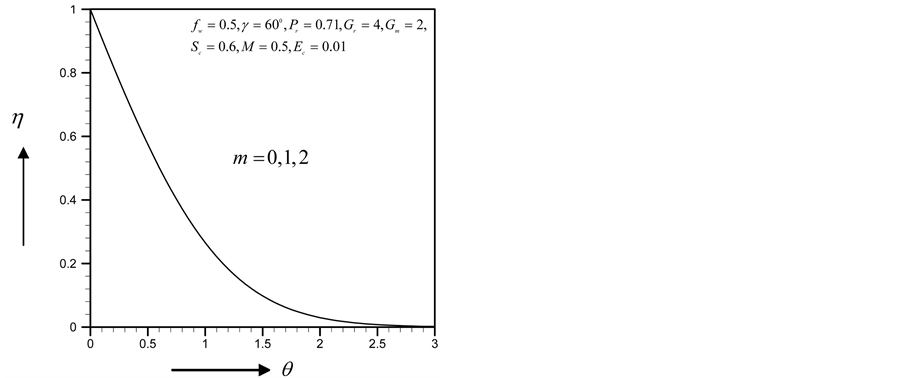
From Figure 34-37, show the velocity, secondary velocity, temperature and concentration profile field has a negligible effect for different values of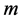
Finally the effect of various parameters on the skin friction coefficients (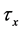

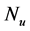
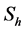
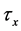
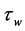


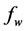

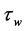
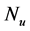

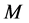
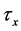

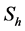
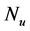

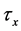

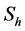



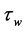
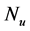
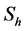
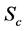
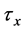
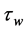
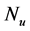
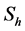
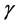
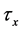
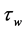


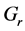
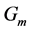
Figure 34. Primary velocity profile for m.
Figure 35. Secondary velocity profile for m.
Figure 36. Temperature profile for m.
Figure 37. Concentration profile for m.
5. Conclusions
The effect of viscous incompressible fluid flow about an inclined plate with hall current is analyzed in the present study for constant heat flux. A range of physical parameter values tested over the boundary layer flows. The variation of different physical parameters instigated different flow pattern as increasing, decreasing and cross flow in the dimensionless primary and secondary velocity, temperature and concentration distribution as well as in the profile of skin friction coefficients, Nusseltand Sherwood number. The findings of the present investigation are briefly:
・ As suction parameter increases, the primary velocity, secondary velocity, temperature and concentration profiles decrease gradually. However for the same parameter effects, the skin friction coefficient decreases and Nusselt and Sherwood numbers increase.
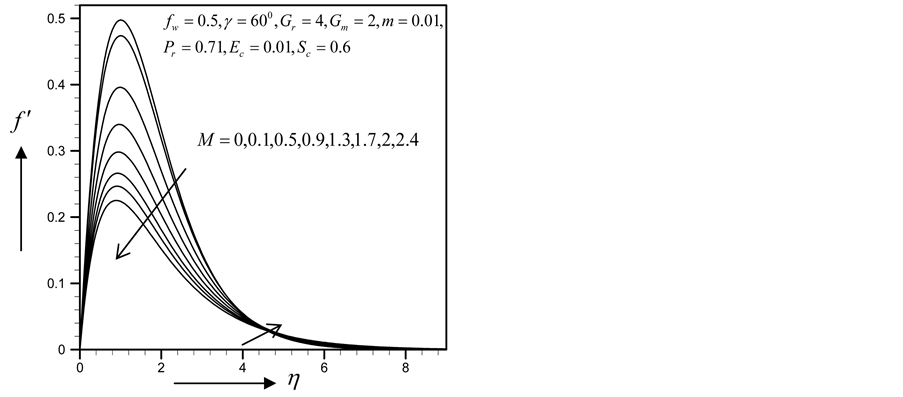
・ The primary velocity, secondary velocity profiles as well as the skin friction coefficient, Nusselt and Sherwood numbers decreased as magnetic parameter increased whereas the reverse effects found in the profile of temperature and concentration.
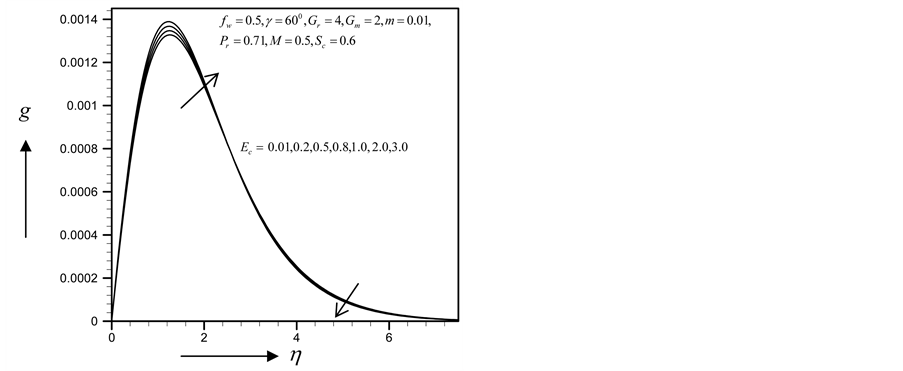
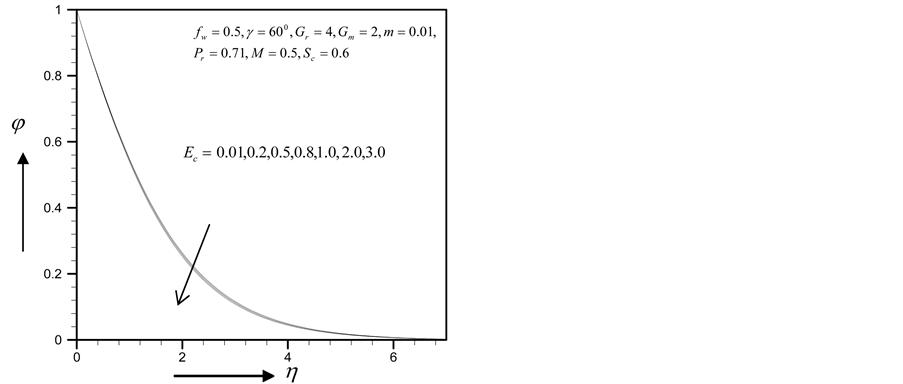
・ The cross-flow of primary and secondary velocity observed as Eckert number increases whereas temperature profile increases and concentration profile decreases for the same parameter effects. Also for the similar parameter effects skin friction coefficient and Sherwood number increase whereas Nusselt number decreases.
・ The increasing effect of Schmidt number causes primary and secondary velocity profile and concentration profile as well as the skin friction coefficient and Nusselt number decrease whereas the reverse situation observed in the temperature and Sherwood number profiles.
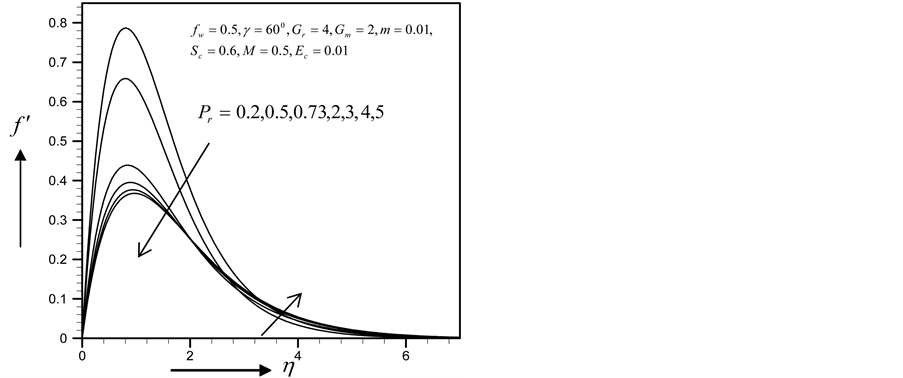
・ The cross flow of the primary and secondary velocity with the increase of Prandlt number has been observed, where both of the profiles first decrease and near the layer the profiles increase. However within the same parameter effects, the skin friction coefficient and Sherwood number decrease and Nusselt number increases.
・ As the parameter 
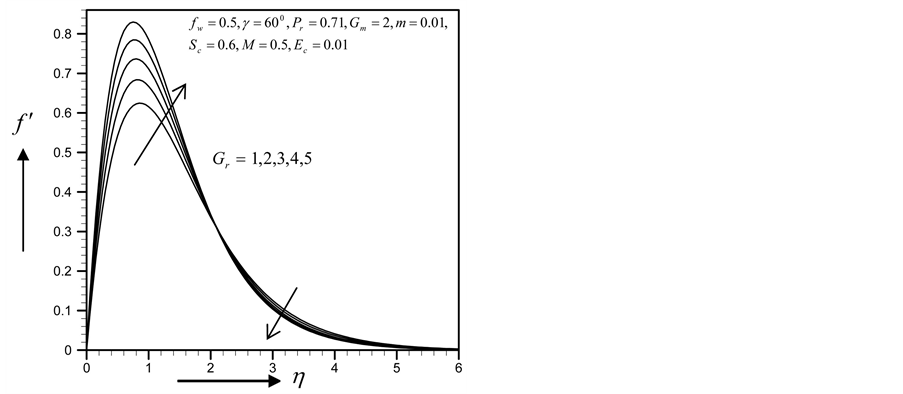
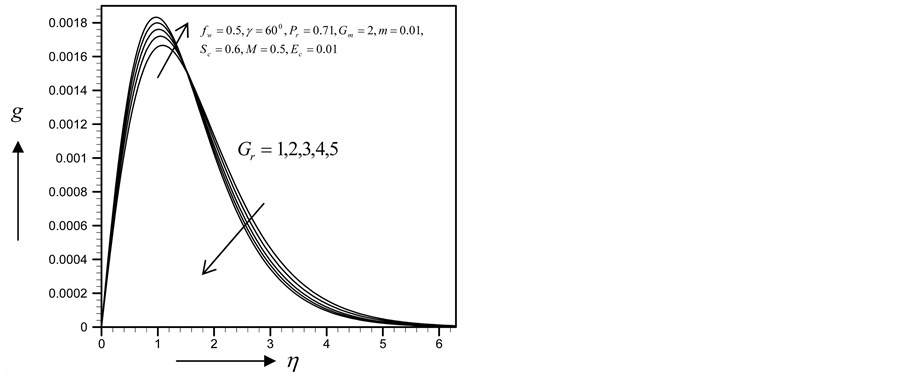
・ The increasing effect of Grashof and modified Grashof number causes the cross flow of the primary and secondary velocity whereas temperature and concentration profile decrease for the similar parameter effects. However the skin friction coefficient, Nusselt number and Sherwood number increase.
Cite this paper
MohammadWahiduzzaman,RunuBiswas,Md. EaqubAli,Md. ShakhaoathKhan,IfsanaKarim, (2015) Numerical Solution of MHD Convection and Mass Transfer Flow of Viscous Incompressible Fluid about an Inclined Plate with Hall Current and Constant Heat Flux. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics,03,1688-1709. doi: 10.4236/jamp.2015.312195
References
- 1. Sato, H. (1961) The Hall Effect in the Viscous Flow of Ionized Gas between Two Parallel Plates under Transverse Magnetic Field. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 16, 1427-1433.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.16.1427 - 2. Yamanishi, T. (1962) Hall Effect in the Viscous Flow of Ionized Gas through Straight Channels. 17th Annual Meeting, Physical Society of Japan, 5, 29.
- 3. Sherman, A. and Sutton, G.W. (1961) Magnetohydrodynamics. Evanston, 173-175.
- 4. Katagiri, M. (1969) The Effect of Hall Currents on the Viscous Flow Magnetohydrodynamic Boundary Layer Flow Past a Semi-Infinite Flat Plate. Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 27, 1051-1059.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.27.1051 - 5. Pop, I. and Watanabe, T. (1994) Hall Effect on Magnetohydrodynamic Free Convection about a Semiinfinite Vertical Flat Plate. International Journal of Engineering Science, 32, 1903-1911.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0020-7225(94)90087-6 - 6. Aboeldahab, M.E. and Elbarbary, M.E. (2001) Hall Current Effect on Magnetohydrodynamic Free Convection Flow Past a Semi-Infinite Plate with Mass Transfer. International Journal of Engineering Science, 39, 1641-1652.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7225(01)00020-9 - 7. Eichhorn, R. (1960) The Effect of Mass Transfer on Free Convection. Journal of Heat Transfer, 82, 260-263.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1115/1.3679928 - 8. Vedhanayagam, M., Altenkirch, R.A. and Echhorn, R.A. (1980) A Transformation of the Boundary Layer Equation for Free Convection Flow Past a Vertical Flat Plate with Arbitrary Blowing and Wall Temperature Variation. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 23, 1236-1288.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0017-9310(80)90059-9 - 9. Lin, H.T. and Yu, W.S. (1988) Free Convection on Horizontal Plate with Blowing and Suction. Journal of Heat Transfer, 110, 793-796.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1115/1.3250564 - 10. Hossain, M.A., Alam, K.C.A. and Rees, D.A.S. (1997) MHD Free and Forced Convection Boundary Layer Flow along a Vertical Porous Plate. Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2, 33-51.
- 11. Saha, L.K., Hossain, M.A. and Gorla, R.S.R. (2007) Effect of Hall Current on the MHD Laminar Natural Convection Flow from a Vertical Permeable Flat Plate with Uniform Surface Temperature. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 46, 790-801.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2006.10.009 - 12. Saha, L.K., Siddiqa, S. and Hossain, M.A. (2011) Effect of Hall Current on MHD Natural Convection Flow from Vertical Permeable Flat Plate with Uniform Surface Heat Flux. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 32, 1127-1146.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10483-011-1487-9 - 13. Bég, O.A., Khan, M.S., Karim, I., Alam, M.M. and Ferdows, M. (2013) Explicit Numerical Study of Unsteady Hydromagnetic Mixed Convective Nanofluid Flow from an Exponentially Stretching Sheet in Porous Media. Applied Nanoscience, 4, 943-957.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13204-013-0275-0 - 14. Ferdows, M., Khan, M.S., Alam, M.M. and Sun, S. (2012) MHD Mixed Convective Boundary Layer Flow of a Nanofluid through a Porous Medium Due to an Exponentially Stretching Sheet. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2012, Article ID: 408528.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/408528 - 15. Ferdows, M., Khan, M.S., Bég, O.A. and Alam, M.M (2013) Numerical Study of Transient Magnetohydrodynamic Radiative Free Convection Nanofluid Flow from a Stretching Permeable Surface. Journal of Process Mechanical Engineering, 228, 181-196.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0954408913493406 - 16. Khan, M.S., Karim, I., Islam, M.S. and Wahiduzzaman, M. (2014) MHD Boundary Layer Radiative, Heat Generating and Chemical Reacting Flow Past a Wedge Moving in a Nanofluid. Nano Convergence, 1, 20.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s40580-014-0020-8 - 17. Khan, M.S., Alam, M.M. and Ferdows, M. (2013) Effects of Magnetic Field on Radiative Flow of a Nanofluid Past a Stretching Sheet. Procedia Engineering, 56, 316-322.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.03.125 - 18. Khan, M.S., Karim, I., Ali, L.E. and Islam, I. (2012) Unsteady MHD Free Convection Boundary-Layer Flow of a Nanofluid along a Stretching Sheet with Thermal Radiation and Viscous Dissipation Effects. International Nano Letters, 2, 24.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/2228-5326-2-24 - 19. Khan, M.S., Karim, I. and Biswas, H.A. (2012) Heat Generation, Thermal Radiation and Chemical Reaction Effects on MHD Mixed Convection Flow over an Unsteady Stretching Permeable Surface. International Journal of Basic and Applied Science, 1, 363-377.
- 20. Khan, M.S., Karim, I. and Biswas, H.A. (2012) Non-Newtonian MHD Mixed Convective Power-Law Fluid Flow over a Vertical Stretching Sheet with Thermal Radiation, Heat Generation and Chemical Reaction Effects. Academic Research International, 3, 80-92.
- 21. Khan, M.S., Karim, I. and Islam, M.S. (2014) MHD Buoyancy Flows of Cu, Al2O3 and Tio2Nanofluid near Stagnation-Point on a Vertical Plate with Heat Generation. Physical Science International Journal, 4, 754-767.
http://dx.doi.org/10.9734/PSIJ/2014/9074 - 22. Khan, M.S., Karim, I. and Islam, M.S. (2014) Possessions of Chemical Reaction on MHD Heat and Mass Transfer Nanofluid Flow on a Continuously Moving Surface. American Chemical Science Journal, 4, 401-415.
http://dx.doi.org/10.9734/ACSJ/2014/5422 - 23. Khan, M.S., Wahiduzzaman, M., Karim, I., Islam, M.S. and Alam, M.M. (2014) Heat Generation Effects on Unsteady Mixed Convection Flow from a Vertical Porous Plate with Induced Magnetic Field. Procedia Engineering, 90, 238-244.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.11.843 - 24. Wahiduzzaman, M., Khan, M.S. and Karim, I. (2015) MHD Convective Stagnation Flow of Nanofluid over a Shrinking Surface with Thermal Radiation, Heat Generation and Chemical Reaction. Procedia Engineering, 105, 398-405.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.05.025 - 25. Wahiduzzaman, M., Khan, M.S., Karim, I., Biswas, P. and Uddin, M.S. (2015) MHD Flow of Fluid over a Rotating Inclined Permeable Plate with Variable Reactive Index. Physical Science International Journal, 6, 144-162.
Nomenclature