Open Journal of Social Sciences
Vol.04 No.05(2016), Article ID:66796,8 pages
10.4236/jss.2016.45025
The Impact of Tunneling Behavior on Equity Incentive Plan
―Empirical Evidence of China’s Main Board from 2006 to 2013
Jianglong Zheng*, Cunzhi Tian
College of Economics, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China

Copyright © 2016 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 19 April 2016; accepted 23 May 2016; published 26 May 2016
ABSTRACT
Though the equity incentive plan was introduced into China just for a short time, the number of listed companies that implemented equity incentive plan was growing fast. In order to improve the effect of equity incentive plan on alleviating agent problem between the owners and managers, China Securities Regulatory Commission supports it by the developing the legislation and preferential tax policies. In China, it is a general phenomenon of major shareholders’ tunneling behavior. However, there is little research focusing on the relationship between tunneling behavior and equity incentive plan. This paper mainly researched the effect of major shareholders’ tunneling behavior on the preference of equity incentive plan, using cross-sectional data of A-share listed companies in China security market from 2006 to 2013. Actually, the empirical result showed that, the major shareholders’ tunneling behavior has a negative effect on equity incentive plan. The major shareholders’ tunneling behavior affects the welfare tendency of equity incentive plan, and the companies with serious major shareholders’ tunneling behavior are more likely to choose the welfare-tendency equity incentive plan.
Keywords:
Tunneling Behavior, Equity Incentive Plan, Cross-Sectional Data

1. Introduction
The issue of “The Equity Incentive Regulation of listed company” published in December of 2005 has set a standard for regulating the equity incentive plan of listed companies. Since then, government has promulgated many policies, and the number of companies who have implemented equity-based incentives plan increases rapidly. By 2013, the number of listed company implemented equity incentive plan has increased more than 13 times, and the equity incentive plan plays a significant role in corporation governance.
The main feature of modern enterprise plan is the separation of ownership and operation power, and this may cause information asymmetry and the agency problem between the owner and the manager of the company. The original intention of equity incentive plan is to encourage the manager to perform in accordance with the principle of maximizing the interests of shareholders, reduce or eliminate the manager’ short-term behavior and alleviate the interest conflicts. Equity incentive plan has important meaning on reducing the agency cost, building the firms’ long-term development mechanism, elevating the firms’ competitive ability plan. In order to obtain these benefits that the equity incentive plan brings, the owners of companies are willing to implement this meaningful policy. However, the equity incentive plan cannot achieve these aims by establishing the profit and risk sharing mechanisms between the owner and the manager. What is worse, the equity incentive plan is undermining the corporate governance structure. In real world, the equity incentive plan has gradually become a welfare plan for executives. It is a serious phenomenon that the executives make use of internal control force to lower down the exercise condition of equity incentive plan, so that the executives can get the interest of the equity incentive without any effort to raise the profits of the corporation. For example, in 2012 Jiayu Shares (300117) launched the first equity incentive plan with an exercise condition on the base of the net profit of previous year, and before the announcement of formal periodical financial reports. But two weeks later, Jiayu Shares published financial reports with a sharp drop in net profits. It is impossible not to doubt the reasonableness of the exercise condition of this equity incentive plan.
In recent years, more and more researchers have drawn their attention to the study of studies about equity incentive plan design, but fewer about the reason of welfare-tendency equity incentive plan design in China. Based on the China’s A-share market, we studied the relationship between the large shareholder’ tunneling behavior and the equity incentive strategy. Firstly we constituted an index to evaluate the welfare tendency of the equity incentive plan and severity of the large shareholders’ tunneling. Secondly, we explored how the large shareholders’ tunneling affected the welfare tendency of the equity incentive plan by building an order-probit model. Finally, we studied the consequence of welfare-tendency equity incentive plan on the corporation governance and put forward some feasible improvement suggestion of equity incentive plan.
2. The Literature Review and Research Hypothesis
Up until now the equity incentive plan has been introduced into China just for a short period of time, and the foundation of the equity incentive system is weak. Moreover, there is a big performance gap between companies published equity incentive plan. The current researches about equity incentive system are mainly focus on the effects on promoting the performance and reduce the agency cost. Recently, some studies draw their attention to the equity incentive plan design and indicate the welfare tendency of equity incentive plan in China. Yuhui Wu [1] thought the evaluation target of equity incentive is too easy for the incentive object, and thus increase the exercise probability of the equity incentive plan. The management group can get their interest from the stock option easily even if they do not work hard, so the incentive effects will be greatly reduced. Shufang Xiao [2] found that the evaluation target of equity incentive plan is on the low side, and the evaluation target design is too simple, providing convenience for the manager manipulating the business performance of the company. When the manager manipulates the business performance of base period, the incentive effects will be influenced for the whole incentives period of validity. Changjiang Lv [3] thought the equity incentive plan design is lack of positive incentive, and resulted in a performance manipulation of listed companies. These researches indicate the phenomenon of welfare tendency of equity incentive plan, but do not explain what is contributed to this result.
It is a popular phenomenon that the listed companies have a concentrated ownership structure. Large shareholders play a controlling role in cooperating governance, involving the whole process of the operation and the developing strategy. Liping Xu et al. [4] found that the ownership concentration in China Security Market is higher than other market, and the mean and the median of the shareholding ratio of the top five shareholders is as high as 54% and 56%. The large shareholder is in the absolute active control position of the company, and the agency problem between major shareholders and minor shareholders has become the main object of governance in modern company. As the actual controller of the company, the large shareholders have a strong motivation to tunneling the company in order to maximize their own interests. There are a number of ways for major shareholders to occupy the interest of the minor shareholders, for example, the connected transaction and capital invasion. And recent researches pointed out that it is very commonly some large shareholders expropriating the listed companies by connected transaction and capital invasion.
In order to explore the consequences of tunneling, some studies begin to focus on the ways of large shareholders how to get their interests. Renjun Zhou et al. [5] thought that, there are two ways for the large shareholders to gain their profits, one is get the capital appreciation or the dividend, and the other is tunneling. Large shareholders can enhance the supervision to management, so reduce agency cost, incents and restrict the self- interested behavior of executive. And large shareholders can also get involved in every detail of the company’s operations, providing some useful suggestions, raising the company’ performance. Moreover, large shareholders can conspire with the executive, so that they can tunnel the company without any obstacles coming from the company inside. Dongwei Su [6] found that major shareholders’ tunneling will weaken the negative relationship between executives departures and declining performance. Besides, there is some interest swap between major shareholders and executives. Executives can have higher perk consumption in the company with higher severity of tunneling. Further studies conclusively showed that the large shareholders hollowed the company mainly by conspiring with the executive and constructing some interest exchange tunnel. Pan Yiqing [7] constructed a model to analyze the coordinated behavior between managers and large shareholders, when the tunneling happened and found out that some executive assist to disguise the tunneling. Weimin Xie [8] used 2005-2011 mainboard listed companies as the research sample,and found that share proportion held by social security fund had a positive effect on company performance after controlling other variables’ influences. Jianxin Tang et al. [9] employed non-financial companies from 2003 to 2010 in China as the sample and analyzed whether equity ownership structure and the characteristics of board were conducive to tunneling. Xing Liu and Xianchong Wu [10] found that the nature of state-owned had a negative impact on the fund’s effective of improving the company performance.
On the base of these studies, we can find that, large shareholders exert great influence on corporate governance, not only on the operation of the company, but the design of incentive plan. In order to alleviate the interest conflict caused by tunneling, executive can usually get some convenience provided by large shareholders in earning management or get some direct perk consumption. Even more, large shareholders can reduce the difficulty of exercise equity incentive stock option to compensate the executive. So it is also possible to assume large shareholders exert great influence on the plan design of equity incentive strategy. From the perspective of conspiracy, we look forward to make a study about the relationship between tunneling and equity incentive strategy, and raised the proposed hypothesis as follows:
Hypothesis 1: severity of tunneling has a significantly positive correlation with welfare tendency of the equity incentive plan. That is to say it is more possible to make a welfare-tendency equity incentive plan for the company with higher tunneling.
3. Research Design
3.1. Sample Treatment
The study sample in this paper is sorted from listed company in A-security market in China from year 2006 to 2013. And the data for dependent variables, independent variables and control variables is selected from CSMAR Financial Analysis Index Database, some valuation variables is sorted from the announcement of listed companies. In this paper, in order to get a more reliable result, we processed the sample by following procedures: 1) Excluding financial and insurance companies; 2) Excluding ST, PT companies; 3) Excluding insolvency companies or related data incomplete companies. After the above dispositions, a total of 327 samples obtained.
3.2. Variable Description
Table 1 shows the type, name, symbol and measure method of variables.
3.3. Model Specification
In order to test the relationship between severity of tunneling and welfare-tendency of equity incentive plan, we set welfare-tendency of equity incentive plan as the explained variable, the severity of large shareholders’ tunneling as the main explanatory variables. At the same time, for more reliable result, we also added some appropriate Corporation governance variables and financial characteristic variables as control variables and built an order- probit regression model to verify the hypothesis. When the Orect regression coefficient is significantly negative,
Table 1. Variable description table.
indicating that the higher the tunneling of large shareholders, the low ever difficulty for executive to exercise the stock option. And there is a higher potential for the equity incentive plan tend to be a welfare plan. We can also test the effects of corporate governance on restricting the conspiracy action between manager and large shareholders. When the Ind regression coefficient is significantly positive, indicating that the independent board member can prevent the conspiracy action in some way.
Regression model (1) is as follow:
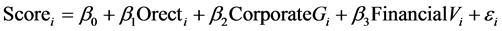 (1)
(1)
Scorei represents the welfare tendency of equity incentive plan of company i that implemented the equity incentive plan. Variable Orecti represents the severity of large shareholder’ tunneling. And CorporateGi represents Corporation governance variables including variables Ind, Dual, Top1, Manho, Countb, Board and Supv. FinancialVi represents the Financial characteristic variables of the company, including variables Incom, Acf, State, Size, Lev and Roa.
4. Hypothesis Test and the Regression Result Analysis
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
To better understand the characteristic of the sample, we listed the results of Descriptive Statistics analysis of whole samples. From 2006 to 2013, there were 371 listed companies implemented the equity incentive plan and we can get 325 effective sample by excluding the incomplete sample. In Table 2 we can find that valuation variable of the welfare tendency of the equity incentive fluctuates between 5 to 12, indicating great disparities between samples. The measure of large shareholders’ tunneling vary greatly, and the maximum and maximum value are 0.181 and 0.009. As to the Corporation governance variables, the median of Ind is 0.315, showing that 31.5% of
Table 2. The result of descriptive statistics.
board member are independent directors; the mean of Dual is 0.353, showing that 35.3% companies chairman and CEO is one of two staff and concentration of power is high. From the point of Financial characteristic variable, we could find that the company implemented equity incentive plan have a good finicial condition, most of the companies get strong profitability.
4.2. The Correlation Test
In order to test the reasonableness of introducing in these variables, we did a Spearman correlation test, which can judge whether there is a serious multicollinearity problem between variables. From Table 3, we could find that the severity of large shareholders is significantly negative correlation with the welfare tendency of equity incentive system, so the hypothesis is preliminarily verified. We also can check the correlation between the corporation goverance variables and the welfare-tendency of equity incentive plan, finding out whether the Mechanism of Internal Corporate Governance is working. The coefficient of Ind is not significant, which means the independent directors have no influence on company’ equity incentive strategy. The coefficient of Dual is significantly positive, showing that the concentration of intern power can breeds self-interested behavior of executives. The coefficient of Manho is also significantly positive, which means the executive have a strong motivation to make some decision selfishly. However the financial condition of companies seem to have no correlation with equity incentive strategy.
4.3. The Empirical Result Analysis
Through using the Cross-section Data from 2006 to 2013, Table 4 shows regression result by using order- probit model. In order to eliminate the effect of multicollinearity among variables, we did a stepwise regression analysis. It can be found from Table 4, the coefficients of Orect (large shareholders’ tunneling) is significant negative from model test, which means the tunneling of large shareholders can have a deeply influence on equity incentive strategy. If the company has a higher tunneling of large shareholders, it will prefer the more welfare-tendency equity incentive plan. The further detail of conclusion is as follows:
From the perspective of institutional background, we could find that coefficient of State is significantly positive, which means the state-owned company prefer the incentive-tendency equity incentive plan comparing with private Internet companies. It is more difficult for manager and large shareholders to conspire in state-owned company. Because the stated-owned receive more and stricter government supervision and public monitoring. If
Table 3.Spearman correlation test.
Table 4. The regression results of model (1) to (9).
Note: *, ** and ***show that regression result is respectively significant at level 10%, 5%, 1%; T statistics are shown in brackets.
the manager and large shareholders want to tunneling, they will take on more risk, and more cost on their conspiracy. Furthermore, the manager in state-owned company is more concerned about their political interests, so they won’t risk their political position promotion.
From the perspective of governance mechanism of the company, no matter whether there was multicollinearity problem between the independent directors proportion and the number of board of supervisors, its effect on
the composite scores were not significant; In the model (1), the coefficient of the number of the board was not significant; But no matter in model (1) or model (7), the coefficients of Dual variable were positive, which showed that the more concentrated the executive power was, the more easily caused the equity incentive as welfare; The coefficient of Countb variable in model (1) was positive and not significant, but which was significant in model (8); The coefficient of Manho variable was negative and only significant in model (9). These conclusions were basically consistent with Changjiang Lv’s etc. (2009) research, they used listed companies which implemented equity incentive from 2006 to 2009 as samples and analyzed the influence factors of the equity incentive draft as welfare, they found that variables reflecting executive right concentration were influenced on the selection of company equity incentive plan, and the more concentrated the executive power was, the more likely to choose welfare equity incentive plan.
From the perspective of the company’s ownership structure, the coefficient of Top 1 variable was different in model (1) and model (7), and they were both not significant, which showed that there was no relationship between the proportion of the first largest shareholder’s stake and the degree of welfare equity incentive plan. But the coefficient of Countb variable was significantly positive, which indicated that the company with high equity restriction ratio was more likely to select welfare equity incentive plan. This conclusion was not same as Yuhui Wu’s (2010) research, their study found that the higher the proportion of the first largest shareholder was, the more restricted executive’s self-interest behavior was, but this paper couldn’t find the same result, the reason may be that the first largest shareholder’s interest is not only achieved through supervision and management, but also can be got by collusion behavior with executives.
From the aspect of the company’s financial characteristics, the coefficient of cash flow、ROA and the increase rate of operating income were all not significant in every model, they didn’t affect the choice of the preference of equity incentive plan. But the financial leverage had significantly positive impact on composite scores in every model, this may be that the higher the leverage ratio is, the more incentive external creditors have to supervise enterprise’s decision-making; the enterprise size was significantly negative correlative with composite scores, which indicated that the larger enterprise size was, the more likely to select welfare equity incentive plan.
From the perspective of the level of tunneling by major shareholders, no matter whether there was a linear relationship between plan background variables and corporate governance variables, the large shareholder’s tunneling level were all negatively related to composite scores, which proved the hypothesis 1 of this paper, the higher the large shareholder’s tunneling level was, the more likely company selected welfare equity incentive plan, which also showed that the large shareholder realized self-interest by collusion behavior with executives and through equity incentive plan. This paper stated that introducing equity incentive plan not only couldn’t improve the first kind of principal-agent cost problem, but also might cause the second kind of principal-agent problems when the corporate governance structure was imperfect.
5. Conclusions and Suggestions
This paper get a conclusion about the tunneling of large shareholders and equity incentive strategy by using the A-share listed companies implemented equity incentive plan in China from 2006 to 2013 as the research sample. Firstly, it makes a theoretical analysis between tunneling and equity incentive strategy. Secondly, it constructs a welfare-tendency Evaluation Index of equity incentive plan. Thirdly, we get a conclusion by making an empirical research as follows: equity incentive system not only eliminates the interest conflicts between owner and managers, but also introduces a conspiracy way for large shareholder to hollowing the interest of minor shareholders. Company with higher tunneling prefers to implement an easier equity incentive plan, and the manager motivated by this kind of plan will have little willingness to work hard. In some way, the welfare-tendency equity incentive plan provides a new tunnel for manager and large shareholder to make a conspiracy.
Through this paper, we can get some implications on equity incentive plan. A good plan to get the desired effects also needs to have a relatively complete supervision of the environment, or it will become a part of the problem.
Cite this paper
Jianglong Zheng,Cunzhi Tian, (2016) The Impact of Tunneling Behavior on Equity Incentive Plan
—Empirical Evidence of China’s Main Board from 2006 to 2013. Open Journal of Social Sciences,04,217-224. doi: 10.4236/jss.2016.45025
References
- 1. Wu, Y.H. and Wu, S.N. (2010) The Selfish Behavior of Executives. Management World, 3, 11-16.
- 2. Xiao, S.F., Liu, Y. and Liu, Y. (2013) Executives’ Earnings Management Behaviours in the Implementation of Equity Incentive—From Perspective of Performance Evaluation for Option Exercise. Journal of Accounting Research, 12, 32-43.
- 3. Lv, C.J., Yan, M.Z. and Xu, J.J. (2010) The Design for Listed Companies’ Plan of Stimulation by Stock Option and Purchase: Is It an Incentive or Welfare? Management World, 7, 24-31.
- 4. Xu, L.P., Xin, Y. and Chen, G.Y. (2006) Ownership Concentration, Outside Blockholders, and OperatingPerformance: Evidence from China’s Listed Companies. Economic Research Journal, 1, 13-24.
- 5. Zhou, R.J. and Gao, K.J. (2012) The Effect of Large Shareholder’s Control on Managers’ Ownership Incentive. Journal of Accounting Research, 5, 18-24.
- 6. Su, D.W. and Xiong, J.C. (2013) Tunneling and CEO Incentive Contract. Economic Research Journal, 12, 34-41.
- 7. Pan, Z.Q. and Zhang, W. (2004) The Collusion of Large Shareholder with Manager and Legal Shareholder Protection. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 6, 27-46.
- 8. Xie, W.M. (2013) The Study of the Influence of the Social Insurance Fund Ownership on Corporate Performance. Price: Theory & Practice, 2, 36-42.
- 9. Tang, J.X., et al. (2013) Equity Ownership Structure, the Characteristics of Board and Tunneling: Empirical Evidence from China’s Listed Companies. Economic Review, 1, 86-94.
- 10. Liu, X. and Wu, X.C. (2011) The heterogeneity of Institutional Investors, Enterprise Property Rights and Company Performance—Based on the Comparative Analysis of before and after the Reform of Non-Tradable Shares. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 5, 183-190.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.




