Advances in Pure Mathematics
Vol.2 No.6(2012), Article ID:24668,4 pages DOI:10.4236/apm.2012.26063
Some Classes of Operators Related to p-Hyponormal Operator
1Department of Mathematics, Gaya College, Gaya, Bihar, India
2Al-Ain University of Science and Technology, Al Ain & Abu Dhabi, UAE
Email: reyaz56@hotmail.com, reyaz56@gmail.com
Received August 11, 2012; revised September 16, 2012; accepted September 28, 2012
Keywords: p-Hyponormal Operator; Monotonicity; Class of Operators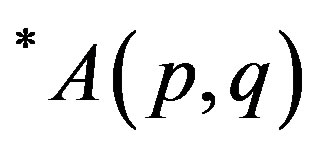 ; *Paranormal Operator; *p-Paranormal Operator
; *Paranormal Operator; *p-Paranormal Operator
ABSTRACT
We introduce a new family of classes of operators termed as *p-paranormal operator, classes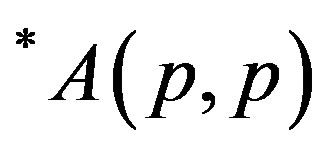 ; p > 0 and
; p > 0 and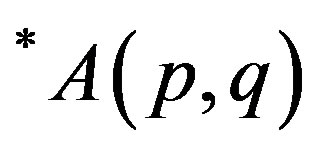 ; p, q > 0, parallel to p-paranormal operator and classes
; p, q > 0, parallel to p-paranormal operator and classes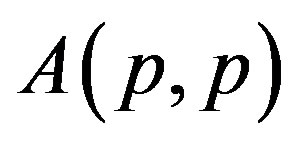 ; p > 0 and
; p > 0 and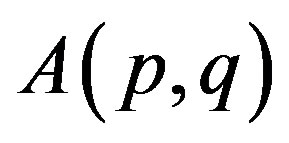 ; p, q > 0 introduced by M. Fujii, D. Jung, S. H. Lee, M. Y. Lee and R. Nakamoto [1]. We present a necessary and sufficient condition for p-hyponormal operator
; p, q > 0 introduced by M. Fujii, D. Jung, S. H. Lee, M. Y. Lee and R. Nakamoto [1]. We present a necessary and sufficient condition for p-hyponormal operator  to be *p-paranormal and the monotonicity of
to be *p-paranormal and the monotonicity of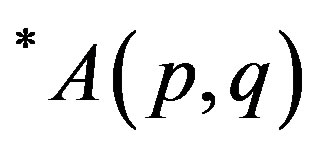 . We also present an alternative proof of a result of M. Fujii, et al. [1, Theorem 3.4].
. We also present an alternative proof of a result of M. Fujii, et al. [1, Theorem 3.4].
1. Introduction
Let 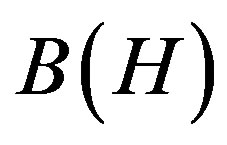 denote the algebra of bounded liner operators on a Hilbert space H. An operator
denote the algebra of bounded liner operators on a Hilbert space H. An operator 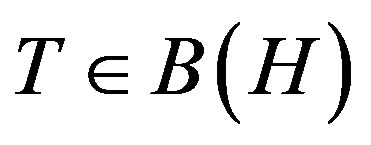 is positive if
is positive if  for all
for all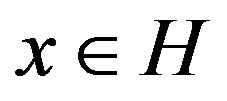 . An operator
. An operator 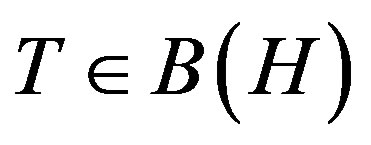 is hyponormal if
is hyponormal if 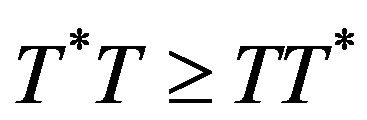 and p-hyponormal if
and p-hyponormal if 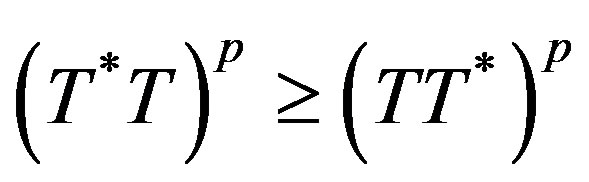 for p > 0. By the well known Lowner-Heinz theorem “
for p > 0. By the well known Lowner-Heinz theorem “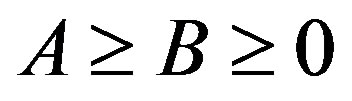 ensures
ensures  for
for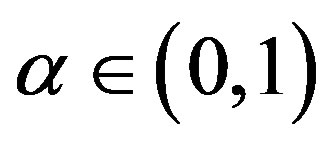 ”, every p-hyponormal operator is q-hyponormal for
”, every p-hyponormal operator is q-hyponormal for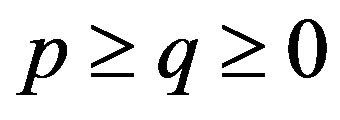 . The Furuta’s inequalities [2] are as follows:
. The Furuta’s inequalities [2] are as follows:
If 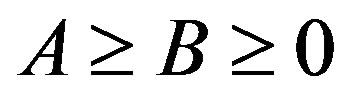 then for each
then for each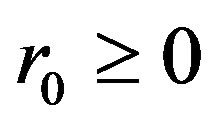
 (1.1)
(1.1)
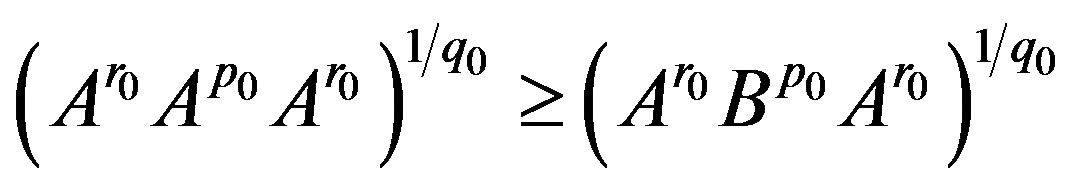 (1.2)
(1.2)
hold for p0 ≥ 0 and q0 ≥ 1 with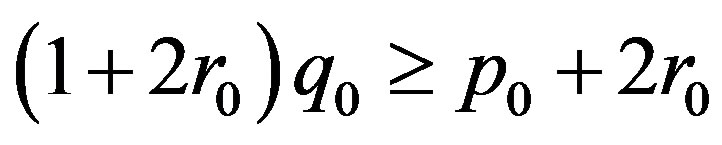 .
.
An operator  is 1) paranormal if
is 1) paranormal if 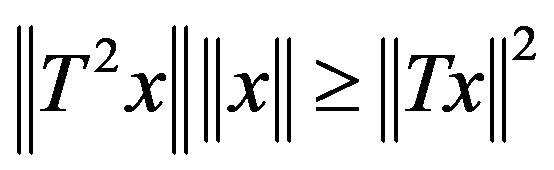 for all
for all ;
;
2) *paranormal if 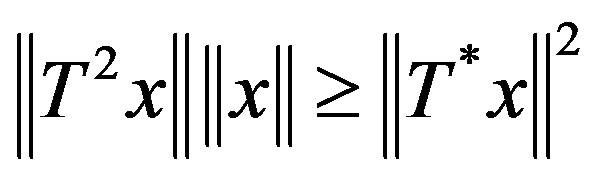 for all
for all .
.
2. Preliminaries and Background
M. Fujii, D. Jung, S. H. Lee, M. Y. Lee and R. Nakamoto [1] introduced the following classes of operators:
An operator  is p-paranormal for p > 0, if
is p-paranormal for p > 0, if
 (2.1)
(2.1)
holds for all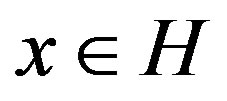 , where U is the partial isometry appearing in the polar decomposition
, where U is the partial isometry appearing in the polar decomposition 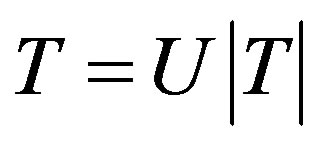 of T with
of T with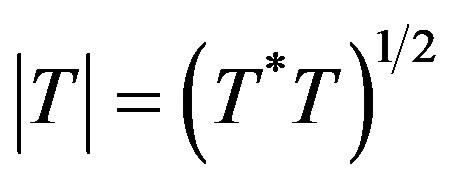 .
.
For p > 0, an operator 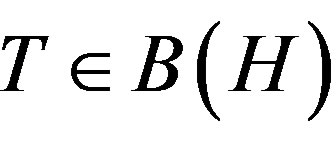 is of class
is of class 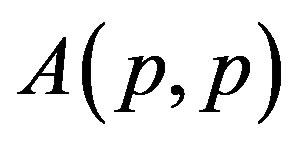 if it satisfies an operator inequality
if it satisfies an operator inequality
 (2.2)
(2.2)
For p, q > 0, an operator 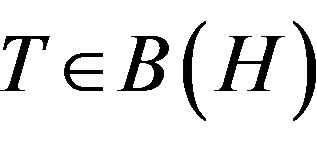 is of class
is of class 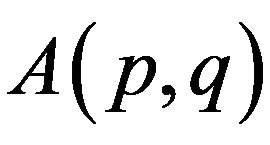 if it satisfies an operator inequality
if it satisfies an operator inequality
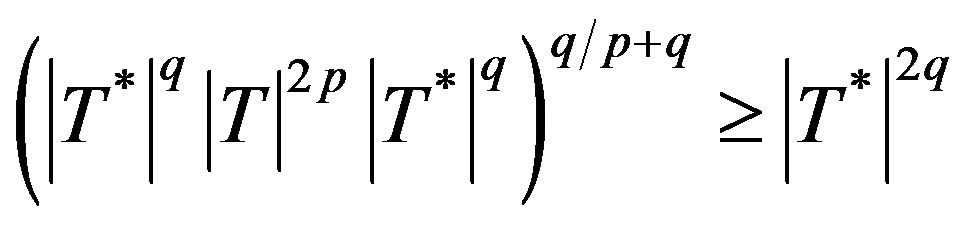 (2.3)
(2.3)
In this sequel we introduce *p-paranormal operator, classes of operators 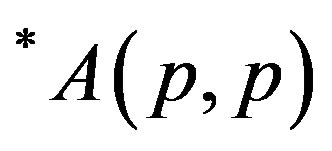 for p > 0 and
for p > 0 and  for p, q > 0 as follows:
for p, q > 0 as follows:
A p-hyponormal operator is *p-paranormal if
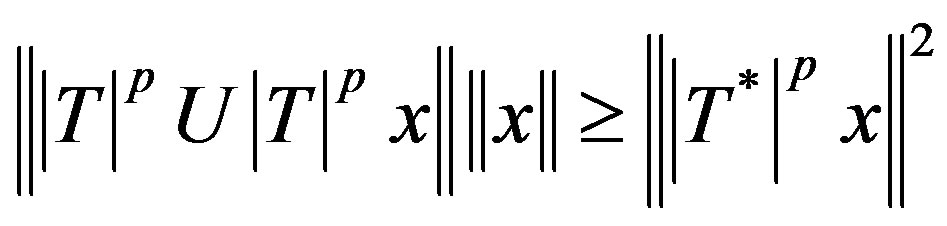 (2.4)
(2.4)
For p > 0 a p-hyponormal operator 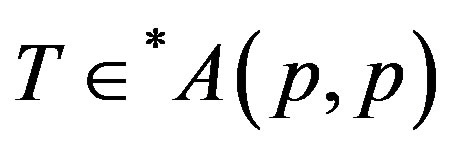 if it satisfies an operator inequality
if it satisfies an operator inequality
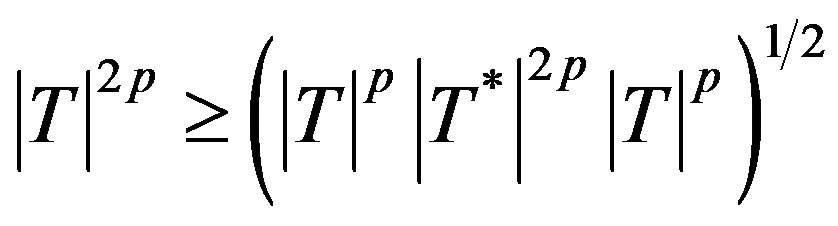 (2.5)
(2.5)
More generally, we define the class 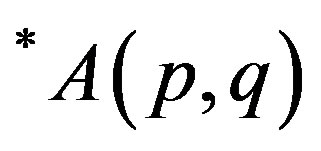 for p, q > 0 by an operator inequality
for p, q > 0 by an operator inequality
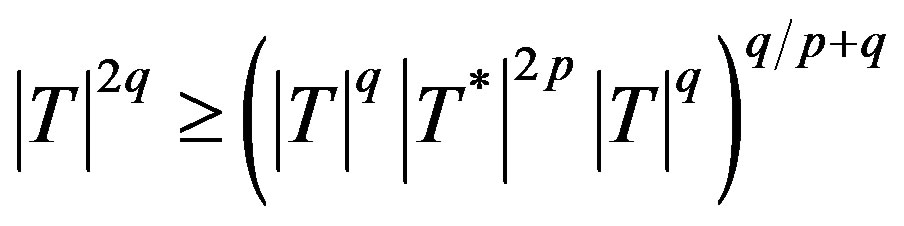 (2.6)
(2.6)
Remark (2.1). If T is p-hyponormal then using Furuta inequality (1.1) (§1) it can be proved easily that 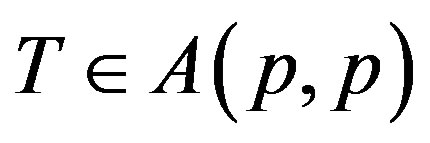 .
.
Remark (2.2). By inequality (2.6) we have

The well known theorem of T. Ando [3] for paranormal operator is required in the proof of our main result.
Theorem (2.3). (Ando’s Theorem): An operator T is paranormal if and only if
 (2.7)
(2.7)
for all real k.
3. Main Results
M. Fujii, et al. [1] proved the following theorem [1; Theorem 3.4].
Theorem (3.1). If  for p > 0 then T is p-paranormal.
for p > 0 then T is p-paranormal.
In the following first we present an alternative way in which Theo (3.1) is proved in [1]. For this we have considered a quadratic form analogous to inequation (2.7) (§2). We also present a necessary and sufficient condition for a p-hyponormal operator T to be a *p-paranormal operator and the monotonicity of class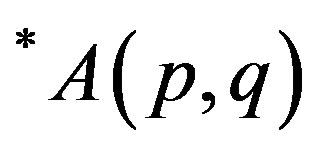 .
.
Theorem (3.2). A p-hyponormal operator 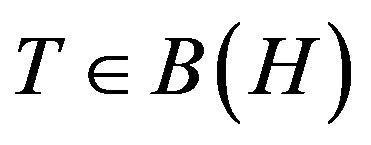 is p-paranormal if and only if
is p-paranormal if and only if 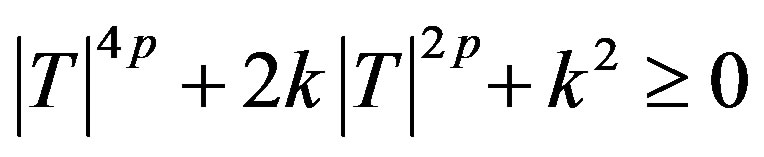 for all
for all  and p > 0.
and p > 0.
Proof. Let T = be p-hyponormal where U is partial isometry, hence
be p-hyponormal where U is partial isometry, hence
 .
.
We have
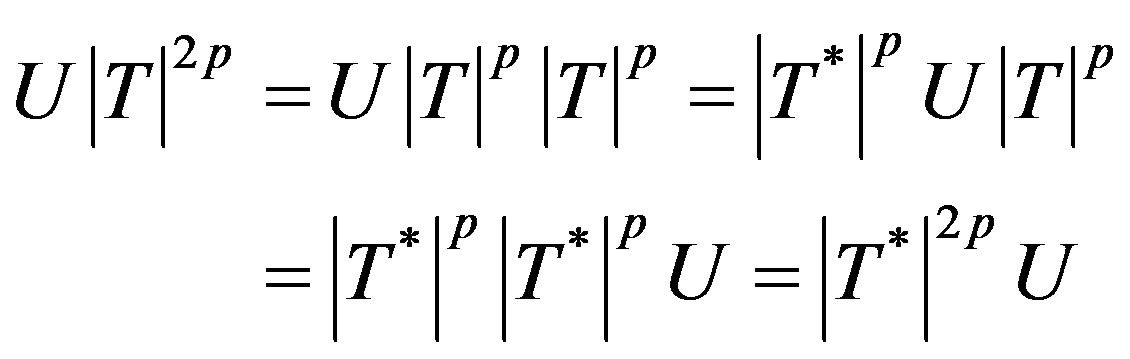
and

Now,
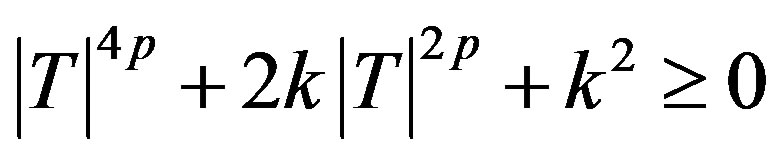
for all 
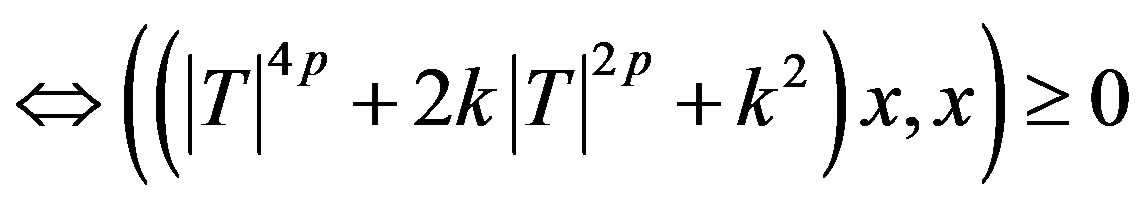
for all 
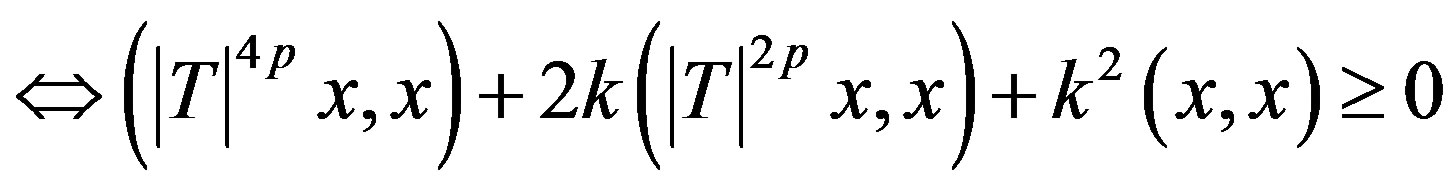
for all 

for all 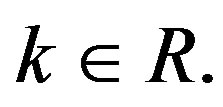
We know that if a > 0, b and c are real numbers then 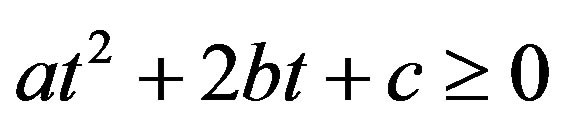 for every real t if and only if
for every real t if and only if 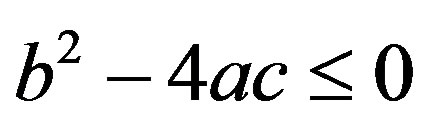 . Hence
. Hence
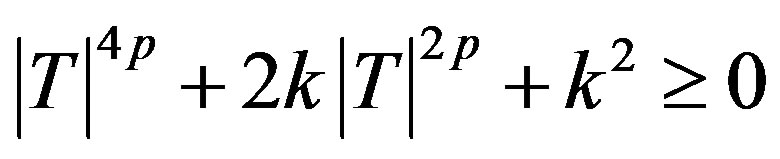
for all 

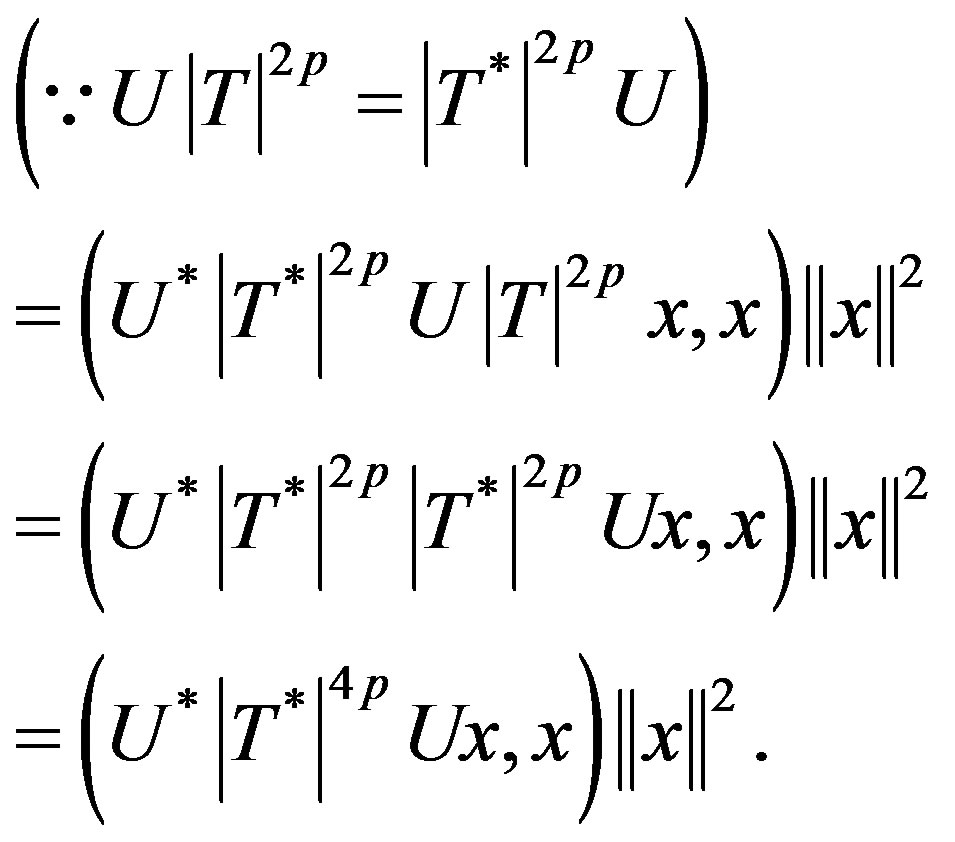
Since T be p-hyponormal, by Remark (2.1) (§2) 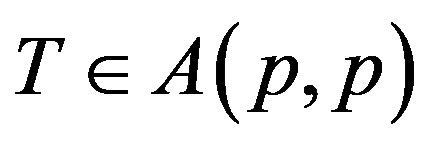 i.e.
i.e.
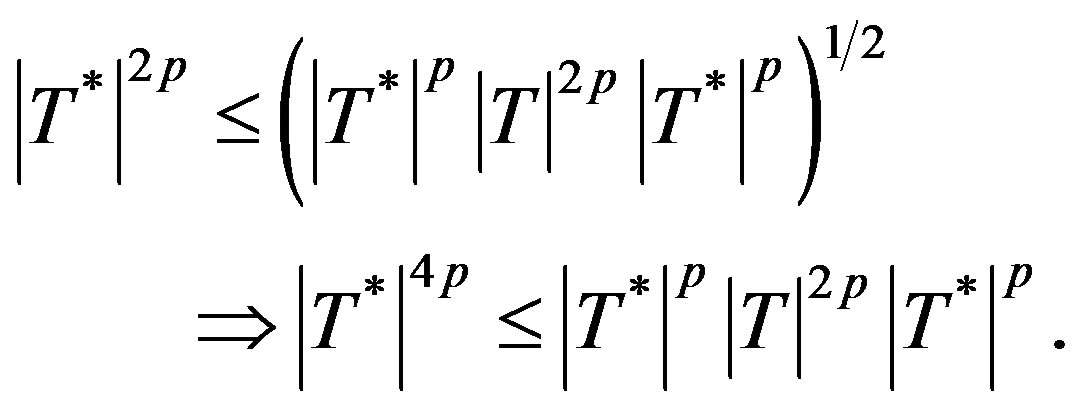
Hence
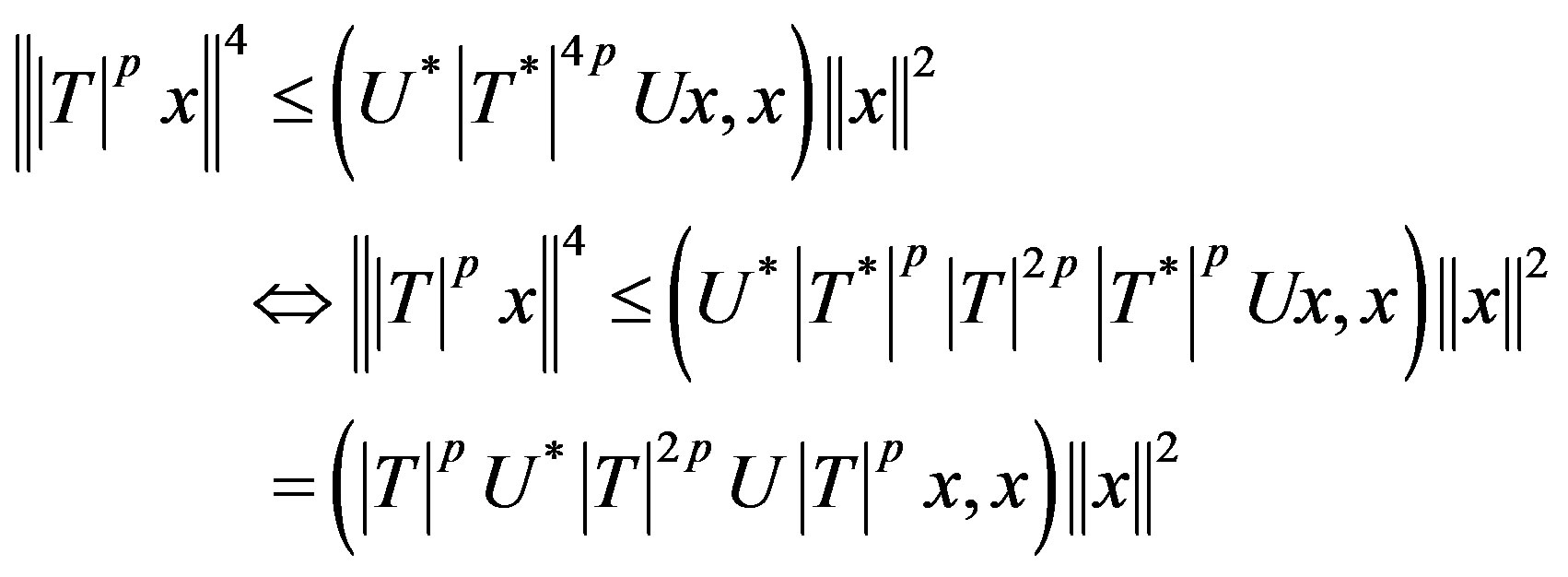
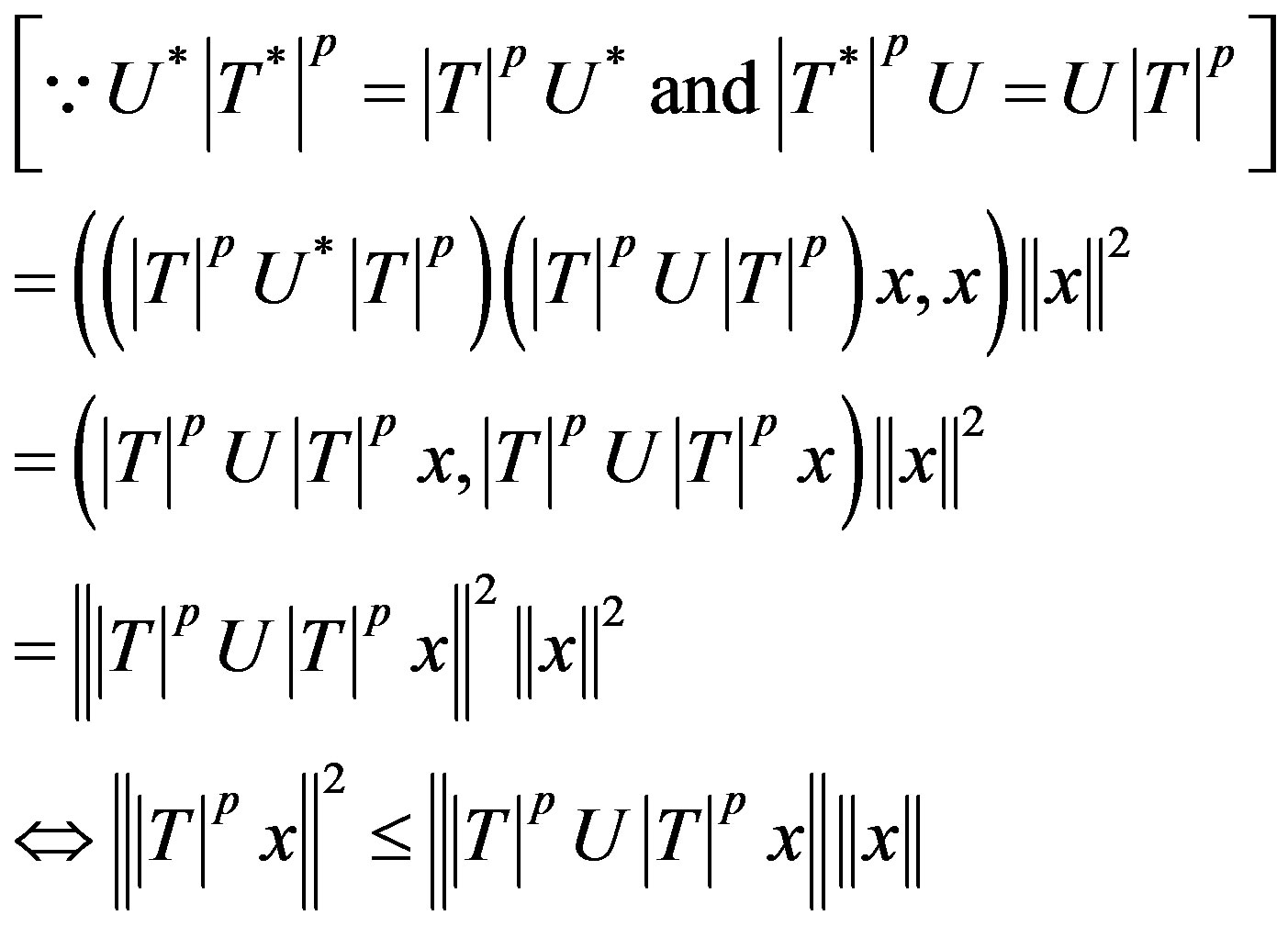
i.e. if and only if T is p-paranormal.
Remark (3.3). Theorem (3.2) is independent of 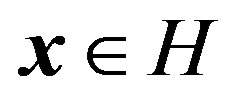 being taken as unit vector where as M. Fujii, et al. [1] have considered
being taken as unit vector where as M. Fujii, et al. [1] have considered 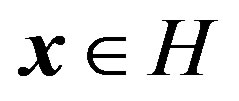 as unit vector in the result [1, Theo. 3.4].
as unit vector in the result [1, Theo. 3.4].
The following result presents a necessary and sufficient condition for p-hyponormal operator T to be a *pparanormal operator.
Theorem (3.4). A p-hyponormal operator T is *pparanormal if and only if
 for all
for all (3.1)
(3.1)
Proof. Let 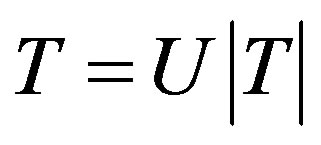 be p-hyponormal operator where U is a partial isometry also let
be p-hyponormal operator where U is a partial isometry also let  so that
so that
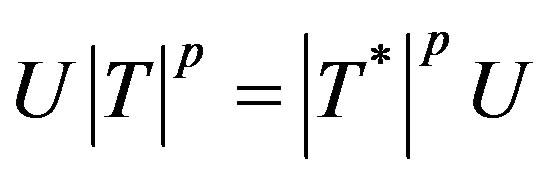 ,
, 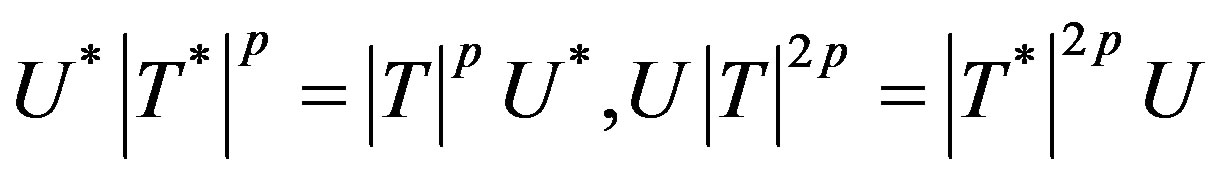
and . Now
. Now

for all 
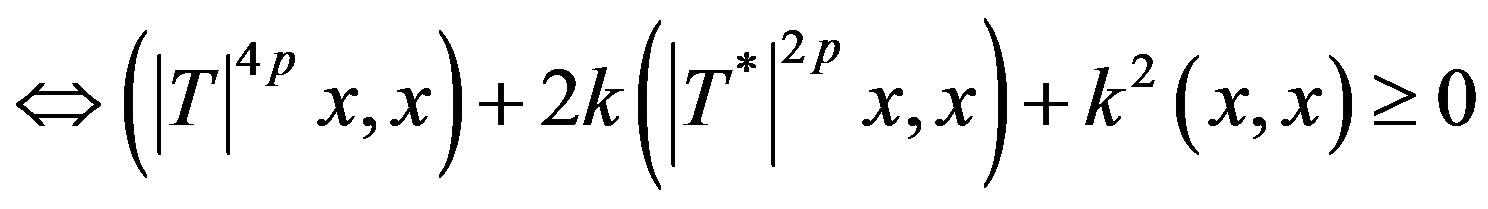
for all 

for all 
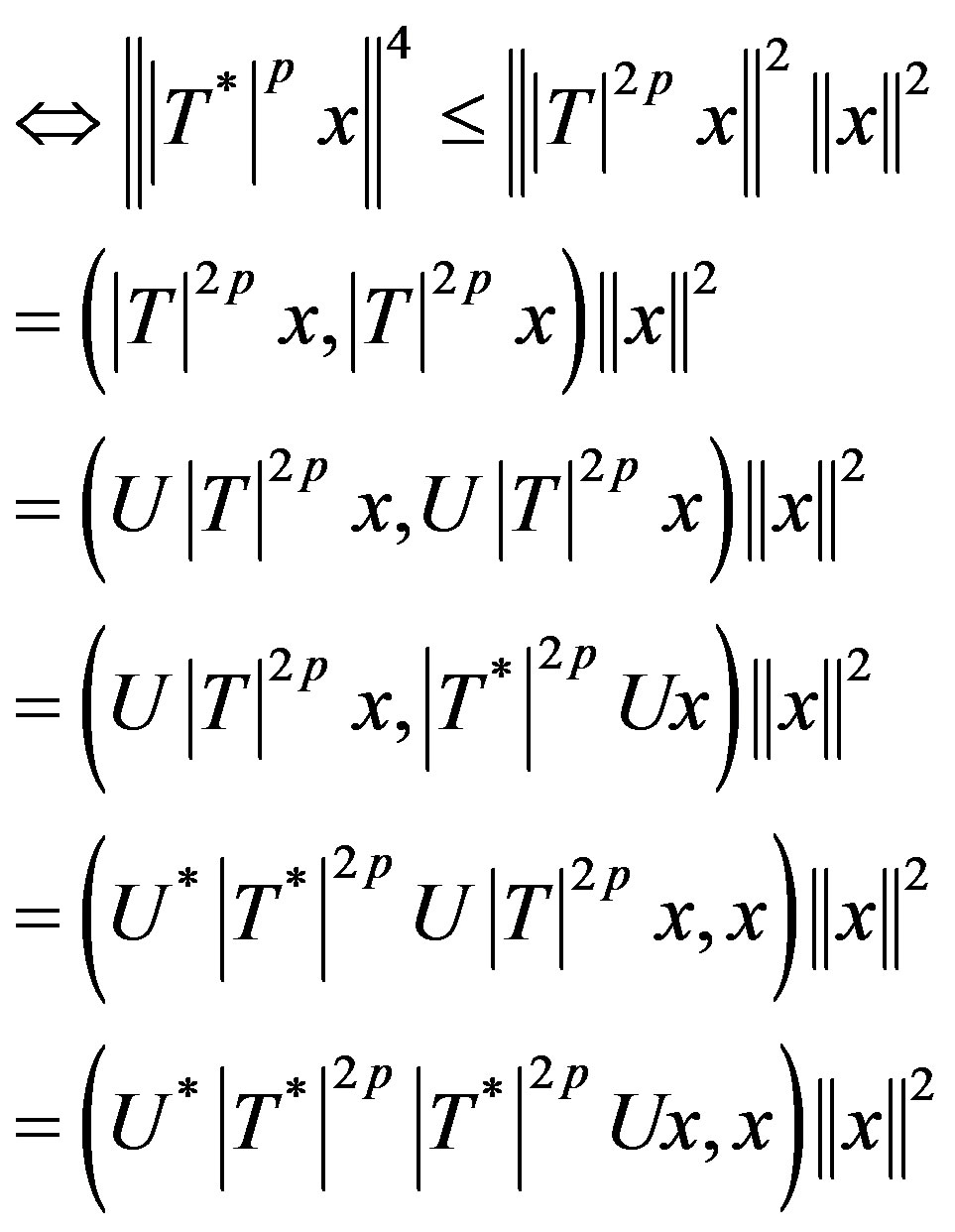
i.e., 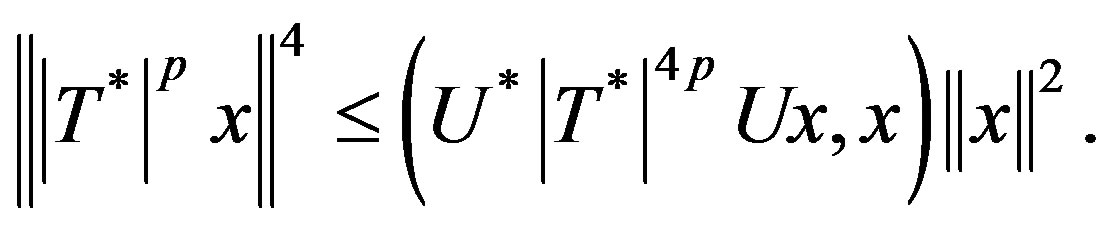 (3.2)
(3.2)
Since T is p-hyponormal so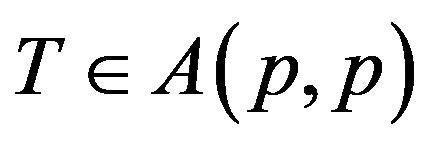 , i.e.
, i.e.
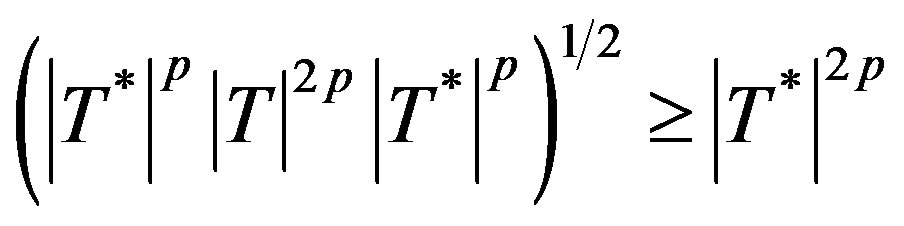
i.e. 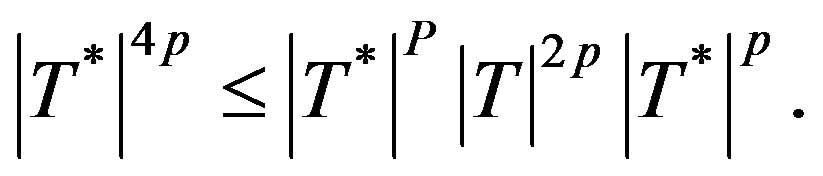 (3.3)
(3.3)
From (3.2) and (3.3), we have
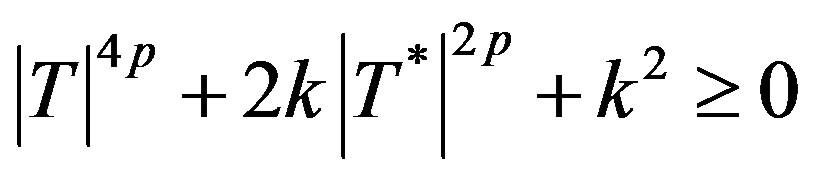
for all 
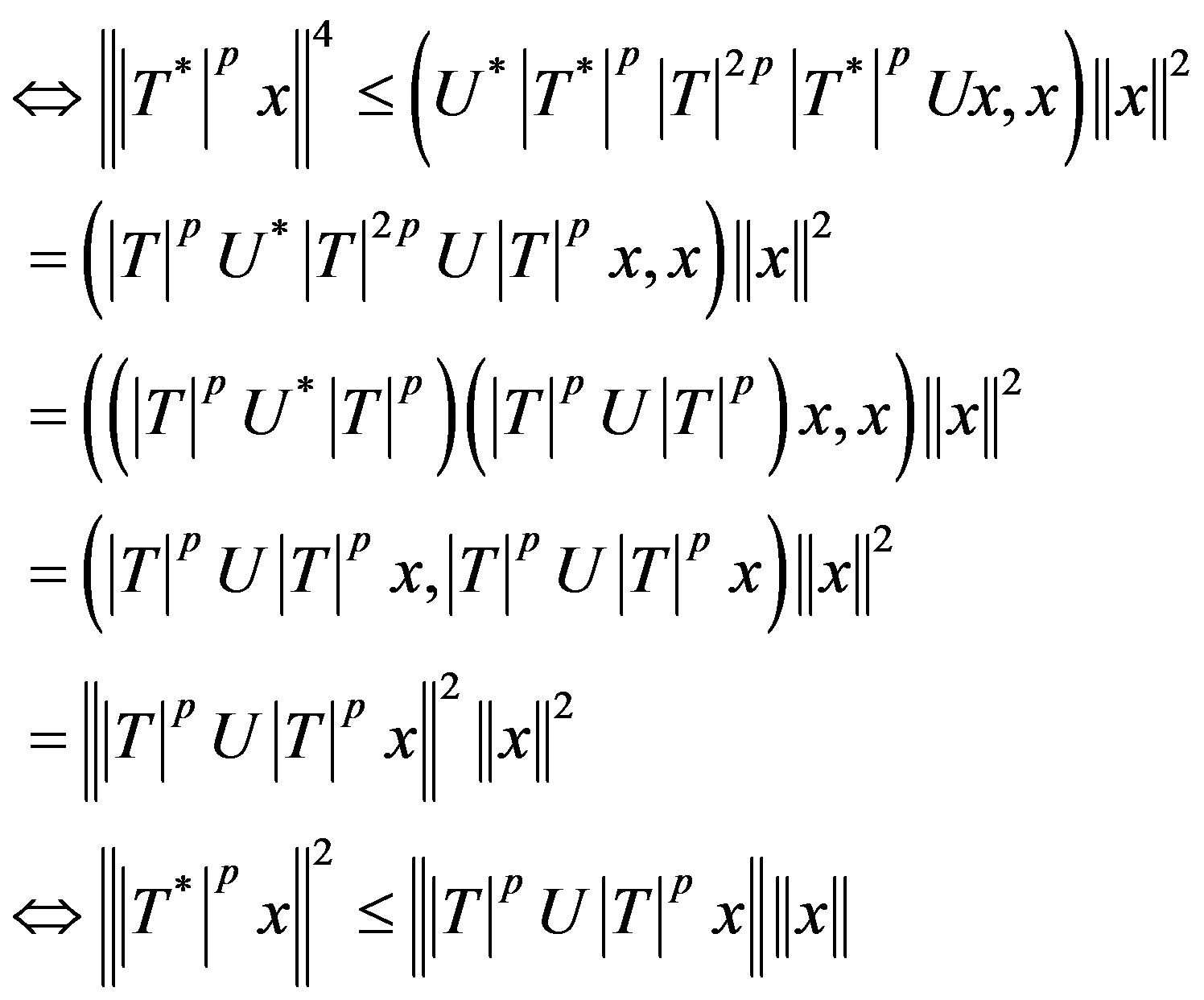
i.e. if and only if T is *p-paranormal.
In the following we present monotonicity of . We need Furuta inequality [2,4] to prove the following theorem, see also [5,6].
. We need Furuta inequality [2,4] to prove the following theorem, see also [5,6].
Theorem (3.5). If 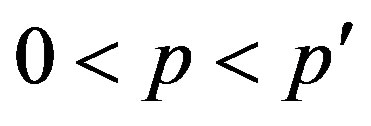 and 0 < q then
and 0 < q then
 .
.
Proof. Let 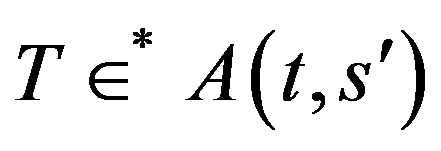 where
where 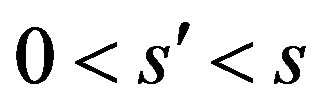 and 0 < t then by the definition of class
and 0 < t then by the definition of class 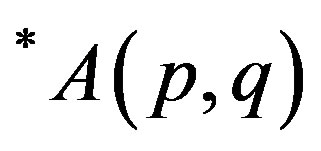 for p, q > 0.
for p, q > 0.
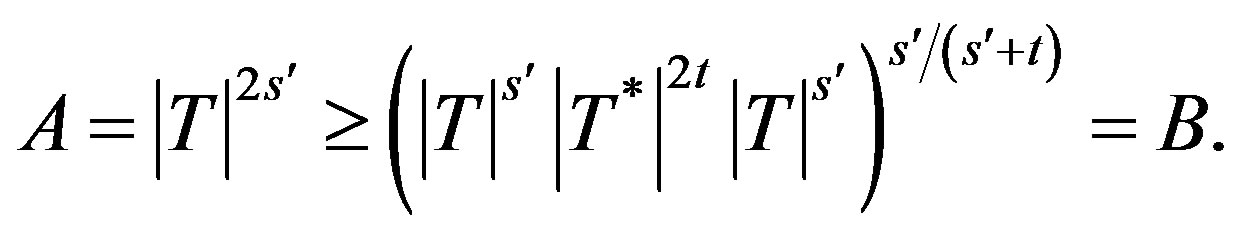
We apply it to (1.2) (§1), in the case when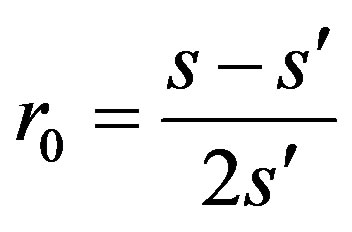 ,
, 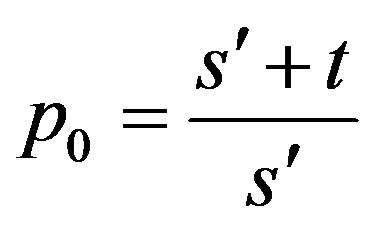 ,
, 
 We have
We have

and
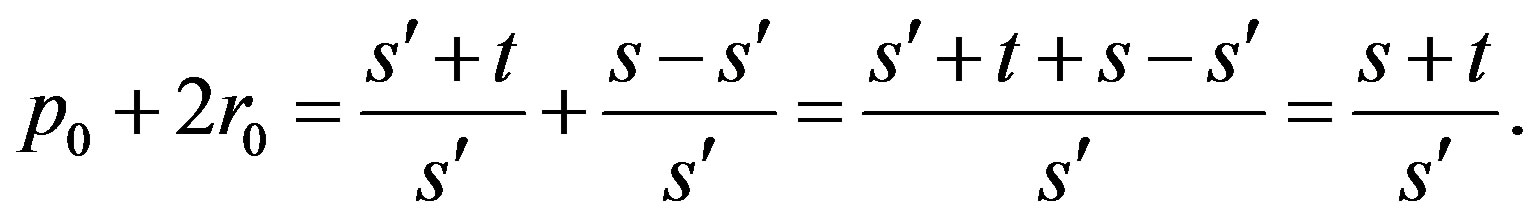
Hence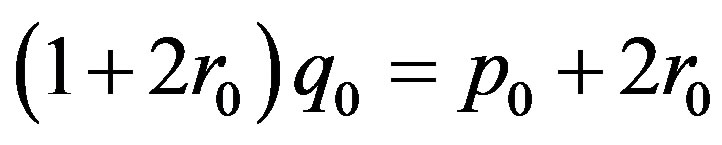 , so that
, so that
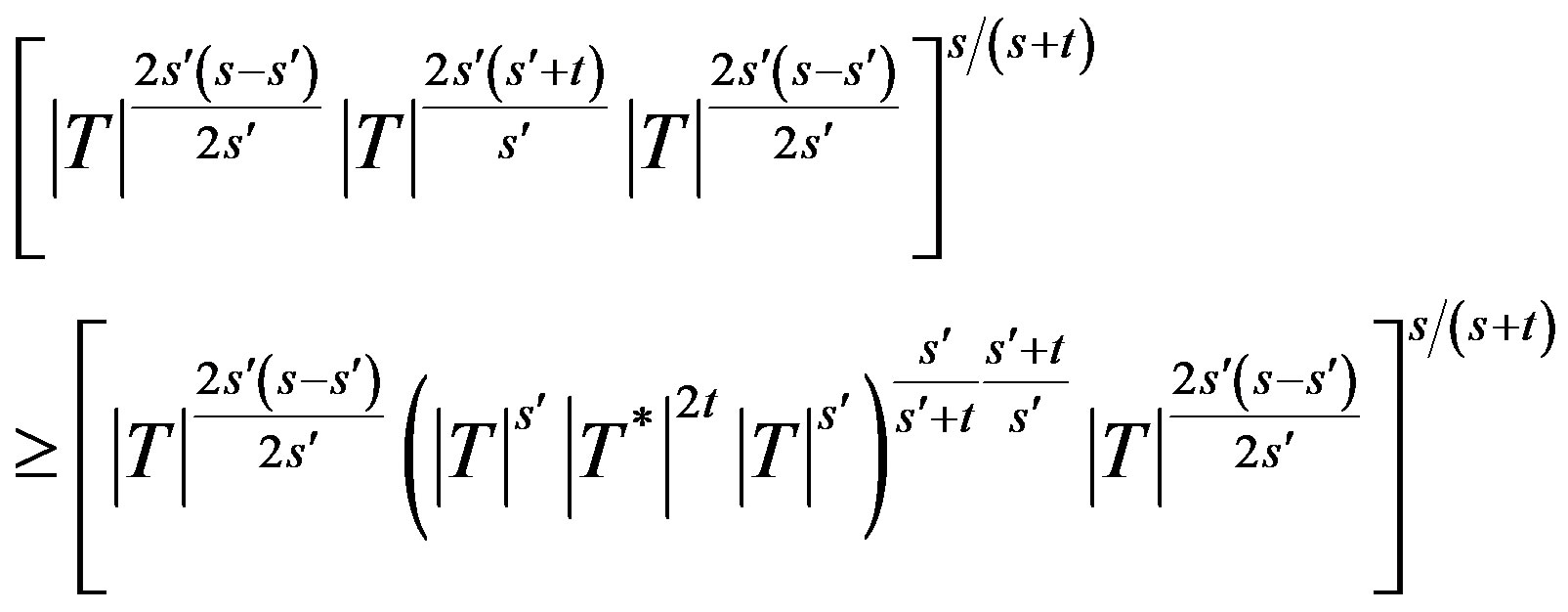
i.e. 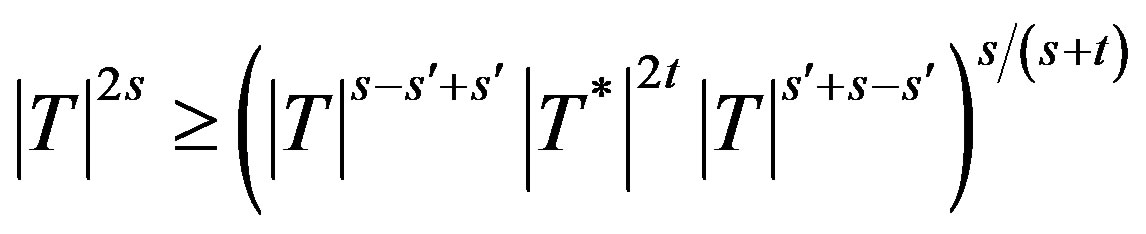
i.e. 
i.e. .
.
Hence
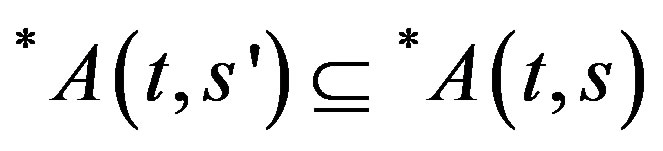 .
.
REFERENCES
- M. Fujii, D. Jung, S. H. Lee, M. Y. Lee and R. Nakamoto, “Some Classes of Operators Related to Paranormal and Log-Hyponormal Operators,” Japanese Journal of Mathematics, Vol. 51, No. 3, 2000, pp. 395-402.
- T. Furuta, “A ≥ B ≥ 0 Assures
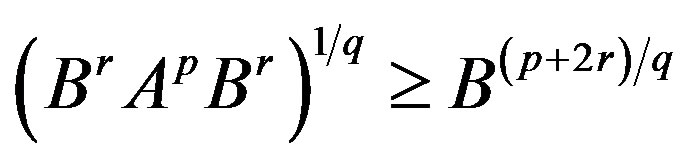 for
for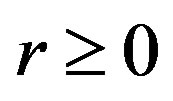 ,
, 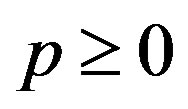 ,
, 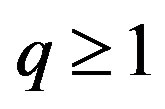 with
with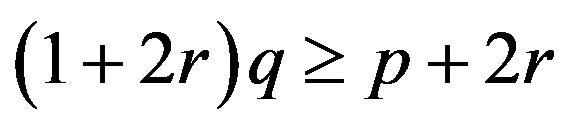 ,” Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 101, No. 1, 1987, pp. 85-88. doi:10.2307/2046555
,” Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society, Vol. 101, No. 1, 1987, pp. 85-88. doi:10.2307/2046555 - T. Ando, “Operators with a Norm Condition,” Acta Scientiarum Mathematicarum, Vol. 33, 1972, pp. 169-178.
- T. Furuta, “Elementary Proof of an Order Preserving Inequality,” Proceedings of the Japan Academy, Vol. 65, No. 5, 1989, p. 126. doi:10.3792/pjaa.65.126
- M. Fujii, “Furuta’s Inequality and Its Mean Theoretic Approach,” Journal of Operator Theory, Vol. 23, No. 1, 1990, pp. 67-72.
- E. Kamei, “A Satellite to Furuta’s Inequality,” Japanese Journal of Mathematics, Vol. 33, 1988, pp. 883-886.

