World Journal of Engineering and Technology
Vol.03 No.04(2015), Article ID:61618,9 pages
10.4236/wjet.2015.34030
Impacts of the Financial Factors on Schedule Delays Risk of the International Contracting Projects: Evidence from Highway BOT Projects in Vietnam
Hong-Anh Vu1, Jianqiong Wang1, Lianxing Min2*, Thihong-Nhung Nguyen1
1School of Economics and Management,
2School of Management,

Copyright © 2015 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).


Received 16 October 2015; accepted 27 November 2015; published 30 November 2015

ABSTRACT
Vietnam has become a major market for construction enterprises from East Asian countries, especially from China, to participate in international project contracting, but serious schedule delays have important adverse effects on local government and foreign investment companies. Based on international engineering contracting mode of Vietnam highway BOT construction projects, we discussed the drive financial factors of schedule delays, using the methods of exploratory factor analysis and questionnaire survey, and evaluated the effects of various factors which are through regression analysis. The empirical results show that the five categories of financial factors, including the policy change, slow payment, financial mismanagement, financial market changes and lack of fiscal, have significant effects on schedule delay. Furtherly, we suggested that strengthening policy research and improving financial management ability should be used to reduce the influence of relevant financial factors on schedule delay, to improve the profitability of international businesses and the motivation of foreign enterprises to participate in Vietnam highway project.
Keywords:
Scheduling Risk Management, Exploratory Analysis, Project Delay, Fiscal Factors, Risk Evaluation

1. Introduction
In recent years, with economic globalization, countries energetically strengthen infrastructure construction, especially the developing countries and regions, such as the Association of South-east Asian Nations (ASEAN), which becomes the main market of international engineering contracting, and is also the main goal of the foreign enterprises to participate in the international engineering contracting business. Before 2002, there was no highway in Vietnam, then the government introduced a series of preferential policies to attract domestic and foreign funds and to encourage investment in various construction methods, especially the form of BOT which promoted the development of highway construction. Vietnamese Prime Minister Nguyen Tan Dung put forward that construction of 2500 km kilometers using diversified funds would be scheduled to end in 2020, but according to the current adjusted planning of Vietnamese Ministry of Transport, only 1800 kilometer would be built before 2020. The most projects of them belong to international cooperation projects, while Chinese companies are the main partner, though these projects are conducted by experienced Chinese enterprise construction, the phenomena of project delay are still very serious, which is the most common problem in Vietnam project construction and affects enterprise’s economic benefit and investment enthusiasm [1] . There are several reasons for these serious phenomena and financial problems, such as fund raising and management has become the main difficulty for current Vietnam and gained concerns of scholars [2] . For highway construction project, especially the international contracting project, has many participation main bodies and project subcontracts; the complexity of project is far more than other general project, which involves many specific financial factors, and has strong correlation between the various factors, and further aggravates the construction schedule delays. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the specific financial factors of delaying highway construction schedule systematically to help Vietnamese government and foreign construction companies take effective measures. These measurements could improve the project financial management level, avoid risk of construction schedule due to the financial shortage and promote the foreign enterprises to participate in Vietnam highway project engineering contracting more actively, to raise the level of the highway project construction in Vietnam.
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypothesis
2.1. Literature Review
Construction delay, which is often encountered in engineering constructions, is defined by scholars as the completion date of the project implementation being later than the planning date which leads to the schedule delays of the whole contract [3] , or the owner and the contractor being not able to meet the completion date on the contract that has been signed [4] . Meanwhile engineering construction delay not only causes the time delay to opportunity cost, resulting in the owner being not able to deliver the project in time so as to reduce investment effect, but also increases cost and reduces the enterprise prestige of the contractor [5] . This problem affects not only the construction industry, but also the whole economy of the country [6] .
This issue is especially obvious in developing countries. Scholars have done a lot of research on the cause of this problem, pointing out that financial factor is one of the main reasons affecting the construction progress. Research has shown that financial factor is one of the main reasons for delays of engineering construction progress and cost overrun in Ghana [7] . In
In different countries and places, under different stages of practice, the risk factors influencing the construction progress are not the same. Scholars have discussed the situation in
To sum up, in developing countries such as
2.2. Research Hypotheses
From the literature and the reality of project management, there mainly are five kinds of fiscal factors which are insufficient funds, slow payment, poor management of cash flow, financial market volatility, and fiscal policy changes, that influenced Vietnam highway construction delay.
2.2.1. Insufficient Funds
Smooth operation of engineering construction must be supported by enough money. Some scholars think that the contractor’s financial ability is one of the 9 major factors influencing the construction period and cost [13] . Because the owner’s construction fund is not yet in place before the engineering construction, or the owner is in short of funds in construction process, not being able to pay the contractor the money of the construction schedule in accordance with the contract, the engineering construction progress is influenced seriously.
H1: Risk of insufficient funds has positive influence on construction schedule delays.
2.2.2. Slow Payment
Slow payment means that completed work cannot be paid in time as specified in the contract agreement, so that the broken capital chain affects the construction delays. All participate in the project may cause the slow payments, as long as one party pays slowly will affect the entire process, and that will bring the project financial difficulties. The influence of this factor has been confirmed [14] .
H2: Risk of slow payment has positive influence on construction schedule delays.
2.2.3. Poor Management of Cash Flow
Money management is the biggest factor that affects the project finance [15] , for cash flow management directly affects the capital turnover of the construction units, and even leads to the capital chain scission during the construction process, which will affect the engineering construction progress.
H3: Risk of poor management of cash flow has positive influence on construction schedule delays.
2.2.4. Financial Market Volatility
Under the changes in financial markets, the price changes for the supply of resources such as materials, mechanical losses as well as the exchange rate of foreign currency affect the plan for resource supply, leading to construction schedule delays. The study of project delay in Ghana shows that besides slow payment, the difficulty for loans and price fluctuations are fiscal factors affecting project delays as well [14] .
H4: Risk of financial market volatility has positive influence on construction schedule delays.
2.2.5. Imperfect Construction of Policies and Regulations
The external factors such as policy are the important factors that decide whether the project would success [10] . Construction process should strictly obey the national government and the local government department’s related law and policy requirements. Project could go smoothly only in a stable policy environment, which means imperfect policies and regulations will affect the construction progress.
H5: Risk of imperfect construction of policies and regulations have positive influence on construction schedule delays.
3. Questionnaire Design and Data Collection
Survey questionnaire consists of two parts: the first part is mainly statistics description, surveying the professional field, work experience and position and so on, in order to understand the main risk factors of the delay in project time limit for a project from different angles , then it can reduce the respondents’ subjective influence brought by itself; the second part is the principal part of the questionnaire, namely the part of scale which uses measured variables to measure the latent variables. At the same time, the scale uses Likert 5 level metrics (e.g. level 1 stands for small, and level 5 stands for great. The higher scale score indicates the greater impact).
3.1. The Design of Variable Index
For the relevant financial factors affecting construction schedule, the author put forward a total of 26 indicators through comprehensive reference above and other authors, combined with interviews of 8 Vietnamese experts who have 20 years of experience in the field of engineering construction, to characterize the 5 potential variables above. The specific composition is shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Latent variables and measurement indicators.
3.2. Data Collection
Questionnaires are distributed by mail, send hair and personnel access. A total of 300 questionnaires were distributed, and 278 copies were collected. The recovery rate was 90.5%, and 238 valid questionnaires were obtained excluding the ones of missing data. The ratio of the sample size and the observation variable has been reached the requirement that it should be higher than the ratio of 1:5 at least [16] .
The investigation object basically covers all of the existing highway projects in Vietnam, which effectively reduces the non-random risk and error of the sample. In order to enable the most accurate reflection of risk that the Vietnam highway engineering may occur, the investigation objects mainly come from the relevant staff on Vietnam highway construction projects that have some experience in engineering project, such as project management units, supervision units, contractor and owner's staff. The specific composition is shown in Table 2.
4. Empirical Analysis
In this study, we make exploratory factor analysis on data by SPSS20 statistical software, and the factor analysis was conducted by principal component analysis and maximum variance method.
4.1. The Results of Factor Analysis
The first step is model checking. Table 3 shows the corresponding test results, in which the KMO value is 0.823 (>0.5) indicating that the variables are suitable for factor analysis. The Bartlett sphericity approximate chi- square test value is 2494.461, and the significant p = 0.000 (sig < 0.05) shows that there is a strong correlation suitable for factor analysis among the variables.
The second step is to find the characteristic value and the contribution rate. From Table 4, we can select 5
Table 2. Respondents constitute.
Table 3. KMO test and Bartlett sphericity test.
Table 4. Component Matrix after rotating.
factors according to the principle of the characteristic value λi > 1 and the cumulative contribution rate of the selected 5 factors reached 73.255 (>50%). It shows that the selected 5 factors basically reflect the most information of construction delay.
The third step is to build the factor load matrix. According to the results of matrix exploratory factor analysis (see Table 4), the factor index load can be divided into 5 categories, ZC1, ZC2, ZC3, ZC4, ZC5 are more associated with the first factor, namely the construction policies and regulations not perfect factor; ZF1, ZF2, ZF3, ZF4, ZF6 are more associated with the second factor, namely the slow payment factor; JRSC1, JRSC2, JRSC3 are more related to the third factor, namely the financial markets change factor; CZM1, CZM2, CZM3 are more relevant with the fourth factor, namely the financial mismanagement factor; CZ1, CZ2, CZ3 are more relevant with the fifth factor, namely the lack of financial factor. While the correlation between the rest of the variables and factors does not conform to the research setting, therefore, we delete them in the further data analysis.
The fourth step is to obtain the factor score. The factor model can make the variables expressed as a linear combination of a common factor, meanwhile it can make the common factors expressed as a linear combination of the original variables, and the factor score coefficient is obtained by the following Formula (1).
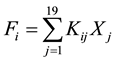 (1)
(1)
Among them, Fi represents the factor scores, i ≤ 5; Kij represents the weight coefficient for the j-th index in the i-th factor; Xj represents the j-th indicator’s observation values.
4.2. Regression Results
Results of regression equation are shown in Table 5. The adjusted R-squared value is 0.627, which shows that the influence factors are more comprehensively taking into account. The value of F is 80.69, both significantly on the level of 1%, indicating that the model settings are reasonable.
The standardized coefficient of each factor is positive when we view them from the standard coefficient and significant level (Table 5), so each factor has a positive impact on the delay of construction schedule, and the test results of the 5 factors both have the significant feature of p < 0.01, therefore the assuming H1, H3, H2, H4, H5 could be established.
From the standard path coefficient we can find that the impact of all kinds of factors on the construction schedule delay is different, and the estimated value varies from 0.177 to 0.472. The largest impact on the construction schedule delay is Imperfect factor of construction policies and regulations (0.472), followed by the slow payment factor (0.309), financial mismanagement (0.459), the financial markets change factor (0.287), the financial lack factor (0.177).
5. Discussion
The construction speed of Vietnam domestic highway is becoming more and more rapidly. Many foreign companies are very active in participating Vietnam Project, especially the Chinese companies. Considering the poor management in the project construction process, common schedule delays and the increasing cost of the project, the investors from domestic and foreign have reduced the investment enthusiasm on these projects. Financial factors are thought to be the main causes of this phenomenon. So we focus on the potential financial factors of Vietnam highway construction delays in this paper, through the methods of questionnaire, factor analysis and regression analysis. The empirical results show that there are five kinds of risks of Vietnam financial factors which cause construction delays. According to the descending lever of its influence, there are imperfect factors of building policies and regulations: slow payment factor, inappropriate financial management factor, the change factor of financial markets and financial lack factor.
Therefore, as for the special condition of Vietnam highway project, we suggest that we should take the following targeted measures to avoid or reduce the potential effect of related financial factor on project delays.
(1) Advice on avoiding risks of imperfect building policies and regulations: Currently Vietnamese basic building system is not so perfect. The project management mechanism is from centralized management of national transition to market mechanism which consists of multi-component consortium management. In the progress of mechanism transition, the change of policies will inevitably affect the related financial risk of construction schedule. The construction schedule will be affected by national macroeconomic policies, for example, the compensation policy is often changing, we do not have uniform standards, the compensation fees are not
Table 5. Regression analysis results.
Note: *** stands for level 1% significantly, **stands for level 5% significantly, *stands for level 10% significantly.
implemented, and the price of compensation cost and resettlement provision is always changing. As a result, we have many difficulties in land acquisition, and the situation of the project funds is affected seriously. And the change of infrastructure investment policy may set limits for some investors and thus affecting the project finance. The bidding process is not so standardized and it is difficult to maintain fair and open. And the contractors and employers often collude in advance; they will bid in a low price and then increase the project price or employ other companies to bid together. Some scholars estimate that because of bureaucracy and bribery and such wrongful act in Vietnam, the loss of building funds may be 20% - 40% of total funds [3] . So the project participants should put more attention to the analysis and prediction of relevant laws and regulations system, and they should take some appropriate measures such as government guarantees and claims in order to make reactions timely when the policy changes. When they place with the employers of the contract, they should make the payments and the time of land transfer clear, the employers will take full responsibility if the loss is caused by delayed payment and land transfer.
(2) Advice on avoiding risk of slow payment: In Vietnam, international investment projects, the phenomena that employers do not give payment timely often take place. So contractors should choose employers with abundant capital when bidding in order that they can give the payment timely. Before the building is started, the contractors should allocate and arrange construction schedule legitimately according to the employers’ capacity of money supply, in order to avoid slow payment caused by employers’ inappropriate financial management. In the process of project implementation, we should make more communication and coordination with the project management and supervision department, and deal with many kinds of engineering contradiction such as increased work when settling accounts and slow acceptance and so on. At the same time, we should prepare bill of quantities well in order to recover unsettled payments from the employers, and to maintain the construction funds in place in time in the construction process.
(3) Financial management strengthening: The lack of funds will affect international engineering project operations deeply. So the contractors should consider the risk of their own funds, loans factors and the operation of project funds seriously when bidding, and then make reasonable bidding price. The contractors can make cooperation with banks, and they can make use of banks’ own funds and credit to provide credit guarantees for contractors to manage risks. Or they are expected to make more cooperation with other companies to integrate resources, and try to avoid vicious price competition and the risk of fund lack in the form of united bid.
(4) Advice on avoiding the risk of financial market changes: In the new mechanism of market, the supply and deployment of project resources mainly depend on the market. The participants are not familiar with the market mechanism and there are some defects in the market mechanism, these have become the new effects of delay of construction progress. Before contracting the Vietnam project, the contractors should know more about the Vietnam market, they can adjust the relevant cost through signing the contract according to the changes of Vietnam market, in order to avoid financial risk caused by changes in the price of construction materials, exchange rate fluctuations and changes in interest rates.
Acknowledgements
At the point of finishing this paper, I’d like to express my sincere thanks to all those who have lent me hands in the course of my writing this paper. First of all, I’d like to express my gratitude to my classmates who offered me references and information on time. Secondly, I’d like to thank those leaders, teachers and working staff especially those in the School of Economics and Management. Without their help, it would be much harder for me to finish this paper.
Cite this paper
Hong-AnhVu,JianqiongWang,LianxingMin,Thihong-NhungNguyen, (2015) Impacts of the Financial Factors on Schedule Delays Risk of the International Contracting Projects: Evidence from Highway BOT Pro-jects in Vietnam. World Journal of Engineering and Technology,03,311-319. doi: 10.4236/wjet.2015.34030
References
- 1. Long, N.D., Ogunlana, S., Quang, T. and Lam, K.C. (2004) Large Construction Projects in Developing Countries: A Case Study from Vietnam. International Journal of project management, 22, 553-561.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2004.03.004 - 2. Le-Hoai, L., Dai Lee, Y. and Lee, J.Y. (2008) Delay and Cost Overruns in Vietnam Large Construction Projects: A Comparison with Other Selected Countries. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 12, 367-377.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12205-008-0367-7 - 3. Assaf, S.A. and Al-Hejji, S (2006) Causes of Delay in Large Construction Projects. International Journal of Project Management, 24, 349-357.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2005.11.010 - 4. Aibinu, A.A. and Jagboro, G.O. (2002) The Effects of Construction Delays on Project Delivery in Nigerian Construction Industry. International Journal of Project Management, 20, 593-599.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0263-7863(02)00028-5 - 5. Abdul-Rahman, H., Wang, C., Takim, R. and Wong, S. (2011) Project Schedule Influenced by Financial Issues: Evidence in Construction Industry. Scientific Research and Essays, 6, 205-212.
- 6. Faridi, A.S. and El-Sayegh, S.M. (2006) Significant Factors Causing Delay in the UAE Construction Industry. Construction Management and Economics, 24, 1167-1176.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01446190600827033 - 7. Frimpong, Y. and Oluwoye, J. (2003) Significant Factors Causing Delay and Cost Overruns in Construction of Groundwater Projects in Ghana. Journal of Construction Research, 4, 175-187.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1142/S1609945103000418 - 8. Toor, S.U.R. and Ogunlana, S.O. (2008) Problems Causing Delays in Major Construction Projects in Thailand. Construction Management and Economics, 26, 395-408.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01446190801905406 - 9. Alaghbari, W., Kadir, M.R.A., and Salim, A. and Ernawati (2007) The Significant Factors Causing Delay of Building Construction Projects in Malaysia. Engineering, 14, 192-206.
- 10. Thi, C.H. and Swierczek, F.W. (2010) Critical success Factors in Project Management: Implication from Vietnam. Asia Pacific Business Review, 16, 567-589.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/13602380903322957 - 11. Luu, M.H. (2009) Factors Affecting Risks of Construction Projects in Vietnam. Maastricht School of Management, Maastricht, The Netherlands.
- 12. Ma, D.G. and Li, M.F. (2009) Early-Warning Model of Chinese Currency Crisis and Its Empirical Analysis—Correction and Application Based on the Research of the Factor—Logistic Model. Journal of Shanxi University (Philosophy and Social Science Edition), 32, 83-89.
- 13. Alzahrani, J.I. and Emsley, M.W. (2013) The Impact of Contractors’ Attributes on Construction Project Success: A Post Construction Evaluation. International Journal of Project Management, 31, 313-322,
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2012.06.006 - 14. Fugar, F.D.K. and Agyakwah-Baah, A.B. (2010) Delays in Building Construction Projects in Ghana. Australasian Journal of Construction Economics & Building, 10, 103-116.
http://dx.doi.org/10.5130/ajceb.v10i1/2.1592 - 15. Abdul-Rahman, H., Takim, R. and Min, W.S. (2009) Financial-Related Causes Contributing to Project Delays. Journal of Retail & Leisure Property, 8, 225-238.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1057/rlp.2009.11 - 16. Bollen, K.A. (1998) Structural Equation Models. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.



