Paper Menu >>
Journal Menu >>
 J. Service Science & Management, 2010, 3: 130-137 doi:10.4236/jssm.2010.31016 Published Online March 2010 (http://www.SciRP.org/journal/jssm) Copyright © 2010 SciRes JSSM Study of the Instant Incentive Mechanism for Zero-Time Enterprise Yang Hu1,2, Xinrong Yang1 1School of Economics and Management, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, China; 2School of Economics and Management, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China. Email: drhuyang@sina.com Received December 19th, 2009; revised January 12th, 2010; accepted February 11th, 2010. ABSTRACT The zero-time enterprise’s mission is response to the market and customer needs in “zero tim e” in order to gain more customers and competitive advantages. To realize zero-time response to market and customers, it should inspire the employees’ work enthusiasm and creativity, so that they can do their work conscientiously to ensure quick and smooth going. This paper discussed how to establish an effective instant incentive mechanism for zero-time enterprise, which is a problem of rich practical significan ce. Firstly, based on the briefly explanation of zero-time enterprise, it analyzed the characteristics and princip les of zero-time enterprise; and then elaborated the important ro les of instant incentive. Fi- nally, it proposed the basic contents of instant incentive and the “Trine” realization mechanism. Keywords: Zero-Time Enterprise, Instant, Incentive 1. Introduction Enterprise competitions and changes in business envi- ronment prompting the mode of competition to transfer from price-based competition to quality and variety- based competition, and now to the time-based competi- tion (Time-based competition, TBC). TBC doesn’t mean to take no account of price, quality and variety, but under the premise of meeting all these factors, it is to immedi- ately respond to customer needs [1]. Meanwhile, due to customer needs have become personalized and diversi- fied. These factors have posed a challenge to the modern enterprises’ operations. They have to strive for customers in order to survive and develop in current rapidly chang- ing time characterized as TBC, the instant response to customer needs of personalized and diversification has become an irrefutable fact. According to the actual re- quirement that instant response to customer needs, the concept of zero-time [2] has been proposed, and the study of zero-time enterprises begins to be concerned by scholars. Modern enterprise management is attributed to the management of human resources. It hopes that through the effective deployment of personnel to get immediate response to customer needs, so that realizing the strategic development. Human resources are strategic resources of modern enterprises, but also the most critical factor in the enterprise survival and development, and incentive is an important part of human resources. The most fundamen- tal purpose of incentive mechanism proposed by enter- prises is to correctly direct the employees’ work motiva- tion, enabling them achieve business goals while achiev- ing their own needs, increasing their satisfaction, so that their enthusiasm and creativity could be maintained and carried forward. This is one of the necessary conditions that immediate response to customer needs of individual and various. In fact, nowada ys in enterprises, quite a few of staff would have been able to achieve even greater success, but they did not. This is not due to they lack of skills, but a lack of motivation and passion to work, it is the enterprises lack o f imme diate and effective incentives for them. Therefore, how to establish an effective incen- tive mechanism is a very important problem for each enterprise facing and urgent needing to solve. This paper is for zero-time enterprise, to explore the important issue how to establish an effective instant incentive mechanism. 2. The Connotation of Zero-Time Enterprise and Characteristics of Incentives 2.1 The Connotation of Zero-Time Enterprise The concept of zero-time, firstly proposed by Raymond T. Yeh and Keri Pearlson in 1998, in their paper, “Zero time: A Conceptual Architecture for 21st Century Enter- prises”. In 2000, Raymond T. Yeh, Keri Pearlson and  Study of the Instant Incentive Mechanism for Zero-Time Enterprise Copyright © 2010 SciRes JSSM 131 George Kozmetsky co-authored of “Zero Time: Provid- ing Instant Customer Value—Every time, All the Time!” [2] in detail discussing the zero-time philosophy and 5 rules. In China, Bo sheng Zhou and Dongping Fan (2000 ) [3] gave an explanation of introduction for the zero-time concept. Briefly, zero-time is a philosophy or a concept, refers to the shortest time applied to respond to customer needs. It is similar to zero-defect for quality control and zero-inventory for production management. The proposal of zero-time is an important contribution to the theory of TBC, it extremely promote the concept of enterprise com- petition, and gives the most brilliant general of t he concept. The 21st century is a rapid changing era characterized as explosive expansion of information, the changes of competitive environment and affecting competition fac- tors have made the birth of zero-time enterprise to be a necessity. So called zero-time enterprise, in short, refers to the enterprise operated in accordance with zero-time concept and rules, “within the organization, every busi- ness process based on response to customer needs, should be implemented immediately, if needed with automatic learning. Managers and employees possess the knowledge and capabilities to make police (decisions) and vendors can provide the required parts and services immediately”, its essential characteristic is to instantly respond to customer’s personalized requirements [4]. The ultimate goal for zero -time enterprise is not only “enab le customer to trust, do as product leader, make operation excellent”, also far from being market share, but rather to “permanently occupy the market”, that is to say, by pro- viding instant personalized products and services in the existing untapped market to occupy a dominant position, and through the constant release of innovative products to gain market dominance, which is performed as spiral process of innovation, new products, new services and market, is similar to the waves in the sea, constantly al- ternating emerge, and never cease. Traditional enterprise must overcome some deficiencies firstly to become zero-time enterprise. The reference [3] point that there are 5 kinds of gaps in operations between the traditional enterprise and zero-time enterprise, namely: zero value gaps, zero learning gaps, zero management gaps, zero process gaps and zero inclusion gaps. In the course of business oper ations, if an y one of the 5 gaps wa s delayed, it would impede the enterprise to make quick response to customer needs and changes of business environment. This paper is based on the special operation and arch i- tecture concept for zero-time enterprise, discusses the issue how to effectively motivate internal staff to instant respond to customer needs. 2.2 The Characteristics and Principles of Zero-Time Enterprise Incentive The zero-time enterprise’s mission is response to the market and customer needs in “zero time” in order to gain more customers and competitive advantages. To respond to the market and customers in zero-time, it must ensure the employees with high enthusiasm and creativ- ity, and have a strong sense of responsibility or urgency, so that they can do their work conscientiously to ensure quick and smooth implementation. All behaviors of em- ployees are in pursuit of some kinds of benefits or avoid some disadvantages, thus physically and psychologically inevitably effects in the corresponding preferences and aversion. Incentive is to promote the common tendency of preferences and aversion in order to promote the sus- tainable development of enterprise. Of course, this ten- dency is different for different people, but one thing is in common, that is to be instant and appropriate. To this end, it is necessary to give employees the appropriate incen- tives, but also to motivate them immediately. In appropri- ate incentives, overweight or too light incentives can not really realize the purpose; while the incentives are out of time, too early or too late, it would lose the original meaning of incentives. It follows those instant and ap- propriate incentives critical. Therefore, the zero-time enterprise is characterized as instantaneous. The appro- priation is the core principle of enterprise incentives, manifested in details as follows: 1) The appropriate intensity. Incentives are divided to positive and negative one, positive incentives shall be rewarded, and negative incentives shall be punished. Rewards and punishments will directly influence the in- centive effects. The overweight reward will make staff generate the feelings of pride and satisfaction, inducing loss of desire to further enhance themselves; the too ligh t reward will not induce the incentive effects, or to make them get the feeling of not being taken seriously. The excessive punishment will make staffs feel injustice, or loss the identity to enterprise, and even induce the emo- tions of cacanny or damage; too light punishment will make staff underestimate the seriousness of the error, which may also continue to make the same mistake. 2) The appropriate fair. The appropriate fair is one of the most important principles in staff motivation, any unfair treatment will affect their work efficiency and emotion, so that affect the incentive effects. The staff with the same achievements should receive the same level of incentives; similarly, the staff committing the same mistakes should subject to the same level of pun- ishment. If it is failure to do so, the managers prefer not to award or not to pu ni sh. 3) The appropriate time. The core of instant incentives is “quick”, as the saying in the ancient book of “Si Ma Art of War”, which promoted “never miss the right op- portunity to reward, and cannot wait to punish until sol- dier leaves the group.” That emphasized only instant in- centives could make people be quickly aware of the re- sults of doing good or bad. “Execute an example of re- wards and punishments to a hundred”, which generates  Study of the Instant Incentive Mechanism for Zero-Time Enterprise Copyright © 2010 SciRes JSSM 132 the shock and sensational effects, in order to achieve the goal that “found credit of rewards, and retain force of punishments”. Enterprise always strives for benefits, maximum bene- fits is pursuit, while the employees’ maximum achieve- ments itself is the basis for enterprise to maximize bene- fits. Therefore, managers must grasp the instant character of incentives, so that to maximize employees’ achieve- ments. Managers are required to be familiar with the specific characteristics of opportunity in order to iden tify and apply at all times. One character is that opportunity is always hidden, it is impossible for staffs to expose all their desires, but often to be hidden. Through the tortuous courses and complicated mental activities, reflecting in words, behaviors and expressions, and then it is observed by others. Therefore, it is required that managers should learn to carefully weigh up employees’ words and watch their expressions, gain an insight into their mentality. Second, opportunity is transient. Th e desires do not keep unchanging, but always go with people’s needs and so- cial values changes. Third, opportunity is changeable, it is similar to the transient, for example, a person takes more emphasis on material motivation at one time, how- ever, when his family’s economic condition has been greatly improved, his needs would be more transferred to the spirit (that is, honor awards). Accord ing to these three characteristics, managers can more easily and more ac- curately grasp the principles of appropriate incentives. 4) The appropriate method. There are several kinds of incentives. It is required to apply appropriate incentive method according to the different objects. The objects and method should be matched to get the incentive ef- fects. As the different requirements of different employ- ees, the same incentives would play a variety of incentive effects. Even the same person at different times or envi- ronment, would also have different needs. As the incen- tive is depended on the internal feelings of staff, the in- centives must vary in person. During the process of for- mulation and implementation incentive method, firstly, it required to make a thorough investigation what are their actual needs. Organize, classify, and then determine the appropriate incentives. 5) The appropriate object. This principle mainly sug- gests that incentives need to seek truth from facts, re- quiring the subjected object should be the right person or team who has actually made contribution. In other words, reward those who should be subjected to reward, punish those who should be punished. 6) The appropriate place. This principle mainly pro- poses that incentives should be based on specific condi- tions. It can not mechanically carry out the positive in- centives and negative incentives. For any positive incen- tives, reward on the right spot can execute an example of rewards to a hundred; for some negative incen tives, pun- ishment on the spot can not execute an example of pun- ishments to a hundred, oppositely, it will bruise staffs’ self-respect and enthusiasm. Generally, instantaneous and appropriation are inter- related and complementary. The core of appropriation principle is required that incentives are consistent with merits and demerits. It is undesirable that neither award is greater than or less than achievements, nor punishment is greater than or less th an mistakes, but only appropriate instantaneous and instan t appropriation can maxi mize the effects of incentives. There is moderation for ev erything, inappropriate control may induce going too far or not getting the expected result, both of which should be avoided in management. In short, it should pay attention to the following six points: First, never reward without any achievements, or never punish without any mistakes; second, cannot lightly reward great achievements, or cannot lightly punish big mistakes; third, cannot grandly reward small achievements, or cannot heavily punish little fault; fourth, the nu mber of incentives should not be too much, nor too low; f if th, can no t rew ard mistak es and punish the achievements; sixth, appropriate incentives should be based on specific situations, including different person, issues and conditions. It can not mechanically carry out rewards an d p unishme nts. 3. Instant Incentive Mechanisms for Zero-Time Enterprise 3.1 The Important Roles of Instant Incentives Indubitably, instant incentive plays an extremely impor- tant role in promoting the immediate response to the market and customer needs. As the lack of instant incen- tives will make employees unable to judge whether they work correctly or not, it is difficult for them to develop good habits, eventually leading to lower efficiency and therefore it would be impossible to immediately respond to the market and customers. Instant incentive is not on ly an incentive approach, but also a business strategy. Thus its roles are significant, which are as follows: 1) Instant incentive is the enterprise’s power system. Under the established business strategy, it can be accel- erated by instant incentives. Incentive to employees just like accelerating running car on the highway that it is required to step on it in orde r to make the car able to ac- celerate to a specific speed. Similarly, employees also need incentives to encourage them work hard, allowing have full of enthusiasm and strong innovation. If you can not give an immediate incentive, employees will gradu- ally become slack, would be difficult to effectively im- plement business strategies, and thus it’s unable to achieve instant response to customer and market. There- fore, instant incentive is enterprise’s power system and accelerator as well. 2) Instant incentive is the correction system for busi- ness strategy implementation. Under the established busi-  Study of the Instant Incentive Mechanism for Zero-Time Enterprise Copyright © 2010 SciRes JSSM 133 ness strategy, employees’ hard working play important role in achieving business’s objectives, thus it’s highly necessary to ensure them positively and efficien tly throw in to gear. Instant incentives indicate that: What is right and what is wrong. Instant incentive is charged with the correction system functions for business strategy imple- mentation, emplo yees will be more concentrated on wo rk when their acts have been affirmed and strengthened, while some of their acts can be immediately rectified if they did not meet the requirements, so as to ensure the smooth implementation of the strategy. 3) Instant incentive is the activator used to make em- ployees change behaviors. Effective instant incentives can form collective memories, prompt them to develop good habits, and improve work efficiency as well. Every one has the instinct of self-motivation, which can fully satisfy his demands, while stimulate the enthusiasm and drive to improve efficiency. Therefore, the instant incen- tive can be used to activate staff’s passion. In conclusion, instant incentive has an extremely im- portant role in motivation, however, how to fully play the role of incentives, which required establishing an effec- tive implementation mechanism for instant incentiv e. 3.2 The Basic Contents and Realization Mechanisms of Instant Incentives The realization mechanisms of instant incentives are de- termined by their basic contents, only in accordance with the contents can build practical and concrete realization mechanisms. The basic contents include: understanding the actual needs of employees, formulate reasonable in- centive systems, grasp the appropriate opportunity to motivate staff, establish incentive model for the knowl- edge team based on the psychological contract, and form “Trine” implementation mechanism. 1) Understand the actual needs of employees. The managers need to really take consideration on the employees’ position, to think about their work motiva- tion and hardship paid for work; from their points of view to consider their work and should be paid remu- neration and reward issues. For the staff with success on a particular position, certainly there would be other mo- tives and needs o ther than h is daily responsibilities set b y organization. For example, he may want to make more money, to travel abroad with his girlfriend, as well as to repay his family; or if he wants to promote himself and to be a manager in order to win the admiration and so on. All these are his motives and needs outside of the daily responsibilities; managers must dig out these motives, so as to truly understand the emp loyees in order to establish instant and effective in centive schemes. Most of time, people have been accustomed to using tower type “Need-hierarchy theory”, which was p roposed by Abraham · H · Maslow in the 50 years of 20th century [5], to explain the employee needs and guide the formu- lation of incentives. In fact, if we change the perspective of the employee needs, perhaps it may be more realistic and more practical. We believe that whether employees can keep mind on work and even work hard, depending on the ability of the business or how to meet employees in the following four aspects: material benefits, career ideals, sense of belonging, and marginal pursuit. Material benefits: To determine a person whether is willing to work in the enterprise, an impor tant variable is the level of material benefits provided by the enterprise. Obviously, the employees not only want to have accu- mulation under the premise of feeding themselves and families, but also need access to a cultural-sociological identity, as in a particular social environment, the salary is an important aspect reflecting social status. In addition, quite high proportions of senior human talents tend to judge how much respect and the value of their cognition they would get in the enterprises by the level of material benefits provided by their business. However, material benefits it is not the one and only factor for all the staffs to choose business and to fulfill their responsibilities. Obviously, if the employee is highly devoted to business, but he was not placed in appropriate positions closed to his profession, even if be paid much better material benefits, he could also hardly concentrate on work. Career ideals: it is the person’s wish that he would like to make achievements in his favorite area, being enviab le and satisfactory or proud of himself, even if this wish may be just a staged achievement. The person’s career ideals are commensurate with his education, working and living environment, personal hobbies, personality and personal pursuit, and related to the particular social val- ues as well. For the person with strong career ideals, the enterprise may not be attracted to him by the high wages, but merely provide him with training opportunities for learning and displaying his talent. For such employee, it’s just required to provide him with a platform to achieve personal ambition, he might be satisfied, and then throw himself into work. Sense of belonging: the sense of belonging is an inte- grated sense for the employees’ own businesses, such as whether they feel security in enterprise, whether it is worthwhile to throw h imself into work , with or without a sense of honor, whether be respected, whether there are harmonious interpersonal relations, whether the enter- prises treat employees friendly, with or without long- term development and so on. In essence, every one will hope to work in the enterprise with a sense of belonging. Once the staff feels that he is working for the enterprise without any sense of belonging, he would not keep his mind on the work, and also can not effectively complete his own duties. Marginal pursuit: Someone work in enterprise, simply because of taking the enterprise as springboard, that is to accumulate capitals/create conditions/pass time for his  Study of the Instant Incentive Mechanism for Zero-Time Enterprise Copyright © 2010 SciRes JSSM 134 further new job opportunities, we call this pursuit as “marginal pursuit”. In fact, not only the person, who takes enterprise as springboard, is possessed of marginal pursuit, but also all of whom would have the possibility of the similar pursuit. For example, someone may prefer to living in a certain city, so as to choose a company in this city; someone may not change another company just because his current located one is closed to his family; someone may not be attracted by another company’s higher wage just because he could access to higher social assessment now. The concept of marginal pursuit is pro- posed for the meaning that, if companies are good at dig- ging and encourage their staffs to obtain the marginal pursuit, it will be conductive to improving the relation- ship between staffs and companies, that is to increase the attraction of companies to staffs, and staffs’ loyalty to company. For example, if a senior worker cannot keep his mind on work due to the distance from his family, the enterprise could just try to solve the decantation of his wife, which comes up to satisfy his marginal pursuit, so that he could thro w himself into work afterwards. In practice, when company managers try to understand the actual needs of employees, they need to considerate from the vertical and horizontal two angles. From the vertical view, the employees with different levels of knowledge and salaries would also possess different de- mands. As for the employees with lower salary, it will focus on meeting their material benefits and sense of belonging, that is, to improve their living conditions. As for the employees with higher salary, it should pay more attention to meet their career ideals and marginal pursuit. From the horizontal view, for the employees in same levels, the focuses of their demands are also different because of the differences of their personality and living environments. Someone may highly focus on material benefits due to personality characteristics; someone may much like to be praised, and enjoy the spiritual sense of achievement; and also someone may be good at studying techniques, be possessed of strong learning desires, while not deeply need money. Therefore, it’s required to “tai- lor-made” list of requirements for different employees. In conclusion, as the staff needs are complex and di- versified, it’s really not easy to truly understand every- one’s needs. The managers need to make more effort, from the vertical and horizontal angles of view, in order to summarize the real demands of each staff, then to find the two or three dominant demands and give targeted incentives for them. 2) Reconstruct the balanced model for organiza- tional structure under zero-time competition. Management contingency principle indicated that various kinds of management methods are effective, but the most suitable one is the best one. To accord with the fundamental principles of contingency management, it’s required to appropriately combine the organization stra- tegic goals, organizational structure and employee condi- tions, etc., to carry through self-summarization, self- creation, so as to develop a suitable organizational as- sessment model. TBC environment has broken up the original balance of the organizational structure, which urgently needs to be restructured, through changing con- trol method and control structures. In a new balance, all levels of staffs should be clear about themselves roles and responsibilities. It is encouraged to achieve “free hand” management and bottom-up participation, and it will be applied to a new performance management sys- tem, so as to enhance the flexibility of performance management. However, it’s useless to just orally appeal “free hand” management and bottom-up participation, but also needs some quick and effective methods. Such as the power down, so that making decisions by the most qualified person, and entrusting the people in different levels with different freedom of making discretions (As for the general small proposals can be assessed by the staff themselves to take action, while the more important proposals are assessed and determined by sector manag- ers, and the major ones are handled by the leaders in charge of the whole department, and so on). Meanwhile, the proposal can also step across the traditional bot- tom-up approving process, establishing the proposals management department, which makes the acceptance, evaluation, submission and the numbers of proposals adopted by company be included to the assessment of proponents. 3) Construct the integrated evaluation model for performance results and behaviors under zero-time competition. Usually, the performance evaluation, which is focus- ing on results, is results-oriented, focusing on work’s final performance, and its evaluatio n contents are mainly concentrated on the actual outcomes; while the perform- ance evaluation, which is process-oriented, is concen- trated on employees’ behaviors, effort intensity and work attitudes in process of their working. As the working process in Zero-Time Enterprise is much more compli- cated, the employees’ performances have significantly compounded characteristics, it should synthetically evaluate their work process and behavioral outcomes. The performance evaluation for non-procedural worker, it should be result-oriented as far as possible; while for procedural knowledge worker, it can use behav- ior-oriented approach. If it is uncertain to find the em- ployees’ performance results, the outcome itself is not easy to be quantified, the value reflecting is lagging, and it is of strong professionalism and innovation, then its performance evaluation needs to combine the behav- ior-oriented approach and result-oriented one. In recent years, objective management, key perform- ance indicators, balanced scorecard and other perform- ance assessment methods become very popular in many  Study of the Instant Incentive Mechanism for Zero-Time Enterprise Copyright © 2010 SciRes JSSM 135 companies, but they often ignore the behavioral anchors titration, behavioral observ ation scales such as the use of technology for performance evaluation. In fact, from the view of development of performance management in western enterprises, objective management, key per- formance indicators, balanced scorecard, etc., are the tools for strategic performance assessment, which would be able to connect employee performances to the strategy of the whole organization. However, the tools for strate- gic performance assessment are inseparable from the performance evaluation methods and technology support. Many performance evaluation techniques such as behav- ioral anchors titration and behavioral observation scales can directly provide specific behavioral degrees and evaluation scales, for the evaluator to establish a uniform evaluation standa rd, will not only help managers to make objective evaluation, but also help to guide staffs’ per- formance behaviors. 4) Construct double evaluation model of individ- ual-team under zero-time competition. The staffs in Zero-Time Enterprise in many cases are in the form of teamwork, the character of this work de- termines that the performance evaluation can not only be aimed at individual work, but should also evaluate the working conditions of the entire team. If only consider the individual performance indicators, it would induce employees to focus only on the quality of their own work and performance, so as to lack of team spirit, be poor in collaboration, this will reduce the efficien cy of the entire team, and even lead to team conflicts and confusion. Therefore, in the design of evaluation indicators, on the one hand that it should consider the individual behavior and work results; on the other hand, it has to consider the work progress, work quality and team cohesion an d other factors, to pay attention to the integration and consis- tency of individual and team indicators. Including the team indicators into the performance evaluation system of knowledge-based staffs, will help to improve the sprint of teamwork, encourage the cooperation among the staffs, so that the team can efficiently complete the intended objectives. 5) Grasp the appropriate incentives opportunity. Incentives need to follow the principle of appropriate opportunity. Generally, it’s required to be accorded with the strongest stage of the staffs’ desires of winning award, so as to get the best incentives efficiency. As to the re- wards aspect, Marshall who is the famous general in United States, believes that the troop of outstanding per- formance in the battle should be praised promptly, he said that awards can run immediately, be announced to the press; while clerical work can be followed up, its requirement of filling in a variety of forms would cause time delay, which would reduce the incentives value to the lowest perception. Any delaying ideas and behaviors always lost the incentive role of reward, resulting in empty result of reward. Of course, the instant incentive is not simply to be done quickly. It mainly reflects the style of speedy and strict enforcement, but not mechanically implement, its premise is based on the right clear and accurate incen- tives. If the incentive objective is error, and its character is not exact, it would be not only meaningless, but also cause harmful effects. Therefore, the principle of instant incentives, is not for the sake of speed, but must be strictly controlled. 6) Establish incentive model for knowledge-based team based on psychological contract. Zero-Time Enterprise should be knowledge-based en- terprise, the composition of its team members should be knowledge-based workers. Therefore, incentives for knowledge-based team should focus on the achievement and growth of knowledge-based workers. Only if fully encourage their enthusiasm, it would drive them all to- gether to work hard, so as to make team play greater synergistic effect and to create better performances; as to incentive method, it emphasizes the combin ation of indi- vidual incentives, team incentives and organizational incentives; as to incentive time effect, it should combine their short-term incentives and long-term incentives, which stresses the long-term positive effect of incen tives for human talent; as to the design for incentive compen- sation mechanism, it would have to establish incentive model for knowledge-based team based on psychological contract [6]. The incentive model for knowledge-based team based on psychological contract is shown in Figure 1 (dashed lines represent the feedback lines, while solid lines rep- resent the causal relations). The incentive model for knowledge-based team based on psychological contract, transfers from the single eco- nomic contract-based model to the model combined with psychological contract and economic contract, with par- ticular emphasis on the important role of psychological contract in the incentives. Firstly, psychological contract for external compensa- tion and benefits is the basis of incentiv es, which directly influent the effectiv eness of material motivation; second, psychological contract for internal reward values is the core of incentives, which can enhance mutual sense of responsibility, sense of duty, self-discipline and self- control, so as to lead values of both sides to convergence, and form intrinsic motivation; third, the psychological contract for work atmosphere is the guarantee for incen- tives, which can provide more relaxed atmosphere for organization, form a democratic management style with sufficient authority to built interpersonal relationships full of trust, compassion and respect, so as to construct an internal contract system with the guarantee of mutual support; finally, the key to incentives are the recognition 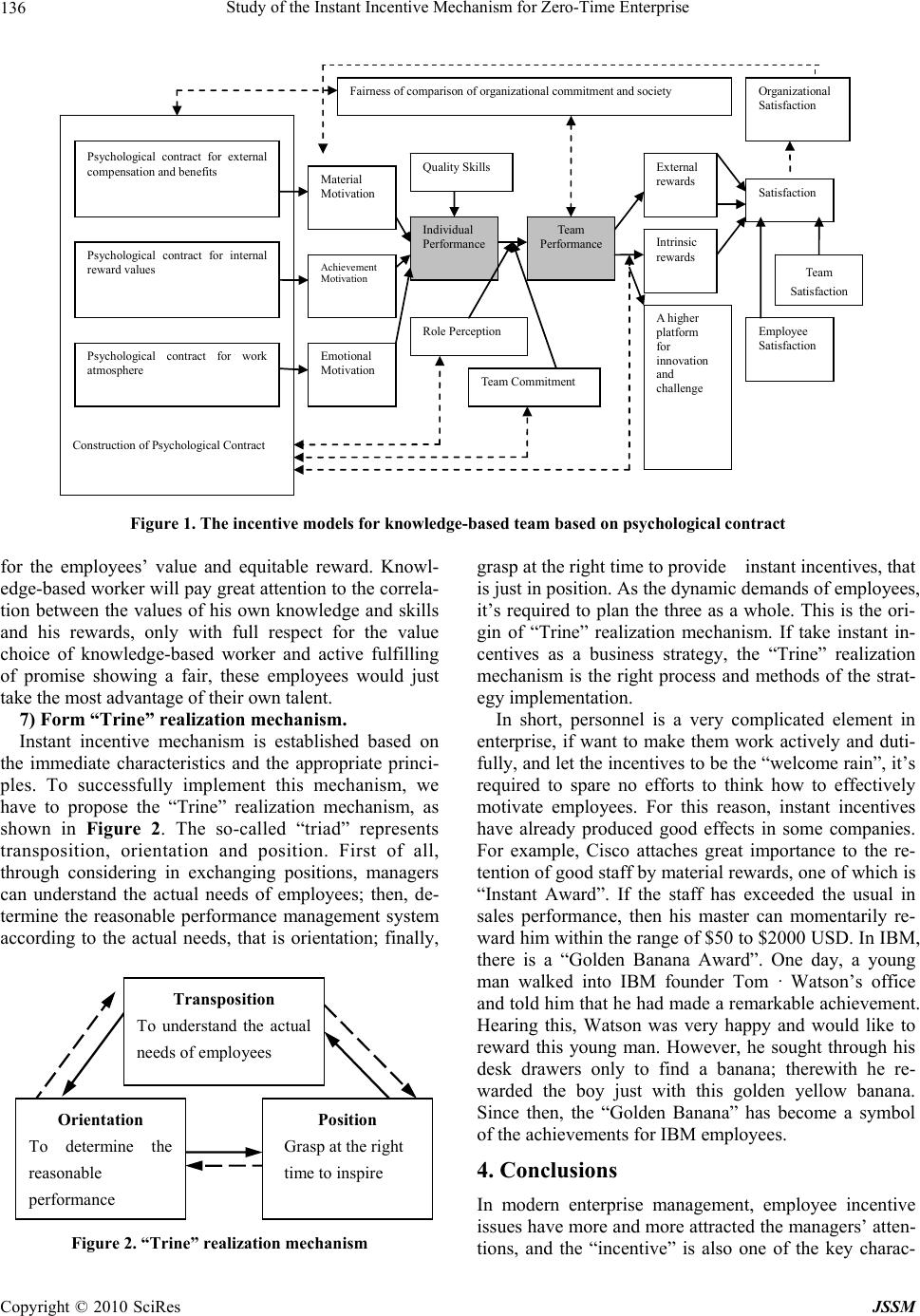 Study of the Instant Incentive Mechanism for Zero-Time Enterprise Copyright © 2010 SciRes JSSM 136 Construction of Psych ological Contract Emotional Motivation Achievement Motivation Psychological contract for work atmosphere Psychological contract for external compensation and benefits Material Motivation Individual Performance Quality Skills Role Perception Team Co mm itme n t Team Performance External rewards Intrinsic rewards Ahighe r platform for innovation and challenge Satisfaction Employee Satisfaction Team Satisfaction Organizational Satisfaction Fairness of comparison of organizational commitment and society Psychological contract for internal reward values Figure 1. The incentive models for knowledge-based team based on psychological contract for the employees’ value and equitable reward. Knowl- edge-based worker will pay great atten tion to the correla- tion between the values of his own knowledge and skills and his rewards, only with full respect for the value choice of knowledge-based worker and active fulfilling of promise showing a fair, these employees would just take the most advantage of their own talent. 7) Form “Trine” realization mechanism. Instant incentive mechanism is established based on the immediate characteristics and the appropriate princi- ples. To successfully implement this mechanism, we have to propose the “Trine” realization mechanism, as shown in Figure 2. The so-called “triad” represents transposition, orientation and position. First of all, through considering in exchanging positions, managers can understand the actual needs of employees; then, de- termine the reasonable performance management system according to the actual needs, that is orientation; finally, Orientation To determine the reasonable performance Position Grasp at the right time to inspire Transposition To understand the actual needs of employees Figure 2. “Trine” realization mechanism grasp at the right time to provide instant incentives, that is just in position. As the dynamic demands of employees, it’s required to plan the three as a whole. This is the ori- gin of “Trine” realization mechanism. If take instant in- centives as a business strategy, the “Trine” realization mechanism is the right process and methods of the strat- egy implementation. In short, personnel is a very complicated element in enterprise, if want to make them work actively and duti- fully, and let the incentives to be the “welco me rain”, it’s required to spare no efforts to think how to effectively motivate employees. For this reason, instant incentives have already produced good effects in some companies. For example, Cisco attaches great importance to the re- tention of good staff by material rewards, one of which is “Instant Award”. If the staff has exceeded the usual in sales performance, then his master can momentarily re- ward him within the range of $50 to $2000 USD. In IBM, there is a “Golden Banana Award”. One day, a young man walked into IBM founder Tom · Watson’s office and told him that he had made a remarkable achievement. Hearing this, Watson was very happy and would like to reward this young man. However, he sought through his desk drawers only to find a banana; therewith he re- warded the boy just with this golden yellow banana. Since then, the “Golden Banana” has become a symbol of the achievements for IBM employees. 4. Conclusions In modern enterprise management, employee incentive issues have more and more attracted the managers’ atten- tions, and the “incentive” is also one of the key charac-  Study of the Instant Incentive Mechanism for Zero-Time Enterprise Copyright © 2010 SciRes JSSM 137 ters for modern human resources management being dif- ferent from the traditional one. There is no t only regular- ity, but also strong skill or artistry in incentive manage- ment. Managers must be good at deep analyzing and studying the characteristics of enterprise management and the workforce based on specific situations, take the effective and targeted measures, so that employees’ in- ternal energy are fully inspired in order to provide pow- erful driving force for business development. Although the instant incentiv es were not newly proposed, it is nec- essary to actively study for effective good use of instant incentive mechanism, and different business practices would be different. 5. Acknowledgements This paper is supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (supporting ID: 20090460995). REFERENCES [1] R. Q. Chen, “Research of new technologies and new methods in operation management time-based competi- tion,” (An application report of National Natural Science Foundation), September 2003. [2] R. T. Yeh, K. Pearlson, and G. Kozmetsky, (translated by D. Q. Tang, W. H. Tang, and H. P. Shao), “ Zero time: Providing instant customer value—every time, all the time!” Electronic Industry Press, 6th Edition 2002. [3] B. S. Zhou and D. P. Fan, “Zero time: The concept of enterprise in 21st century,” China Mechanical Engineer- ing, No. 2. 11(1–2): pp. 89–92,113, Ⅻ, 2000. [4] Y. Hu and G. H. Zhang, “The analysis on performance management modes for zero-time Enterprise,” China Human Resources Development, Vol. 12, pp. 26–30, 2009. [5] H. Mintzberg and Y. Q. Chen, “Strategic skill”, IT man- agers in the world, No. 4, 2004. [6] N. J. Allen and J. P. Meyer, “The measure meat and an- tecedents of affective, continuance and normative com- mitment to the organization,” Journal of Occupational Psychology, Vol. 63, pp. 1–18, 1990. |

