302 M. A. Elblbesy / J. Biomedical Science and Engineering 3 (2010) 300-303
Copyright © 2010 SciRes JBiSE
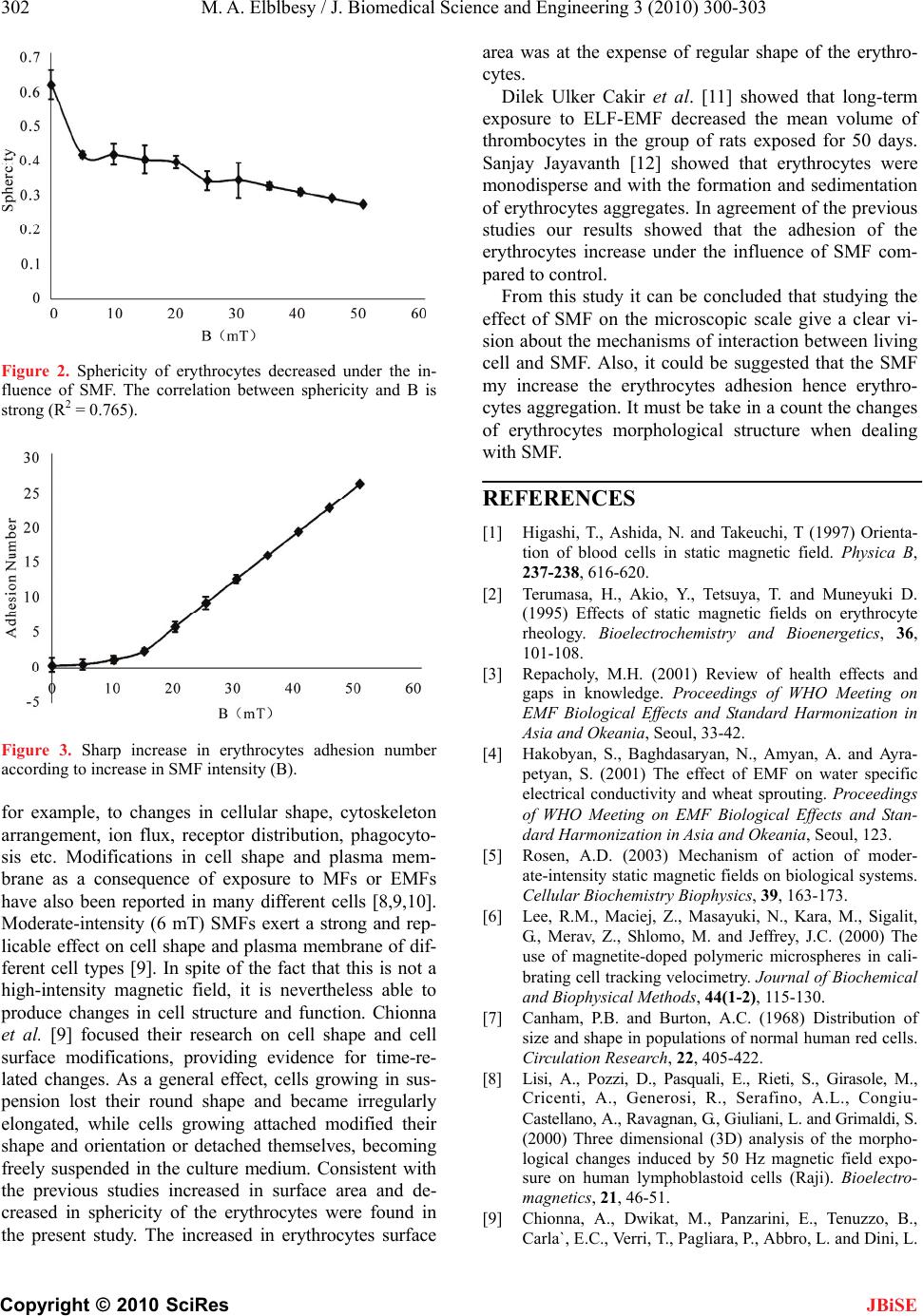
Figure 2. Sphericity of erythrocytes decreased under the in-
fluence of SMF. The correlation between sphericity and B is
strong (R2 = 0.765).
Figure 3. Sharp increase in erythrocytes adhesion number
according to increase in SMF intensity (B).
for example, to changes in cellular shape, cytoskeleton
arrangement, ion flux, receptor distribution, phagocyto-
sis etc. Modifications in cell shape and plasma mem-
brane as a consequence of exposure to MFs or EMFs
have also been reported in many different cells [8,9,10].
Moderate-intensity (6 mT) SMFs exert a strong and rep-
licable effect on cell shape and plasma membrane of dif-
ferent cell types [9]. In spite of the fact that this is not a
high-intensity magnetic field, it is nevertheless able to
produce changes in cell structure and function. Chionna
et al. [9] focused their research on cell shape and cell
surface modifications, providing evidence for time-re-
lated changes. As a general effect, cells growing in sus-
pension lost their round shape and became irregularly
elongated, while cells growing attached modified their
shape and orientation or detached themselves, becoming
freely suspended in the culture medium. Consistent with
the previous studies increased in surface area and de-
creased in sphericity of the erythrocytes were found in
the present study. The increased in erythrocytes surface
area was at the expense of regular shape of the erythro-
cytes.
Dilek Ulker Cakir et al. [11] showed that long-term
exposure to ELF-EMF decreased the mean volume of
thrombocytes in the group of rats exposed for 50 days.
Sanjay Jayavanth [12] showed that erythrocytes were
monodisperse and with the formation and sedimentation
of erythrocytes aggregates. In agreement of the previous
studies our results showed that the adhesion of the
erythrocytes increase under the influence of SMF com-
pared to control.
From this study it can be concluded that studying the
effect of SMF on the microscopic scale give a clear vi-
sion about the mechanisms of interaction between living
cell and SMF. Also, it could be suggested that the SMF
my increase the erythrocytes adhesion hence erythro-
cytes aggregation. It must be take in a count the changes
of erythrocytes morphological structure when dealing
with SMF.
REFERENCES
[1] Higashi, T., Ashida, N. and Takeuchi, T (1997) Orienta-
tion of blood cells in static magnetic field. Physica B,
237-238, 616-620.
[2] Terumasa, H., Akio, Y., Tetsuya, T. and Muneyuki D.
(1995) Effects of static magnetic fields on erythrocyte
rheology. Bioelectrochemistry and Bioenergetics, 36,
101-108.
[3] Repacholy, M.H. (2001) Review of health effects and
gaps in knowledge. Proceedings of WHO Meeting on
EMF Biological Effects and Standard Harmonization in
Asia and Okeania, Seoul, 33-42.
[4] Hakobyan, S., Baghdasaryan, N., Amyan, A. and Ayra-
petyan, S. (2001) The effect of EMF on water specific
electrical conductivity and wheat sprouting. Proceedings
of WHO Meeting on EMF Biological Effects and Stan-
dard Harmonization in Asia and Okeania, Seoul, 123.
[5] Rosen, A.D. (2003) Mechanism of action of moder-
ate-intensity static magnetic fields on biological systems.
Cellular Biochemistry Biophysics, 39, 163-173.
[6] Lee, R.M., Maciej, Z., Masayuki, N., Kara, M., Sigalit,
G., Merav, Z., Shlomo, M. and Jeffrey, J.C. (2000) The
use of magnetite-doped polymeric microspheres in cali-
brating cell tracking velocimetry. Journal of Biochemical
and Biophysical Methods, 44(1-2), 115-130.
[7] Canham, P.B. and Burton, A.C. (1968) Distribution of
size and shape in populations of normal human red cells.
Circulation Research, 22, 405-422.
[8] Lisi, A., Pozzi, D., Pasquali, E., Rieti, S., Girasole, M.,
Cricenti, A., Generosi, R., Serafino, A.L., Congiu-
Castellano, A., Ravagnan, G., Giuliani, L. and Grimaldi, S.
(2000) Three dimensional (3D) analysis of the morpho-
logical changes induced by 50 Hz magnetic field expo-
sure on human lymphoblastoid cells (Raji). Bioelect ro-
magnetics, 21, 46-51.
[9] Chionna, A., Dwikat, M., Panzarini, E., Tenuzzo, B.,
Carla`, E.C., Verri, T., Pagliara, P., Abbro, L. and Dini, L.