Applied Mathematics
Vol.05 No.17(2014), Article ID:50601,9 pages
10.4236/am.2014.517262
A Recursive Approach to the Kauffman Bracket
Abdul Rauf Nizami, Mobeen Munir, Umer Saleem, Ansa Ramzan
Division of Science and Technology, University of Education, Lahore, Pakistan
Email: arnizami@ue.edu.pk, mobeenmunir@gmail.com, umerlinks@hotmail.com, ansaramzan@yahoo.com
Copyright © 2014 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 26 July 2014; revised 28 August 2014; accepted 10 September 2014
ABSTRACT
We introduce a simple recursive relation and give an explicit formula of the Kauffman bracket of two-strand braid link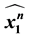 . Then, we give general formulas of the bracket of the sequence of links of three-strand braids
. Then, we give general formulas of the bracket of the sequence of links of three-strand braids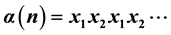 . Finally, we give an interesting result that the Kauffman bracket of the three-strand braid link
. Finally, we give an interesting result that the Kauffman bracket of the three-strand braid link
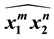 is actually the product of the brackets of the two- strand braid links
is actually the product of the brackets of the two- strand braid links
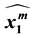 and
and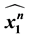 . Moreover, a recursive relation for
. Moreover, a recursive relation for
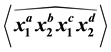 is also given.
is also given.
Keywords:
Recursive Relation, Kauffman Bracket, Braid Link

1. Introduction
The Kauffman bracket polynomial was introduced by L. H. Kauffman in 1987 [1] in concern with link invariants. The bracket polynomial soon became popular due to its connections with the Jones polynomial, dichromatic polynomial, and the Potts model. While the HOMPLY polynomial and the bracket polynomial are distinct with different topological properties, there is a very beautiful relationship between them due to F. Jaeger [2] , and it is also observed in a special case by Reshetikhin [3] .
The Kauffman bracket (polynomial) is actually not a link invariant because it is not invariant under the first Reidemeister move. However, it has many applications and it can be extended to a popular link invariant, the Jones polynomial. In the present work we shall confine ourselves to the Kauffman bracket to avoid this work from unnecessary length and to leave it for applications.
This paper is organized as follows: In Section 2 we shall give the basic ideas about knots, braids, and the Kauffman bracket. In Section 3 we shall present the main results.
2. Basic Notions
2.1. Links
A link is a disjoint union of circles embedded in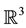 . A one-component link is called a knot. Links are usually studied via projecting them on a plan; a projection with extra information of overcrossing and undercrossing is called the link diagram.
. A one-component link is called a knot. Links are usually studied via projecting them on a plan; a projection with extra information of overcrossing and undercrossing is called the link diagram.
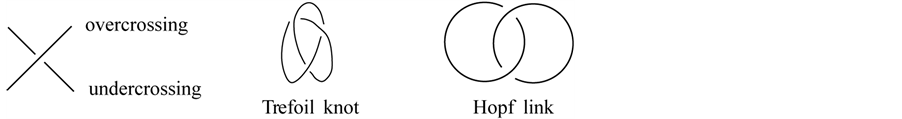
Two links are isotopic if and only if one of them can be transformed to the other by a diffeomorphism of the ambient space onto itself. A fundamental result by Reidemeister [4] about the isotopic link diagrams is: Two unoriented links
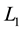 and
and
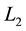 are equivalent if and only if a diagram of
are equivalent if and only if a diagram of
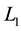 can be transformed into a diagram of
can be transformed into a diagram of
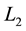 by a finite sequence of ambient isotopies of the plane and the local (Reidemeister) moves of the following three types:
by a finite sequence of ambient isotopies of the plane and the local (Reidemeister) moves of the following three types:
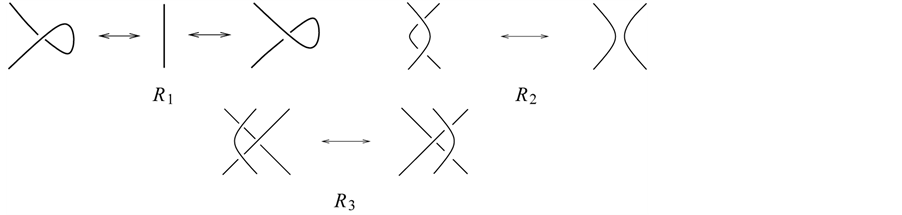
The set of all links that are equivalent to a link
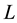 is called a class of
is called a class of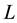 . By a link
. By a link
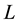 we shall always mean the class of
we shall always mean the class of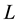
The main question of knot theory is Which two links are equivalent and which are not? To address this question one needs a knot invariant, a function that gives one value on all links that belong to a single class and gives different values (but not always) on knots that belong to different classes. The present work is basically concerned with this question.
2.2. Braids
Braids were first studied by Emil Artin in 1925 [5] [6] , which now play an important role in knot theory, see [7] -[9] for detail.
An n-strand
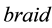
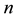
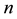
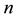
The product
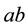
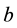
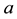
A braid with only one crossing is called elementary braid. The ith elementary braid
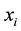
A useful property of elementary braids is that every braid can be written as a product of elementary braids. For instance, the above 2-strand braid is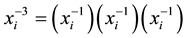
The closure of a braid
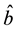
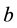
An important result by Alexander [10] connecting knots and braids is: Each link can be represented as the closure of a braid. This result motivated knot theorists to study braids to solve problems of knot theory.
Remark 2.1 In the last section, all the concerned links will be closures of products of elementary braids.
2.3. The Kauffman Bracket
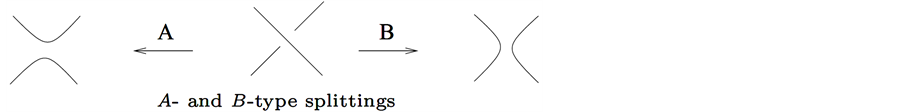
Before the definition it is better to understand the two types of splitting of a crossing, the A-type and the B-type splittings:
In the following, the symbols
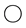
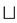
Definition 2.2 The Kauffman bracket is the function
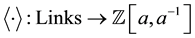
Here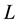
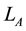
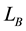
Proposition 2.3 The Kauffman polynomial is invariant under second and third Reidemeister moves but not under the first Reidemeister move [11] .
3. Main Results
In this section we shall introduce a recursive relation for the Kauffman bracket, shall give an explicit formula of
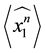
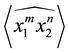
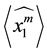
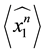
First of all we give the Kauffman bracket of the
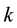
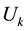
Lemma 3.1 The Kauffman bracket of the
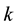
Proof. We prove it by induction on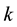
The case
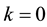
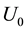
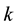
Theorem 3.2 (A recursive relation) The following relation holds for any
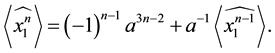
Proof. We prove it using directly the definition and Lemma 3.1:
From this recursive relation, we get the explicit formula for the 2-strand braid link
Proposition 3.3 The Kauffman bracket of the link
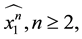
Proof. We prove it by induction on
For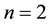
which satisfies the recursive relation.
With the assumption that the relation holds for an arbitrary n, we, using Theorem 3.2, get
This completes the proof. ,
In the following we give the Kauffman bracket polynomial of the closure of the braid
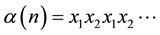
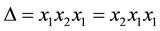
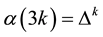
Proposition 3.4 The Kauffman bracket of
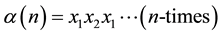
Proof. Simply, apply the definition for different values of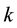
Lemma 3.5 The Kauffman brackets for
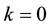
Proof. The proofs of first three cases are given (proofs of remaining cases are similar):
Theorem 3.6 For any
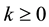
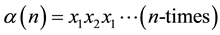
Proof. We prove it by induction on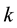
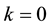
For instance,
In connected sum
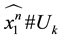
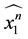
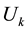
Lemma 3.7
Proof. We prove it by induction on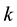
For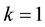
Now, with the assumption that the result holds for an arbitrary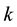
as required. ,
The following result confirms that the Kauffman bracket of
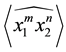
Theorem 3.8 For any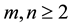
Proof. We prove it by induction on
When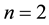
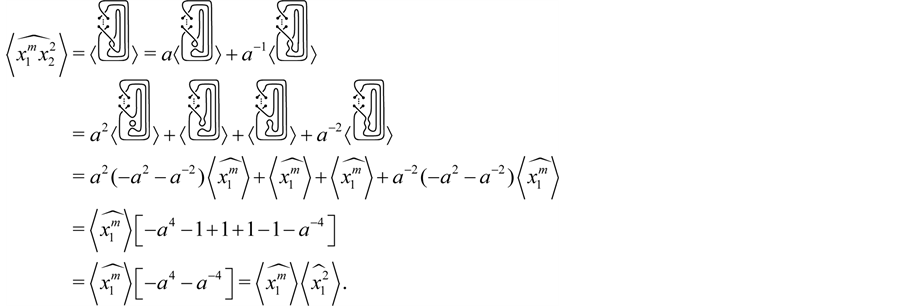
Suppose the result holds for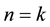
Now, using Lemma 3.7, we have
This completes the proof. ,
Corollary 3.9
Proof. It is obvious:
Corollary 3.10
and
Proof. The result follows immediately from Theorem 3.8 as
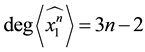
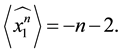
For the following, let us fix the notation
and
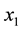
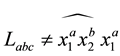
Proposition 3.11 The Kauffman bracket of the link
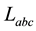
Proof. We prove it by induction on
For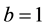
Now, with the assumption that the result holds for an arbitrary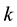
as required. ,
Proposition 3.12 The Kauffman bracket of the link
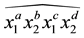
Proof. We prove it by induction on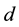
For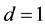
Now, with the assumption that the result holds for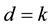
as was required. ,
References
- Kauffman, L.H. (1987) State Models and the Jones Polynomial. Topology, 26, 395-407. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0040-9383(87)90009-7
- Jaeger, F. (1990) A Combinatorial Model for the Homy Polynomial. European Journal of Combinatorics, 11, 549-555.
- Reshetikhin, N.Y. (1988) Quantized Universal Enveloping Algebras, the Yang-Baxter Equation and Invariants of Links, I and II. LOMI Reprints E-4-87 and E-17-87, Steklov Institute, Leningrad, USSR.
- Reidemeister, K. (1948) Knot Theory. Chelsea Publ and Co., New York.
- Artin, E. (1925) Theorie der Z
pfe. Abhandlungen aus dem Mathematischen Seminar der Universität Hamburg, 4, 27-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02950718
- Artin, E. (1947) Theory of Braids. Annals of Mathematics, 48, 101-126. http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/1969218
- Birman, J.S. (1974) Braids, Links, and Mapping Class Groups. Princeton University Press, Princeton.
- Manturov, V.O. (2004) Knot Theory. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Boca Raton. http://dx.doi.org/10.1201/9780203402849
- Murasugi, K. (1996) Knot Theory and Its Applications. Birkh
User, Boston.
- Alexander, J. (1923) Topological Invariants of Knots and Links. Transactions of the American Mathematical Society, 20, 275-306.
- Adams, C.C. (1994) The Knot Book. W H Freeman and Company, New York.





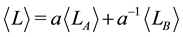
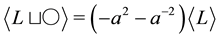
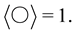


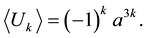
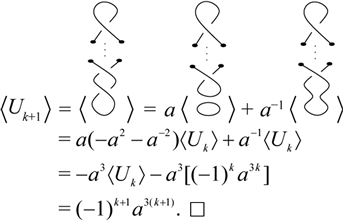
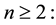
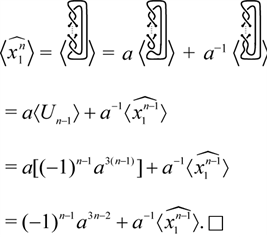
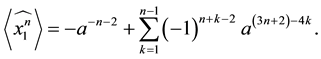
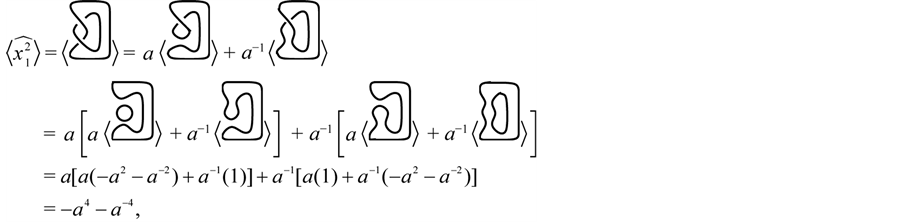
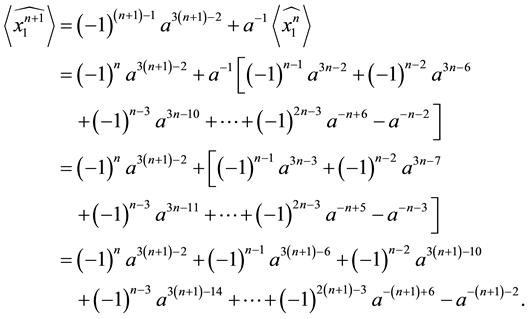
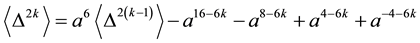
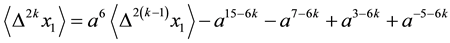
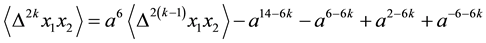
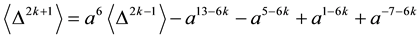
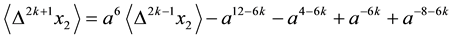
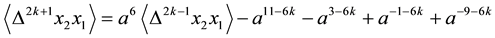
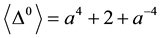
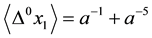
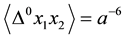
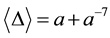
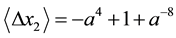
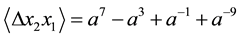

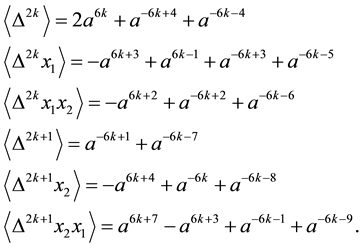
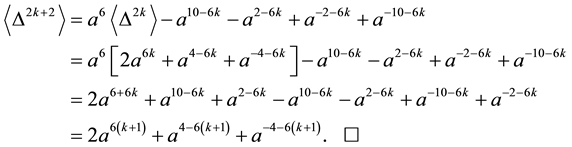

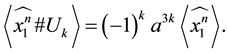
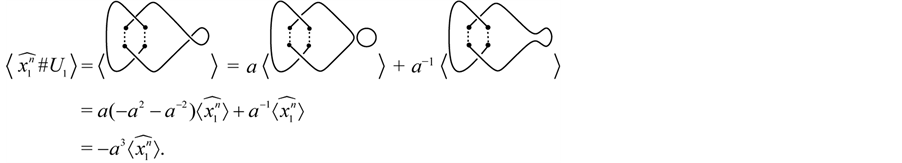
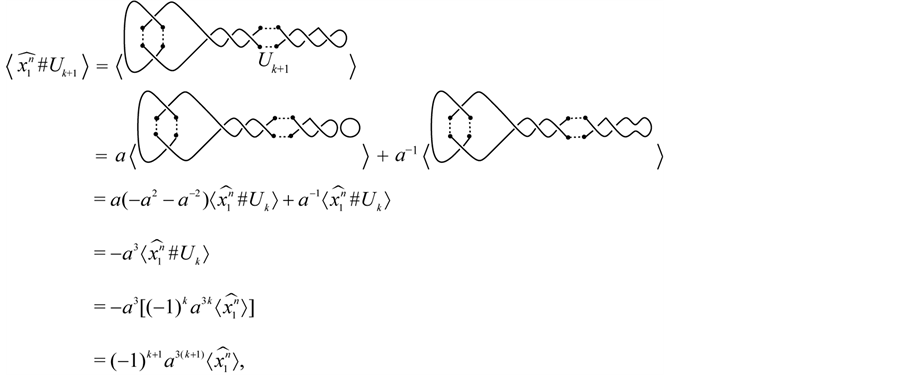
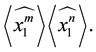
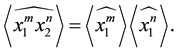
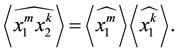
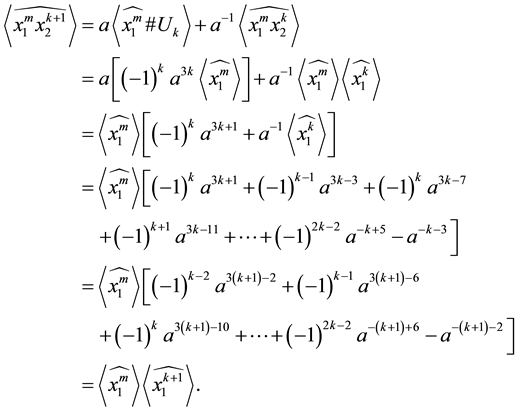
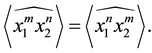
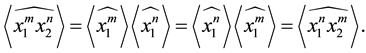
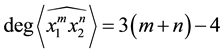
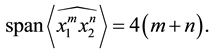

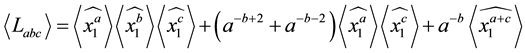
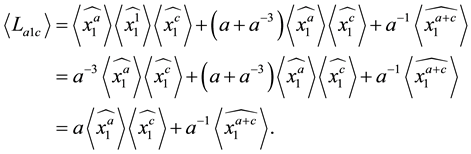
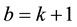

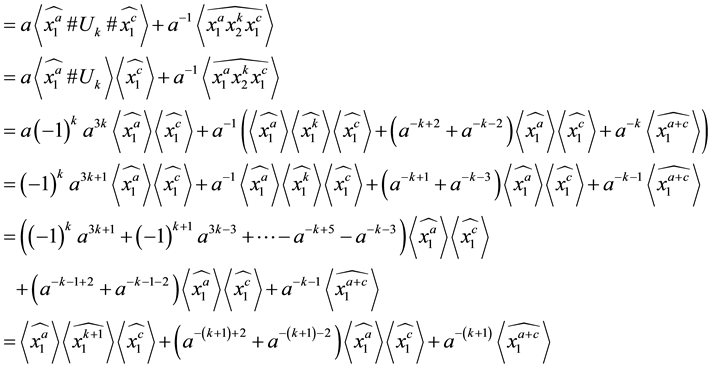
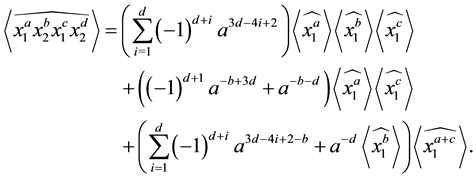
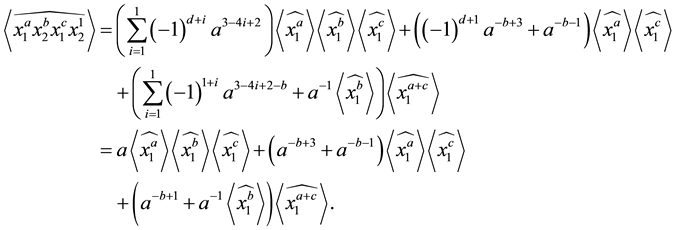
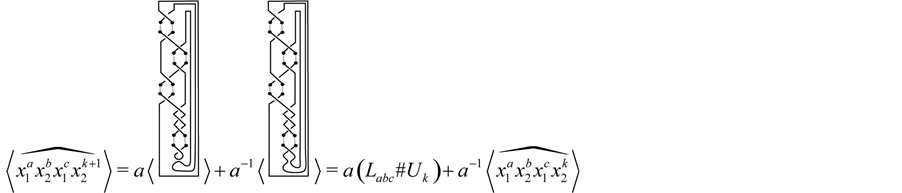

 pfe. Abhandlungen aus dem Mathematischen Seminar der Universität Hamburg, 4, 27-72.
pfe. Abhandlungen aus dem Mathematischen Seminar der Universität Hamburg, 4, 27-72.  User, Boston.
User, Boston.