Applied Mathematics
Vol.05 No.19(2014), Article ID:51237,8 pages
10.4236/am.2014.519289
Natural Oscillations of Viscoelastic Lamellar Mechanical Systems with Point Communications
Safarov Ismail Ibrahimovich, Teshaev Muhsin Hudoyberdievich, Madjidov Maqsud
Bukhara Engineering-Technological Institute, Bukhara, Republic of Uzbekistan
Email: muhsin_5@mail.ru, muhsin.teshayev@rambler.ru
Copyright © 2014 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 17 August 2014; revised 14 September 2014; accepted 8 October 2014
ABSTRACT
We investigated the natural oscillations of dissipative inhomogeneous plate mechanical systems with point connections. Based on the principle of virtual displacements, we equate to zero the sum of all active work force, including the force of inertia which obtain equations vibrations of mechanical systems. Frequency equation is solved numerically by the method of Muller. According to the result of numerical analysis we established nonmonotonic dependence damping coefficients of the system parameters.
Keywords:
Plate, Viscoelastic Properties, Natural Frequencies, Damping Ratios, Structurally Homogeneous and Structurally Heterogeneous

1. Introduction
Studies related to the definition of inherent characteristics of plates with attached masses are discussed in [1] - [3] . In these studies, to determine the main forms and vibration frequencies a variational principle of Hamilton- Ostrogradskii is applied. In [1] , in the derivation of the frequency approach, AS Gershgorin is used [4] . Various mounting and mass concentration of the plate limits the scope of application of this approach. In [5] - [7] the authors take into account the viscoelastic (dissipative) material property records and deformable elements. Free oscillations of dissipative systems are damped. The amplitude of vibration modes decreases with time, so this process is not strictly periodic. But the frequency of the corresponding forms at the same time remain constant [7] , and in this sense the dissipative system can be studied as a system that has its own vibrations. In this paper we consider the linear problem of natural vibrations of viscoelastic rectangular plates (or package of rectangular plates) having a connection point.
2. Statement of the Problem and Their Solutions
We will consider the mechanical system consisting of N isotropic viscoelastic plates, occupying volume 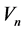 and limited by surfaces
and limited by surfaces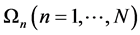 . It is assumed that one linear dimension of each plate is much less than the other two. At each n on part of a surface of n-th plate uniform
. It is assumed that one linear dimension of each plate is much less than the other two. At each n on part of a surface of n-th plate uniform 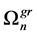 boundary conditions are set, on other free surface
boundary conditions are set, on other free surface 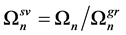 in final number of points communications of kinematic and dynamic character are imposed: dot rigid, elastic and (or) viscoelastic hinged type of a support (rigid support can be jammed), the rigid elastic and (or) viscoelastic shock-absorbers connecting bodies (at
in final number of points communications of kinematic and dynamic character are imposed: dot rigid, elastic and (or) viscoelastic hinged type of a support (rigid support can be jammed), the rigid elastic and (or) viscoelastic shock-absorbers connecting bodies (at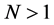 ), the concentrated masses
), the concentrated masses 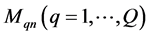 . The arrangement of communications and masses on surfaces is any
. The arrangement of communications and masses on surfaces is any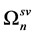 . Generally dissipative properties of elements of system are various. Special case of such structurally non-uniform viscoelastic system is the system with elastic and viscoelastic elements. For the last case
. Generally dissipative properties of elements of system are various. Special case of such structurally non-uniform viscoelastic system is the system with elastic and viscoelastic elements. For the last case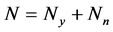 , where
, where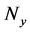 ?quantity of elastic elements of system,
?quantity of elastic elements of system,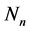 ?quantity of viscoelastic elements. For N = 1 the rack available. Required to determine the natural frequency of the viscoelastic system, as well as to evaluate its damping capacity.
?quantity of viscoelastic elements. For N = 1 the rack available. Required to determine the natural frequency of the viscoelastic system, as well as to evaluate its damping capacity.
Mathematically, the viscoelastic problem is as follows. Let all the n-th point of the body are subject to a harmonic law fluctuations, i.e.
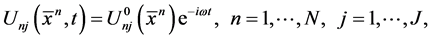 (1)
(1)
where 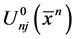 j-th component of the displacement vector of n-th body, J?number of components of the displacement vector,
j-th component of the displacement vector of n-th body, J?number of components of the displacement vector, 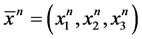 the radius vector of the n-th body,
the radius vector of the n-th body,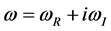 ?desired complex frequency of the system, and
?desired complex frequency of the system, and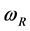 ?the natural frequency,
?the natural frequency,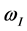 ?damping coefficient
?damping coefficient
For rectangular plates 

where x, y?coordinate. Proceeding from the principle of possible movements, we will equate to zero sum of works of all active forces, including inertia forces on possible movements

where

where







We will determine physical ratios for n-th viscoelastic body of system by equality [6]

where

here




Considering (1), time function in equality (5) will be with slowly 


where
Time allows to exclude it from the variation equation integrated members and, finally. In a symbolical look it can be presented in a look

We will write out concrete representation of functionality of G, for example, for a package of rectangular plates with dot communications:
where




where

instant rigidity according to of n-th plate, of l-th shock-absorber, of l'-th support. In an elastic case 

The similar functionality can be written down for system of covers of rotation.
Components of a vector of movements 


It was necessary to impose rigid dot communications which don’t make work at fluctuations on system. Terms of hard hinged support the n-th body in 

where
If the part of support has jamming, conditions will be added

where

Existence of rigid racks between n-th and (n + 1)-th body at 

where

Thus, on a vector of movements restrictions of types (8)-(11) are in addition imposed. On system dot communications we will consider imposing by means the method of Lagrange multipliers. Then the variational Equation (10) will correspond in a look

where
It is necessary to find a range of complex own frequencies


3. Algorithm of Realization of a Variation Method at the Solution of a Viscoelastic Task on Own Fluctuations
Approach the solution of the variational Equation (12), as well as in case of an elastic task, we look for in the form of the approximating form made of fundamental functions, satisfying both to the equation, and the set geometrical boundary conditions on surfaces of 


where
Previously 





Without providing concrete calculations, we will write down this system in a matrix look:

where






Structurally matrixes A and B are similar described in work [6] . Generally they differ from each other parameters of kernel relaxation. If all elements of the viscoelastic rheological properties are the same, then
The degeneracy of the matrix B as a resilient problem is caused in the introduction of additional point connections (rigid supports and pillars). The transformed matrixes will have dimension 

which, unlike a case of an elastic task, will be complex. The most effective way of the solution of the similar equations, apparently, is the method of Müller [7] which and here was used. Without opening frequency to define, and calculating on each step only its value for the fixed value


Systems of rectangular plates and with dot communications are considered. We will consider the design representing a package from two parallel square elastic plates with the shock-absorber and the attached weight. The relaxation kernel for the shock-absorber is chosen in a look
where




Real illustration of this effect is existence of a point of intersection of schedules of damping coefficients 




Figure 1. Dependence of frequencies and damping coefficients from rigidity of the shock-absorber.

where An?a numerical matrix of the total instantaneous stiffness of viscoelastic elements of the system.After an exception linearly dependent the component from system also can be written down (15) transformed matrixes of the generalized instant

where





The second example provides the mechanical system consisting of two parallel identical mechanical properties and geometry of the elastic plat in
connected by a weightless viscoelastic damper. The parameters of its core relaxation



In this problem, we investigate the following variant: shock absorber is located in the center of the plates, the masses are the central axis of the structure, and М1 is fixed to the first (bottom) plate at a distance of 0.04 m from the absorber, and the position of the mass М2 to the second (upper) plate was varied along the central axis of the structure.
Figure 2 shows plots of the first two natural frequencies and damping coefficients of the position of the mass М2. Calculation showed a strong dependence of the damping of the first global form 



Figure 2. Shows plots of the first two natural frequencies and damping coefficients of the position of the mass М2.
suitable arrangement of added mass. Symmetry of the left and right branches of the graph provides an opportunity to obtain the maximum (and equal) the effectiveness of the shock absorber arrangement as cargo on either side of him (left leg), and on one side (right branch).
Described effect shows that the energy of the system depends not only on the rheological properties of the damping material, but also on the geometry of the structure as a whole. Similar effect was observed for the system with finite number of degrees of freedom [10] [11] . This effect does not occur if the system is structurally homogeneous viscoelastic.
Cite this paper
Safarov Ismail Ibrahimovich,Teshaev Muhsin Hudoyberdievich,Madjidov Maqsud, (2014) Natural Oscillations of Viscoelastic Lamellar Mechanical Systems with Point Communications. Applied Mathematics,05,3018-3025. doi: 10.4236/am.2014.519289
References
- 1. Andreyev, L.V., Dyshko, A.L. and Pavlenko, I.D. (1988) Dinamika of Plates and Covers with the Concentrated. Mashinostroyeniye, Nauka, Moscow, 200p.
- 2. Gershgorin, S.A. (1933) Fluctuations of the Plates Loaded by Concentrated Mass. PMM, T.1, Volume 1, No. 1, 25-37.
- 3. Andreyev, L.V., Dyshko, A.L. and Pavlenko, I.D. (1980) Otsenki of the Main Frequency of Fluctuations of Plates and the Covers Bearing the Concentrated Weight. Izv.Vuzov. Aircraft Equipment, No. 2, 89-93.
- 4. Zhigalko, Yu.P. and Dmitriyev, L.I. (1978) Dinamika of Ridge Plates and Covers. Research on the Theory of Plates and Covers. Kazan, Issue 132, 3-30.
- 5. Majboroda, V.P., Troyanovskiy, I.E. and Safarov, I.I. (1983) Free and Forced Vibrations of Systems of Rigid Bodies in the Inhomogeneous Viscoelastic Dampers. Izv.AN USSR. Ser. “Engineering” No. 3.
- 6. Bozorov, M.B., Safarov, I.I. and Shokin, Yu.I. (1966) Numerical Modeling of Fluctuations of Dissipatively Uniform and Non-Uniform Mechanical Systems. Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Science, Novosibirsk, 188p.
- 7. Safarov, I.I., Teshayev, M.H. and Madjidov, M.A. (2014) Damping of Fluctuations Dissipatively—Non-Uniform Mechanical Systems. LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing, Germany, 97p.
- 8. Kravchuk, A.S., Mayboroda, V.P. and Urzhumayev, Yu.S. (1985) Mekhanika of Polymeric and Composite Materials: Experimental and Numerical Methods. Nauka, Moscow, 304p.
- 9. Koltunov, M.A. (1976) Polzuchest and Relaxation. M.: The Highest Scale, 277p.
- 10. Safarov, I.I. (1992) Waves in Inhomogeneous Media and Dissipative Structures. Nauka, Tashkent, 250p.
- 11. Safarov, I.I. (1985) Damping Structurally Inhomogeneous System with a Finite Number of Degrees of Freedom. Differential Equations and Their Applications to Mechanics, Nauka, Tashkent, 288-294.












