iBusiness
Vol.2 No.3(2010), Article ID:2709,5 pages DOI:10.4236/ib.2010.23038
The Analysis on Environmental Effect of Logistics Industry FDI
![]()
School of Management, Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian, China.
Email: wangyang@djtu.edu.cn
Received April 10th, 2010; revised June 9th, 2010; accepted July 17th, 2010.
Keywords: Logistics, FDI, Environmental Effect
ABSTRACT
Whether it is positive or negative effect for FDI to the host environment, the theoretic problem exists in argument. The paper analyzes influence factors, mechanism, environmental regulations and so on of FDI environmental effect, use Spearman rank correlation coefficients to calculate, and believes that in the reality, the host country is the main factor of the environmental effect, based on the stage of China’s economic development, environmental carrying capacity and the advanced technologies and management concepts of TNC, to promote logistics FDI to play an positive environmental effect.
1. Introduction
Environmental standards and industry regulations among developed countries don’t differ much, so the environmental effect has been ignored from the perspective of developed countries as investment countries. However, developing countries or underdeveloped countries are generally lower than the requirements of developed countries, so the environmental effect has been ignored from the perspective of developing countries, which is the reason of few research results about environment effect. However, with the limit of environmental carrying capacity of the host country, economic growth and industry upgrading, increased income to the environmental requirement, the improved capacity of environment due to increasing national wealth, environmental effect of FDI has become an important subject of theoretic research.
The problem about environmental effect of FDI is the transfer of polluting industries, dividing into positive and negative effect, if it is transferring the pollution industry, which will be believed to produce negative effect, and if it is not transferring the pollution industry, which will not produce negative effect. Correspondingly, the basis for the formation of environmental effect should be divided into two areas: in open economy, environmental standards will influence the capital inflow among countries, and pollution industries of high standard areas invest to low standard areas, which produces transferred pollution. “Pollution haven hypothesis” [1] well explains the source of transferring the pollution industries among countries. Pollution-intensive industries will transfer from the countries with high environmental costs to the lower ones, so the countries with low environmental standards become “sanctuary” of world pollution and pollution-intensive industries. With global trade liberalization, increased competition make less developed countries to reduce environmental standards or relax regulations, so it appears the phenomenon of “race to bottom”. The state of race to bottom in environmental standards is called “races effect” or “bottom race hypothesis” [2]. In the literature of most foreign scholars, only a few demonstrate the existence of hypothesis. The explanatory theory of positive effect of FDI environment are only by Kevin Grey and Duncan Brank [3], proposing “pollution halo effect”, which shows that multinational corporations establish and promote TNCs, provide a good learning chance for the host enterprises to adopt the similar management techniques, and further promote the domestic enterprises to implement ISO 14001 environmental management system. Obviously, environmental problems exists the fight of national interest. In the analysis of FDI pollution-intensive industries and the reason of influencing environment, the scholar XiaYoufu [4] found that international trade and investment theory don’t consider the issue of environmental protection, some theories such as comparative advantage in international trade, Vernon’ s product life cycle theory, the expansion of marginal industry, provide a theoretical basis for developed countries to export pollution to developing countries. Li Huiru [5] makes an initial systematic study on the environmental effect of FDI, explore the mechanisms of the formation of FDI environment and raise the to be solved problems about the environmental effect of FDI: first, in theory, the issue of FDI in positive and negative effect is not significant, needing further theoretic and empirical proof; second, the pathway and impact of environmental effect of FDI are also not clear; third, how much the impact of environmental regulations on environmental effect of FDI; fourth, how to protect environment and effectively coordinate FDI.
2. The Analysis on the Environmental Effect of Logistics Industry FDI
2.1. The Influence Factors of the Environmental Effect in Logistics Industry FDI
The impact of logistics industry on environment is mainly: occupying land due to transport and storage, such as transportation access, site, ground and material storage transportation and handling facilities; consuming fuel, transport and storage equipment; generating wastes; producing loss and waste due to distribution processing; consuming material and processing waste due to reverse logistics, etc.
2.2. The Information Mechanism of Environmental Effect of Logistics Industry FDI
1) The scale of logistics industry FDI to the mechanism of environmental effect, When investment structure, technology, the level of environmental regulations are under the same conditions, the simply logistics FDI expands the scale of investment, which must increase the use of environmental resources. In the same of investment structure and pollution intensity, when the scale of investment expands, it will increase with the same proportion of pollution output, so expanding the scale of logistics FDI investment is not conductive to environmental protection.
On the one hand, if the major role of logistics FDI is capital information and economic growth in the host country, the impact of FDI scale effect on environment is that expand the scale of logistics FDI, economic scale, increase the pressure of ecosystem and lead to vicious exploitation and accelerating depletion. And the production of logistics FDI is in China, the consumption also in China, which will further increase the burden on the environment. Therefore, the cost of simply expanding FDI investment is the emergence of environmental negative effect.
On the other hand, increasing the scale of logistics FDI is helpful to promote the economic growth, thus increase income. Income growth will change people’s demand structure, which leads to an increased demand of environmental quality. Meanwhile, because of income growth, the government is able to increase investment on the environment, when reached a certain revenue, in the early development stage, the increasing trend will decline due to the pollution caused by logistics FDI.A further increasing income will promote the industrial structure, the upgrading and optimization of production technology, leading to virtuous circle of two-way in environmental improvement and economic growth, so when the scale of logistics FDI reached a certain level and economic growth reached a high level, it will produce the positive environmental effect.
2) The structure of logistics industry FDI to the mechanism of environmental effect, When the scale of investment, product technology in the same condition, people generally consider that the second industry occupies the most environmental resources, followed by the first industry, finally the third industry. Therefore, the second, the first industry more reflect negative environmental effect, and environmental effect of the third industry is relatively small, may have a positive effect. The logistics industry is the third industrial area, due to its production characteristics, and in the third industry, it is the largest department of environmental resources occupied, so the change of the investment structure in logistics FDI will lead to different environmental effects.
Logistics FDI investment structure is the same with the logistics industry of the host countries or lower than it, and the phenomenon exists in the early stage of larger space market, which will bring negative effect to the host countries in the low level of market competition and the larger cumulative negative effect, the more difficult to govern. The cost of negative effect has been widespread in attracting investment of developing countries. As the logistics industry is derivative industry, in certain scale of economic and certain logistics needs, low level of logistics market competition will become saturated, When it can not be support by the extrinsic conditions, like policy, etc, non-indigenous disadvantage of logistics FDI will appear, and logistics FDI will tend to shrink or withdraw from the host country. If the logistics FDI is in a small proportion of China’s logistics market, it’s no meaning to discuss logistics FDI.
When the organic composition of logistics FDI is high, the proportion of using low consumption, low emissions, clean energy, high technology and high efficient logistics technology is high, and the investment structure is higher than logistics industry structure of the host country, not only it reduces the occupancy of environmental resources, but promote the upgrading and optimization of logistics industry structure in the host country due to competition. As the spillover effect of technology and management concepts promotes the improvement of logistics industry in the host country, thus bring positive environmental effect to the host country.
Logistics FDI is the type of market-seeking and improving investment structure of the host country is market competition, a voluntary act of FDI, in order to meet the growing economy and increasing income requirements, it is necessary to increase the logistics supply, and less occupancy of environment resource brings positive effect to the host country.
3) The mechanism of environmental effect about the technology of logistics industry FDI, environmental effect of technology, whether domestic or foreign investment, their positive environmental effects are greater than negative environmental effects. Generally, the science and technology of FDI exist in two aspects: on the one hand, improve environment and reduce pollution as a direct purpose of environmental science and technology, with a direct positive effect. On the other hand, improve economic benefit as purpose of science and technology, and these technologies are helpful to save energy, form an indirect effect of environment protection and improvement. The technology effect of logistics FDI refers to with investment liberalization, the formation of logistics specialization and the improvement of logistics technology dissemination, which is helpful to achieve lower element input to per unit of logistics output in a broader range, improve the efficiency of element use, and reduce per unit pollution output. The major purpose of logistics FDI by the transformation of FDI and upgrading the existing technology, improves the potential innovation, and logistics FDI is just the main carrier. Logistics cross-border investment lead to transfer advanced technology and accelerate the speed of transfer, promoting cross-border spread of logistics environmental technology. If the technology of FDI, which is less pollutant and lower energy consumption, is higher than the environmental standards of the host country, it indicates that these can improve environment and the use efficiency of resources, producing positive effect.
But logistics FDI reduces environmental standards to use low technology, or the technology can’t protect environment, and produce negative technology effect in the host country. Mainly in the early attracting foreign investment stage of loose environmental regulations, logistics FDI produce the motive of transferring high-pollution equipments and using double environmental standards and cheaper technology.
The environmental effect of FDI mainly exists in two attitudes: one point is that as logistics FDI expands the scale of economy, produces greater pressure on environment, transfers cross-border pollution and hazardous substances, and exacerbates the environmental deterioration of the host country and world. Another point is that by more reasonable and effective allocation of FDI, so it may widespread ecological technology to help improve and protect environment. In the judgment of investment scale effect, generally, the investment scale will increase environmental degradation. In judgment of investment structure, using clean production technology will improve environment. The structural effect and technology effect are generally larger than the scale effect. So logistics FDI will expand economic structure, increase income, upgrade the industrial structure, and enhance productivity. High productivity can promote economic development, expand the economic scale, strengthen the environmental protection, spread eco-technology, and make productivity reach a new level, finally increase internal ability of environmental cost, promoting sustainable development. The investment scale, investment structure and technology level will act on environment and form interacting mechanism, and ecological and advanced technology is the fundamental way to solve environmental problems. The environmental effect of logistics FDI relates to the economic development, environmental regulations, and environmental element endowments and so on in the host country.
2.3. The Impact of Environmental Regulation on the Environmental Effect of Logistics FDI
Industry regulation directly influences the industry, and the environmental regulations of the host country have a direct impact on the environmental effect of FDI, and the relationship between the two judgments manifests in two aspects: on the one hand, the low level of environmental regulation in the host country will lead to produce negative effect of FDI environment, such as the establishment of “pollution haven hypothesis”; on the other hand, high level of environmental regulations will lead to produce positive effect, such as not the existence of “pollution haven hypothesis”. The majority studies on the casual relationship between environmental regulations and FDI have confirmed the impact of FDI on increasing environmental pollution in China. The scholars Xing, olslad and so on [6] studied on FDI inflows and found that loose regulations of the host country attract pollution-intensive FDI of developed countries, and have little impact on less pollution industry. Logistics industry is the minor pollution of the third industry, so the higher regulations of logistics FDI have little impact on the use of foreign investment. Judith and Mary [7] by the location choice of FDI in China, the analysis showed that the different sources of FDI are inclined to the regions with low cost. Lower environmental taxes only attract FDI, from Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan and other Asian regions, to invest in pollution-intensive industries. For developing countries, FDI of developed countries don’t usually show the preferences on the strict control of pollution, from the FDI of OECD countries, whether to invest in pollution-intensive industries, it isn’t attracted by lower environmental taxes. Porter [8] believed that the pressure of environmental control like the pressure of market competition, encourage clean production or the innovation of clean products, and these innovations can offset some or all of the regulation costs, then logistics FDI can improve pollution control technology, to produce positive environmental effect, achieving a clear advantage in logistics market competition. Yang Tao [9] tested the impact of environmental regulations on FDI inflows, and believed that the strict regulations influence on attracting FDI, but not the main factor. For discussing the long-term change relationship between FDI and environmental regulations, Wu Yuming [10] suggested that the strict regulations will have a real impact on the lag phase of FDI. Compared with other factors, the strict regulation will have a little impact on FDI, and will not affect foreign investment recently. China logistics FDI mainly comes from the multinational corporations of developed countries, of which the level of environmental protection and standards are higher than that of domestic-funded enterprises, and the improvement of environmental regulations is useful to develop the market competition of logistics FDI.
2.4. The Measurement of FDI Environmental Effect
In the process of attracting investment, because the particularity of four municipalities and incomplete data in Tibet, the paper eliminates these five provinces, and use Spearman rank correlation coefficients to do the rank correlation analysis on GDP, FDI, the amount of “three wastes” emissions, the amount of wastewater emissions, the amount of sulfur dioxide emissions and the amount of solid waste in East, West and central regions of 26 provinces [11]. The formula is:
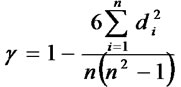 (1)
(1)
Formula 1: n is that the observed values of two variables arrange from big to small, or small to big, and given 1-n grades; d is the difference between the observed values of two variables. Spearman rank correlation coefficients range between –1 and +1, and the greater their absolute values, the greater relevance of two variables; the smaller their absolute values, the smaller relevance of two variables.
Use SPSS to calculate Spearman rank correlation coefficients of GDP, FDI, the amount of “three wastes” emissions, the amount of wastewater emissions, the amount of sulfur dioxide emissions and the amount of solid waste in East, West and central regions of 26 provinces. By analysis, attracting FDI of China distributes in many pollution industries, and east region is much more than in west and central regions. Increasing FDI and expanding production will inevitably affect the environment, giving more pressure on the environment in the region, which reflect in statistical data that is relatively more the amount of “three wastes” emissions. By Spearman correlation coefficients, FDI and “three wastes” emissions have a high correlation, and the correlation coefficients are greater than 0.6.
From the distribution of FDI region, eastern, central and western regions decrease in order, “three wastes” emissions also decrease in order, the same with negative environmental effect. The regional GDP, FDI and the amount of “three wastes” emissions have a high correlation, and a direct proportion relationship with negative environmental effect.
3. Conclusions
Logistics FDI brings environmental effect to the host country, and the absolute amount is negative effect, when logistics FDI meets the increasing economic output of the host country, it must increase the environmental consumption of the host country. However, in the relative amount, logistics FDI may be a positive effect, this is because FDI owns advanced logistics technology and management, when operating the same amount of logistics business, the consumption of environmental resource is lower than the host country. Therefore, logistics FDI of developed countries put into developing countries and underdeveloped countries, which has a positive meaning in the environmental effect.
China’s logistics industry introduce FDI in the early stage from mainly developing countries and regions in Asia, which should change from mainly Europe, the United States, Japan, South Korea and other developed countries to introduce FDI. Use advanced logistics technology in the world, promote high-speed national economic development with the smaller cost of environmental costs, and ensure logistics FDI in China’s sustainable development by environmental regulations.
Introduce advanced logistics technology and management philosophy of developed countries, promote the development of green logistics, making efficient forward logistics and smooth reverse logistics, and form the positive environmental effect of the whole logistics.
REFERENCES
- D. Judy, “Trade and the Environment: A Survey of the Literature,” World Bank Discussion Paper, 1992.
- J. R. Markusen, “Exploring New Markets: Direct Investment, Contractual Relations and the Multinational Enterprise,” NBER Working Papers 5029, National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc., 1995.
- K. Grey and D. Brank, “Environmental Issues in PolicyBased Competition for Investment: A Literature Review,” ENV/EPOC/GSP, 2002.
- X. Youfu, “The Research on the Foreign Investment to China’s Pollution-Intensive Industries of the Status, Consequences and Countermeasures,” Mamagement World, Vol. 5, 1999.
- L. Huiru, “The Study of the Ecological Environment Effects of Foreign Direct Investment,” People’s Publishing Press, Beijing, 2009.
- Y. Q. Xing and C. D. Kolstad, “Environment and Trade - A Review of Theory and Issues,” University of Califonia, Santa Barbara WP (2), 1995.
- M. Judith, E. Mary and H. Wang, “Are Foreign Invertors Attracted to Weak Environmental Regulations?” World Bank Policy Research Working Paper, 2005.
- M. E. Poter, “America’s Green Strategy” Scientific American, 1991; P. M. E. C. van der Linde, “Toward a New Conception of the Environment-Competiveness Relationship,” Journal of Economics Perspect, 1995.
- Y. Tao, “The Empirical Analysis on the Influence of Environmental Regulations on FDI in China,” World Economy Research, Vol. 5, 2003.
- W. Yuming, “The Empirical Analysis on the Causality between Environmental Regulations and Foreign Direct Investment,” Journal of East China Normal University, Vol. 1, 2006.
- W. Jie, “The Countermeasures on the Environmental Pollution of Foreign Direct Investment in China,” Master’s Thesis, Southern Yangtze University, Wuxi, 2008.
NOTES
*Science and technology projects in Liaoning Province, Number [2009 401011] contract number [2009040148-304].

