Applied Mathematics
Vol.07 No.06(2016), Article ID:65172,9 pages
10.4236/am.2016.76052
Fixed Point Theorems in Intuitionistics Fuzzy Metric Spaces Using Implicit Relations
Arun Garg1, Zaheer K. Ansari2, Pawan Kumar3
1Department of Mathematics, NIMS University, Jaipur, India
2Department of Applied Mathematics, JSS Academy of Technical Education, Noida, India
3Department of Mathematics, Maitreyi College (University of Delhi), New Delhi, India

Copyright © 2016 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 23 July 2015; accepted 27 March 2016; published 30 March 2016
ABSTRACT
In this paper, we proved some fixed point theorems in intuitionistic fuzzy metric spaces applying the properties of weakly compatible mapping and satisfying the concept of implicit relations for t norms and t connorms.
Keywords:
Intuitionistic Fuzzy Metric Spaces, Weakly Compatible Mapping Implicit Relations for t Norms and t Connorms

1. Introduction
The concept of fuzzy sets is introduced by Zadeh [1] . In 1975, Kramosil and Michlek [2] introduced the concept of Fuzzy sets, Fuzzy metric spaces. George and Veeramani [3] gave the modified version of fuzzy metric spaces using continuous t norms. In 2005, Park, Kwun and Park [4] proved some point theorems “intuitionistic fuzzy metrics spaces”. In 1986, Jungck [5] introduced concept of compatible mappings for self mappings. Lots of the theorems were proved for the existence of common fixed points in classical and fuzzy metric spaces. Aamri and Moutawakil [6] introduced the concept of non-compatibility using E. A. property and proved several fixed point theorems under contractive conditions. Atanassove [7] introduced the concept of intuitionistic fuzzy sets which is a generalization of fuzzy sets.
In 2004, Park [8] defined intuitionistic fuzzy metric spaces using t-norms and t conorms as a gerenelization of fuzzy metric spaces. Turkoglu [9] gerenelized Junkck common fixed point theorem to intuitionistic fuzzy metric spaces. In this paper, we used E. A. property in intuitionistic fuzzy metric spaces to prove fixed point theorems for a pair of selfmaps. Kumar, Bhatia and Manro [10] proved common fixed point theorems for weakly maps satisfying E. A. property in “intuitionistic fuzzy metrics spaces” using implicit relation.
In this paper, we proved fixed point theorems for weakly compatible mappings satisfying E. A. property in “intuitionistic fuzzy metrics spaces” using implicit relation.
2. Preliminaries
Definition 1.1 (t norms). A binary operation  is a continuous t norms if
is a continuous t norms if 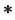 satisfies the following axioms:
satisfies the following axioms:
1)  is commutative as well as associative
is commutative as well as associative
2) 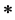 is continuous
is continuous
3) 
4) 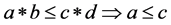 and
and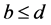 ,
, 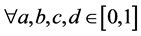
Definition 1.2 (t conorms). A binary operation 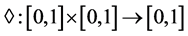 is a continuous t conorms if
is a continuous t conorms if 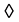 satisfies the following axioms:
satisfies the following axioms:
1) 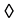 is commutative as well as associative
is commutative as well as associative
2)  is continuous
is continuous
3) 
4) 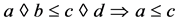 and
and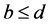 ,
,
Alaca [11] generalized the Fuzzy metric spaces of Kramosil and Michlek [2] and defined intuitionistic fuzzy metric spaces with the help of continuous t-norms and t conorms as:
Definition 1.3 (intuitionistic fuzzy metric spaces). A 5-tuple 



1) 
2)
3) 

4) 
5) 
6) 
7) 
8)
9) 

10) 
11) 
12) 
13) 
Then 


Proposition 1.4. Every fuzzy metric space 



Proposition 1.4. In intuitionistic fuzzy metric spaces



Lemma 1.5. Let 
1) A sequence 


2) A sequence 


3) An intuitionistic fuzzy metric spaces 
Example 1.6. Consider









Then 
Proposition 1.7. A pair of self mappings 


Proposition 1.8. A pair of self mappings 




Proposition 1.9. A pair of self mappings 




3. Implicit Functions
Popa [12] defined the concept of implicit function in proving of fixed point theorems in hybrid metric spaces. Implicit function can be described as, let ∅ be the family of lower semi-continuous functions 
G1: F is non-increasing in variables 
G2: 



G3:
Popa [12] defined the following examples of implicit function too,
Example 2.1. Let 
where
Example 2.2. Let 
where

Example 2.3. Let 
where
Example 2.4. Let 

where
M. Imdad and Javed Ali [13] - [15] added some implicit functions to prove fixed point theorems for Hybrid contraction. Following are examples are as:
Example 2.5. Let 
where
Example 2.6. Let 
where
Example 2.7. Let 

where


If 



Then implicit functions can be defined as 

(F1)
(F2)
(F3)
Example 2.8. 

(F1)
(F2)
(F3)
Example 2.9. 

(F1)
(F2)
(F3)
Example 3.0. 

(F1)
(F2)
(F3) 
4. Main Result
Theorem 3.1. Let 



(3.1.1) T and S satisfying E.A. properties,
(3.1.2) S is the closed subspaces of X,
(3.1.3)



where 

Then S and T have a common fixed point.
Proof. From (3.1.1), we have a sequence 
for some



Therefore

In (3.1.3), taking 

Taking
Since
Similarly
Taking
Since
Hence 
Again T and S are compatible mappings, therefore
Now we are to show that v is common point of T and S. Therefore replacing x and y by z and v in (3.1.3), we have
Since
Similarly
Since

Uniqueness of the point will be proved by contradiction. For that suppose p and q be two fixed points. Therefore from (3.1.3) we have
Since
Similarly
Since
Hence mappings T and S have a unique fixed point.
This completes the proof.
Theorem 3.2. Let 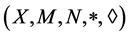



Let T and S be two weakly compatible maps of X satisfying the following conditions:
(3.2.1) T and S satisfying E.A. properties,
(3.2.2) S is the closed subspaces of X,
(3.2.3)

where 
(3.2.4) 
Then S and T have a common fixed point.
Proof. From (3.2.1), we have a sequence 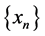
for some



Therefore 

In (3.2.3), taking 

Taking 

Similarly
Taking 

(3.2.5) and (3.2.6) both are the contradiction of (3.2.4).
Hence 

Now we are to show that v is common point of T and S. Therefore replacing x and y by z and v in (3.2.3), we have
This is a contradiction. Similarly
This is a contradiction again. Hence 
Uniqueness of the point will be proved by contradiction. For that suppose p and q be two fixed points.
Therefore from (3.2.3), we have
Similarly
This is the contradiction of (3.2.4).

This completes the proof.
Cite this paper
Arun Garg,Zaheer K. Ansari,Pawan Kumar, (2016) Fixed Point Theorems in Intuitionistics Fuzzy Metric Spaces Using Implicit Relations. Applied Mathematics,07,569-577. doi: 10.4236/am.2016.76052
References
- 1. Zadeh, L.A. (1965) Fuzzy Sets. Information and Control, 8, 338-353.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0019-9958(65)90241-X - 2. Kramosil, I. and Michlek, J. (1975) Fuzzy Metric and Statistical Metric Spaces. Kybernetica, 11, 326-334.
- 3. George, A. and Veeramani, P. (1994) On Some Results in Fuzzy Metric Spaces. Fuzzy Sets and System, 64, 81-89.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0165-0114(94)90162-7 - 4. Park, J.S., Kwun, Y.C. and Park, J.H. (2005) A Fixed Point Theorems “Intuitionistic Fuzzy Metrics Spaces”. Far East Journal of Mathematical Sciences, 16, 137-149.
- 5. Jungck, G. (1976) Commuting Mappings and Fixed Points. The American Mathematical Monthly, 83, 261-263.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/2318216 - 6. Aamri, M. and Mountwakil, D. (2002) Some Common fixed Point Theorems under Strict Contractive Conditions. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 270, 181-188.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0022-247X(02)00059-8 - 7. Atanassov, K. (1986) Intuitionistic Fuzzy Metric Sets. Fuzzy Sets and System, 20, 87-96.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(86)80034-3 - 8. Park, J.S. (2004) Intuitionistic Fuzzy Metrics Spaces. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 22, 1039-1046.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2004.02.051 - 9. Turkogly, D., Alaca, C., Cho, Y.J. and Yaldiz C. (2006) Common Fixed Point Theorems in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Metric Spaces. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computing, 22, 41-424.
- 10. Kumar, S., Bhatia, S.S. and Manro, S. (2012) Common Fixed Point Theorems for Weakly Maps Satisfying E.A. Property in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Metric Spaces Using Implicit Relation. Global Journal of Science Frontier Research Mathematics and Decision Sciences, 12.
- 11. Alaca, C., Turkoglu, D. and Yaldiz, C. (2006) Fixed Point Theorems in Intuitionistic Fuzzy Metric Spaces. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 29, 1073-1078.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2005.08.066 - 12. Popa, V. (2001) Some Common Fixed Point Theorems for Weakly Compatible Mappings. Radovi Matematichi, 10, 245-252.
- 13. Imdad, M., Kumar, S. and Khan, M.S. (2002) Remarks on Some Common Fixed Point Theorems Satisfying Implicit Relations. Radovi Matematichi, 11, 1-9.
- 14. Imdad, M. and Ali, J. (2007) A General Fixed Point Theorem for Hybrid Contraction via Implicit Functions. Southeast Asian Bulletin of Mathematics, 31, 73-80.
- 15. Imdad, M. and Ali, J. (2008) An Implicit Function Implies Contraction Conditions. Sarajevo Journals of Mathematics, 4, 269-285.



























































































