Applied Mathematics
Vol.06 No.03(2015), Article ID:54972,4 pages
10.4236/am.2015.63054
Further Discussion on the Calculation of Fourier Series
Caixia Zhang
College of Mathematics and Statistics, Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing, China
Email: zhangcai6476@163.com
Copyright © 2015 by author and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 9 February 2015; accepted 23 March 2015; published 24 March 2015
ABSTRACT
Fourier series is an important mathematical concept. It is well known that we need too much computation to expand the function into Fourier series. The existing literature only pointed that its Fourier series is sine series when the function is an odd function and its Fourier series is cosine series when the function is an even function. And on this basis, in this paper, according to the function which satisfies different conditions, we give the different forms of Fourier series and the specific calculation formula of Fourier coefficients, so as to avoid unnecessary calculation. In addition, if a function is defined on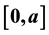 , we can make it have some kind of nature by using the extension method as needed. So we can get the corresponding form of Fourier series.
, we can make it have some kind of nature by using the extension method as needed. So we can get the corresponding form of Fourier series.
Keywords:
Fourier Coefficients, Fouries Series, Period, Series Expansion, Extension

1. Preliminary Knowledge
Definition 1 [1] -[3] Let 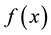 be an integrable function on
be an integrable function on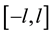 . Then the coefficients
. Then the coefficients 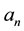 and
and 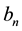 are calculated by
are calculated by

and are called the Fourier coefficients of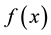 .
.
Definition 2 [1] -[5] Let 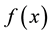 with the period
with the period 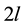 be an integrable function on
be an integrable function on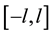 , trigonometric series with the Fourier coefficient are called Fourier series of
, trigonometric series with the Fourier coefficient are called Fourier series of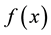 , denoted by
, denoted by
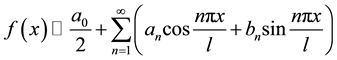
Lemma 1 [6] Let 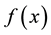 be an integrable function on
be an integrable function on 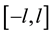 with period of
with period of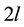 , the Fourier coefficients are calculated according to period of
, the Fourier coefficients are calculated according to period of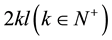 . The calculation indicates there are same results between Fourier
. The calculation indicates there are same results between Fourier
series with period of 

2. Calculating Fourier Series According to the Nature of the Function
Theorem 1 Let 


where


Proof It was clear that the period of 

Let


So we get


Let

Therefore, we obtain
In the same way, we have
In a word, while 

Thus in this case, the expansion reduces to
Theorem 2 Let 


where

Proof The period of 



Let

So we get
Let

We obtain
In the same way, we have
Thus in this case, the expansion reduces to
where

Theorem 3 Let 



(1) While 

where
(2) While 

where
Proof (1) We use the method of periodic extension to 

Because 


Let

Let
We obtain
Thus in this case, the expansion reduces to
where
(2) In the same way, we can prove Theorem 3 (2).
Similarly, we can prove the following Theorem 4.
Theorem 4 Let 



(1) While 

where
(2) While 

where
3. Conclusion
Suppose the function is defined on

use odd and periodic extension, we can get two forms of Fourier series as Theorem 3. If we use symmetry ex-
tension about the line 

Acknowledgements
I would like to thank the referees and the editor for their valuable suggestions.
References
- Department of Mathematics of East China Normal University (2010) Mathematical Analysis. 4th Edition, Higher Education Press, Beijing, 62-72. (In Chinese)
- He, G.Z. (2008) Discussion on a Style of Fourier Series Expansion. Journal of Leshan Teachers College, 23, 27-28. (In Chinese)
- Zheng, C. and Qiu, W.G. (2010) Integration Techniques Based on Fourier. Studies in College Mathematics, 13, 31-32. (In Chinese)
- Wang, B.Y. and Qi, X.S. (2011) Two Methods for Summing Trigonometric Series. Studies in College Mathematics, 14, 33-34. (In Chinese)
- Jiao, H.Y. and Liu, W.H. (2011) Fourier Expansion and a Class of Series. Studies in College Mathematics, 14, 35-36. (In Chinese)
- Ding, X.H. (2004) Several Problems of Fouries Series Expansion. Journal of Daxian Teachers College (Natural Sci- ence Edition), 14, 1-4. (In Chinese)

























