Applied Mathematics
Vol.06 No.09(2015), Article ID:59023,7 pages
10.4236/am.2015.69145
Mixed Saddle Point and Its Equivalence with an Efficient Solution under Generalized (V, r)-Invexity
Arvind Kumar1, Pankaj Kumar Garg2
1Department of Mathematics, University of Delhi, Delhi, India
2Department of Mathematics, Rajdhani College, University of Delhi, Delhi, India
Email: arvind.ch83@gmail.com, akumar1@maths.du.ac.in, gargpk08@gmail.com
Copyright © 2015 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 16 July 2015; accepted 21 August 2015; published 24 August 2015
ABSTRACT
The purpose of this paper is to define the concept of mixed saddle point for a vector-valued Lagrangian of the non-smooth multiobjective vector-valued constrained optimization problem and establish the equivalence of the mixed saddle point and an efficient solution under generalized (V, r)-invexity assumptions.
Keywords:
Nonsmooth Multiobjective Programs, (V, r)-Invexity, Mixed Saddle Point, Vector-Valued Mixed Lagrangian Function

1. Introduction
Jeyakumar and Mond [1] have introduced the notion of V-invexity for vector function and discussed its application to a class of multiobjective problems. Mishra and Mukherjee [2] and Liu [3] extended the concept of V-invexity of multiobjective programming to the case of nonsmooth multiobjective programming problems and duality results are also obtained. Jeyakumar [4] introduced r-invexity for differentiable scalar-valued functions. Also, Jeyakumar [5] defined r-invexity for nonsmooth scalar-valued functions, studied duality theorems for nonsmooth optimization problems, and gave relationship between saddle points and optima. In [6] (Bector), a sufficient optimality theorem is proved for a certain minmax programming problem under the assumptions (B, h)-invexity conditions.
Kuk, Lee and Kim [7] discussed that weak vector saddle-point theorems are obtained under V-r-invexity for vector-valued functions. Bhatia and Garg [8] defined (V, r)-invexity, (V, r)-quasiinvexity and (V, r)-pseudo- invexity for nonsmooth vector-valued Lipschitz functions using Clarke’s generalized subgradients and established duality results for multiobjective programming problems. Bhatia [9] introduced higher order strong convexity for Lipschitz functions. The notion of vector-valued partial Lagrangian is also introduced and equivalence of the mixed saddle points of higher order and higher order minima are provided. In [10] -[13] , saddle point theory in terms of Lagrangian functions was introduced. In [14] (Reddy and Mukherjee), some problems consisting of nonsmooth composite multiobjective programs have been treated with (V, r)-invexity type conditions and also vector saddle point theorems were obtained for composite programs. Yuan, Liu and Lai [15] defined new vector generalized convexity.
In this paper, we define the concept of mixed saddle point for a vector-valued constrained optimization problem and establish the equivalence of the mixed saddle point and an efficient solution under generalized (V, r)- invexity assumptions. Further mixed saddle point theorems are obtained.
2. Preliminaries
In this section we require some definitions and results.
Let
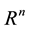 be the n-dimensional Euclidean space and
be the n-dimensional Euclidean space and
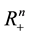 be its nonnegative orthant. Throughout this paper, the following conventions for vectors in
be its nonnegative orthant. Throughout this paper, the following conventions for vectors in
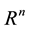 will be used:
will be used:
a)
 if and only if
if and only if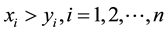 ,
,
b)
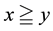 if and only if
if and only if ,
,
c)
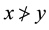 is the negation of
is the negation of .
.
The following non-smooth multiobjective programming problem is studied in this paper:

where
1)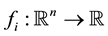 ,
,
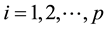 and
and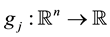 ,
,
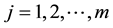 are locally Lipschitz functions on
are locally Lipschitz functions on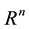 .
.
2) Let
 be the set of feasible solution of problem (MOP). Now let
be the set of feasible solution of problem (MOP). Now let




clearly
Problem (MOP) can be associated to problem
Now, we introduce the following definitions:
Definition 1. A vector function





for every

for every



Definition 2. A vector function




for every
for every


Definition 3. A vector function




for every
If



with

From the definitions it is clear that every strictly (V, r)-pseudoinvex on


Definition 4. A feasible point


and
for all
Definition 5. The vector valued mixed Lagrangian function

where
Definition 6. A vector


Definition 7. A function


1)
2)



For
Now, we have established our main results, to prove equivalence between mixed saddle point and an efficient solution.
3. Main Results
Theorem 1. Let





Further, let



with



Proof. Since



As

Hence, there exist
such that

Now for any

As

From (2) and (10) it follows that

Using the (V, r)-quasiinvexity of



(12) along with the fact


From (8) and (13) and using the sublinearity of


Now using (V, r)-pseudoinvex of



Since

Again for any



(18) along with (2) implies

Therefore, from (19)

Hence

From (17) and (21) and the fact that


Theorem 2. Let


quasiinvex at





Proof. Since


where


Now, for any



Using strict (V, r)-pseudoinvexity of



The fact of


From the sublinearty of V

(25) along with (26) gives

From (V, r)-quasiinvexity of



From (28), proceeding in the same manner as in Theorem (1) we obtain that


Theorem 3. Let








and





Proof. Since






Now as



(30), (31) and (32) imply that conditions (1) to (4) are satisfied. As

Now, using strict (V, r)-pseudoinvexity of



Since,

Again, proceeding in the same manner as in Theorem (1), it is proved that


In the next theorem no invexity or generalized invexity is used.
Theorem 4. If


Proof: Since




From (34), we get

Taking



Moreover,


Thus, we have
Hence,



But as



Now contrary to the result, let




and

(39) and (40) along with (38) give

and

that is


(43) and (44) are contradiction to the fact that
Acknowledgements
The research work presented in this paper is supported by grants to the first author from “University Grants Commission, New Delhi, India”, Sch. No./JRF/AA/283/2011-12.
Cite this paper
ArvindKumar,Pankaj KumarGarg, (2015) Mixed Saddle Point and Its Equivalence with an Efficient Solution under Generalized (V, p)-Invexity. Applied Mathematics,06,1630-1637. doi: 10.4236/am.2015.69145
References
- 1. Jeyakumar, V. and Mond, B. (1992) On Generalised Convex Mathematical Programming. Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society Series B, 34, 43-53.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0334270000007372 - 2. Mishra, S.K. and Mukherjee, R.N. (1996) On Generalised Convex Multi-Objective Nonsmooth Programming. Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society Series B, 38, 140-148.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0334270000000515 - 3. Liu, J.C. (1996) Optimality and Duality for Generalized Fractional Programming Involving Nonsmooth Pseudoinvex Functions. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 202, 667-685.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmaa.1996.0341 - 4. Jeyakumar, V. (1985) Strong and Weak Invexity in Mathematical Programming. Mathematical Methods of Operations Research, 55, 109-125.
- 5. Jeyakumar, V. (1988) Equivalence of Saddle-Points and Optima, and Duality for a Class of Non-Smooth Non-Covex Problems. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 130, 334-344.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0022-247X(88)90309-5 - 6. Bector, C.R. (1996) Wolfe-Type Duality Involving (B, η)-Invex Functions for a Minmax Programming Problem. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 201, 114-127.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmaa.1996.0245 - 7. Kuk, H., Lee, G.M. and Kim, D.S. (1998) Nonsmooth Multiobjective Programs with V-p-Invexity. Indian Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, 29, 405-412.
- 8. Bhatia, D. and Garg, P.K. (1998) (V, p)-Invexity and Non-Smooth Multiobjective Programming. RAIRO-Operations Research, 32, 399-414.
- 9. Bhatia, G. (2008) Optimality and Mixed Saddle Point Criteria Multiobjective Optimization. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 342, 135-145.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2007.11.042 - 10. Antczak, T. (2015) Saddle Point Criteria and Wolfe Duality in Nonsmooth Φ, p-Invex Vector Optimization Problems with Inequality and Equality Constraints. International Journal of Computer Mathematics, 92, 882-907.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00207160.2014.925191 - 11. Gutierrez, C., Hueraga, L. and Novo, V. (2012) Scalarization and Saddle Points of Approximate Proper Solutions in Nearly Subconvexlike Vector Optimization Problems. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 389, 1046-1058.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmaa.2011.12.050 - 12. Chen, G.-Y. (1997) Lagrangian Multipliers, Saddle Points, and Duality in Vector Optimization of Set-Valued Maps. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 215, 297-316.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmaa.1997.5568 - 13. Arrow, K.J., Gould, F.J. and Howe, S.M. (1973) A General Saddle Point Result for Constrained Optimization. Mathematical Programming, 5, 225-234.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF01580123 - 14. Reddy, L.V. and Mukherjee, R.N. (1999) Composite Nonsmooth Multiobjective Programs with V-p-Invexity. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 235, 567-577.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmaa.1999.6409 - 15. Yuan, D., Liu, X. and Lai, G. (2012) Nondifferentiable Mathematical Programming Involving (G, β)-Invexity. Journal of Inequalities and Applications, 256, 01-17.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1029-242x-2012-256



































