Journal of Environmental Protection
Vol.05 No.13(2014), Article ID:50759,8 pages
10.4236/jep.2014.513122
Physico-Chemical Analysis of Eutrophication’s Parameters in a Coastal River (Côte D’ivoire)
Koffi Sébastien Ouffoué1,2*, Moreto Salla3, Denis Yapo Kicho1, Dodiomon Soro3, Kouhété Philippe Da3, Zanahi Félix Tonzibo1
1Laboratoire de Chimie Organique, U.F.R. SSMT, Université Félix Houphouët-Boigny, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire
2Centre Ivoirien Anti-Pollution (C.I.A.POL.), Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire
3Laboratoire de Botanique, U.F.R. Biosciences, Université Félix Houphouët-Boigny, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire
Email: *offoe@yahoo.fr
Copyright © 2014 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/



Received 23 August 2014; revised 18 September 2014; accepted 12 October 2014
ABSTRACT
A study on some physico-chemical and biological variables of water quality was conducted on a coastal river in Ivory Coast. It’s the first assessment on water quality state. Those coastal rivers actually play an important role in the physical, biological and hydrological exchange between lagoons and the sea. Unfortunately, they are not taken into account by the national monitoring for water quality (RNO-CI). The samples were collected along Boubo River body through three stations, in the south of Côte d’Ivoire, during two years. Results show sharp fluctuations of the concentration 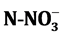 nitrate,
nitrate, 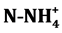 ammonium and chlorophyll a with more than 20% variation. However, small fluctuations were noted for temperature, pH and conductivity with 4% - 20%. Measures are generally inferior to the threshold for hazardous water class. But respective average concentrations of
ammonium and chlorophyll a with more than 20% variation. However, small fluctuations were noted for temperature, pH and conductivity with 4% - 20%. Measures are generally inferior to the threshold for hazardous water class. But respective average concentrations of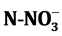 ,
, 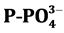 , COD and BOD5 are above natural water threshold, represent- ing 67% of the analyzed samples of
, COD and BOD5 are above natural water threshold, represent- ing 67% of the analyzed samples of 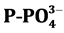 and 100% of the other. These results show that the river is not exempt of pollution: 0.2 mg/l of
and 100% of the other. These results show that the river is not exempt of pollution: 0.2 mg/l of 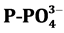 and 0.9 mg/l of
and 0.9 mg/l of  are the limits of appropriate siege for the proliferation of invasive aquatic plants (IAP).
are the limits of appropriate siege for the proliferation of invasive aquatic plants (IAP).
Keywords:
water quality, nutriments, chlorophyll a, pollution, eutrophication, river, Côte d’Ivoire

1. Introduction
Demographic growth in developing countries has brought a fast expansion in urbanization and industrialisation. Côte d’Ivoire, a West African state, possesses a vast hydrographic network, mainly in the southern part. This network is threatened by serious pollutions mainly due to uncontrolled population growth. In 1994, a national monitoring network for water quality was put in place in order to know physico-chemical and ecological quality of waters. The monitoring program has covered 55 fixed stations of water body withdrawal, of sediments and living organisms. 28 stations were counted on inland waterways, 18 stations in Ebrié lagoon of Abidjan Central Basin and 9 stations along the coast from east to west. Actually, this network was focused on three major rivers (Comoé, Bandama, Sassandra) and didn’t take into account many rivers and water sources which play a key role in economic, social and cultural of population’s life. This situation explains the lack of scientific series and data. In the coastal area they are many rivers which represent nutritive and biodiversity resources. Unfortunately they are under pollution impact. These zones are known for decades for intense agricultural activities (industrial and local plantations of coffee, cocoa, pineapple, palm oil…) and mining. The farm covers nearly 44% of the area of this region [1] . The production of these cultures favors the use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers. The residues of chemical products are carried and focused in inland water. It modifies some local waterways quality and leads to deep changes in the composition and structure of animal and vegetable organisms of this hydrosystem [2] .
2. Material and methods
2.1. Sampling area
Boubo River is among the main coastal rivers of the country (figure 1). It stretches from Center to the South coast over 130 Km with a catchment area of 5100 km². Overall, twelve (12) campaigns grouped into four (04) great seasons were realized from May 2009 to April 2010. The campaigns of collect of samples covered the periods of Long Dry Season (LDS), Minor Dry Season (MDS), the Long Wet Season (LWS) and the Minor Wet Season (MWS). Three (03) sampling stations were installed along the stream and heading from upstream to downstream:
Figure 1. Hydrolycal map of Boubo’s river.
· Upstream: Station St1 (station of Divo, 5˚75'N and 5˚31'W) on the deck located on Divo-Lakota route, at 5 km from the downtown.
· In the center: Station St2 (PALMCI-Boubo, 5˚61'N and 5˚25'W) on the bridge located at 400 m from palm oil production unit (PALMCI-Divo).
· Downstream: Station St3 (Station of Adahidougou, 5˚18'N and 5˚11'W), on the bridge, 25 km to Grand-La- hou town.
2.2. Physico-Chemical Parameters
The parameters studied are temperature, pH, conductivity, transparency, nitrates (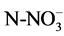 ), ammonium (
), ammonium (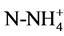 ), orthophosphates (
), orthophosphates ( ), Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD5 or DBO5), Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and chlorophyll a.
), Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD5 or DBO5), Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and chlorophyll a.
2.2.1. Physical Parameters Measurement
The pH, conductivity (µS/cm) and water temperature (˚C) are measured in situ with calibrated multiparameters probe. The transparency of water (m) is measured using Secchi disc.
2.2.2. Chemical Parameters Analysis
The nutrients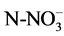 ,
, 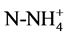 and
and 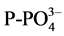 are analyzed at the laboratory. The concentrations determined by [3] calorimetric method for nitrates and method for orthophosphates [4] . The nitrate concentrations are determined by difference, once they are reduced into nitrites on a Cd-Cu column that enables nitrites analyzed. The concentration of nitrate is determined by difference of the initial nitrites concentration in the sample. Orthophosphate is determined as follow: with antimonies, ammonium molybdate form a complex with orthophosphates; that complex is reducible by ascorbic acid. The blue coloration reduced form, absorbs wavelength at 885 nm, helping to know ion phosphate concentration in the dosed sample. After the value solution, vessel sample is placed in the spectrophotometer to see ion content.
are analyzed at the laboratory. The concentrations determined by [3] calorimetric method for nitrates and method for orthophosphates [4] . The nitrate concentrations are determined by difference, once they are reduced into nitrites on a Cd-Cu column that enables nitrites analyzed. The concentration of nitrate is determined by difference of the initial nitrites concentration in the sample. Orthophosphate is determined as follow: with antimonies, ammonium molybdate form a complex with orthophosphates; that complex is reducible by ascorbic acid. The blue coloration reduced form, absorbs wavelength at 885 nm, helping to know ion phosphate concentration in the dosed sample. After the value solution, vessel sample is placed in the spectrophotometer to see ion content.
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD or DCO): a V1 volume of water is treated in a test tube containing a specific COD reagent. They are all placed in a digester under 120˚C during 2 hours. We let the mixture cool down and then we measure with the help of the spectrophotometer that gives a concentration (mg/l) corresponding to the DCO value.
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD5 or DCO5): a V2 volume of water sample is poured into an oxi-top glass flask (1 liter colored flask). The flask is clogged by a closure with a digital display for DBO5 reading. The flask is then placed into an incubator for 5 days. At the 5th day, we proceed to the reading of DBO5 value on the screen (mg/l).
2.3. Chlorophyll A Analysis
Chlorophyll a dosage is done using NFT90-117 method. A volume of 250 ml is filtered through GF/C ruled filter paper. The filtrate is placed into a tube containing 90 degree ethanol. Then we move to the centrifugation at 3000 r.p.m for 15 minutes. The organics phase is used to measure chlorophyll with calibrated spectrophoto-me- ter [3] .
3. Results
Quantitative analysis of variables (Table 1(a), Table 1(b) and figure 2)
· Temperature (Temp): extreme values are measured at St2: Boubo River, center, during Major Dry Season (MDS) between 24˚C and 25.8˚C with an average of 25.82˚C.
· PH: values of water are between 5.8 and 7.3 with an average of 6.53. Minimal value is obtained at Station St2 during Long Dry Season (MDS).
· Conductivity (Cond): values are between 88 and 160.7 µS/cm with an average of 117.91 µS/cm. The low values are obtained at Station St2 during the Minor Wet Season (MWS). The maximal conductivity is measured during the Minor Dry Season (MDS).
· Transparency (Transp): water transparency is measured between 0.2 and 0.9 with an average of 0.62 m. the lowest measure was determined at Adahidougou Station (St3), downstream during the Long Wet Season
Table 1. (a) Physical-chemical and Chl a data of the Boubo River; (b) Physical-chemical and Chl a data of the Boubo River.
(LWS).
· Nitrate (
· Ammonium (c): ammonium concentration varies between 0.01 and 0.04 mg/l. The average is of 0.02 mg/l. The lowest values are measured downstream (St1) and in the Center (St2) during Long Dry Season (LDS). The highest content in stations is measured St1 and St3 during Minor Wet Season (MWS).
· Orthophosphates (
Figure 2. Variation of physico-chemical parameters according to the seasons on the three stations of the Boubo River.
· Biological Oxygen Demand BOD5 and COD extreme values vary respectively between 14 and 44 mg/l and 44 and 116 mg/l with averages of 29.17 mg/l and 77.33 mg/l. Lowest contents in BOD5 and COD are determined at station St3, upstream, during Long Wet Season (LWS) and highest value at Station St3 during Minor Wet Season (MWS).
· Chlorophyll a: the concentrations for Boubo River water vary between 7.6 and 27.1 mg/l. The averages of chlorophyll a value for these waters are 14.62 mg/l. The lowest chlorophyll is determined at station St1, during Minor Dry Season (MDS) and the highest at station St3, during Minor Wet Season (MWS).
We generally notice a fluctuation of the different variable measurement from one station to another and from season to another (Table 2). The importance of this fluctuation is evaluated with the ratio of the standard deviation and the average. It appears, along the rivers, strong fluctuations of concentration of nutriments


4. Discussion
Seasonal and spatial variation
The study shows that extreme temperatures in PALMCI-BOUBO station (St2) located in the Center (Figure 3). The average temperature calculated 25.71˚C on most of the stations is between 25˚C - 29˚C like most of tropical rivers in Côte d’Ivoire [2] [5] and estuarial water rivers in France [6] . Differences in temperature of the water in the tropical zone are relatively low in comparison to those of temperate countries. A very large rise in temperature is caused by the intrusion of hot water of industrial liquid effluents. The St2 station, which is located in the area of the production palm oil, is not affected by the warm waters of these effluents. This situation can be explained by the fact that the temperature drop as far as we move away from the point of discharge. Water found the average surrounding equilibrium temperature. Temperature is an important factor in the development of phytoplankton. Authors have noticed that an increase of the water temperature would facilitate chemical reactions with the mineralization of organic matter into nutrients. The increase in temperature reduces the solubility of the gases dissolved in the water. Authors have shown that an increase of 7˚C causes a fall of 13% O2. An elevated temperature promotes the degradation of matter organic in oxidation. Extreme measures of the BOD5 and COD vary respectively between 17 and 44 mg/l 43 and 116 mg/l. These results show the presence of organic matter naturally and quickly biodegradable in equilibrium with little degradable organic matter. The organic matter with little degradable matter is an index of chemical contamination. The mineralization of organic matter into nutrients (


The river Boubo presents in average, low acid PH 6.5. The extreme values are obtained during the Long Dry Season (5.8) and the Minor Dry Season (7.3). These values are comparable to the pH generally measured from coastal rivers between 6.4 and 7.5. The tendency to the acidity of the waters of the Boubo’s river would be justified by the localization in coastal zone. In according to Iltis & Lévêque’s studies in 1982, coastal rivers have a slightly acidic and alkaline pH [7] . Also it had been showed that the weakly acidic or slightly alkaline waters are favorable to the development of many Desmidiales [5] [8] . When the values of pH are between 6.4 - 8, the nutrients are in their ionic and dissolved forms. Thus ammoniac nitrogen is in ionic form dissolves (
Table 2. Comparison table of the measured average values and levels of quality of waters according to Deborah.
Figure 3. Box plot of the variation of parameters physico-chemicals on the three stations of the Boubo River.
non-toxic, favorable to the development of algae. There is also the phosphorus as
In temperate zone, Andresen Leitão in 1984 proposed a scale of 444 µS/cm. This value corresponds to the limit of mineralization [12] . In comparison, the results of conductivity obtained, show that the river’s Boubo is weakly mineralized. The respective averages of nutrients are 0.94 mg/l for the





In natural waters, nitrogen and phosphorus are naturally present. The respective levels are lower than 0.1 mg/l for the both 


The water quality class is defined by many de references: p.ex WHO, European Directives, EPA or the using and constraints of the national water regulations (Table 2). In absence of official references for watersheds in Côte d’Ivoire, the variables of this studied are used. The mean and extreme values had been compared with the data in the literature on the quality waters reported by Deborah Chapman (1992) [16] . The Table 2 summaries the value of the limit in natural water and the threshold of the exposure to pollution. Most of measures are significantly lower than the classified waters polluted. However, as the result, it appears that the average of



5. Conclusion
The study is based on the parameters: temperature, pH, conductivity, transparency, nitrates


Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank AIEA projects RAF 7/008 and RAF 7/009: Supporting an Integrated Approach for Marine Pollution Monitoring Using Nuclear Analytical Techniques for providing financial and technical support for this research.
References
- Anonyme (2001) Recensement National de l’Agriculture (RNA) 2001. Région du Sud-Comoé. Ministère d’État, Ministère de l’Agriculture, Direction des statistiques, de la documentation et de l’informatique de Côte d’Ivoire, 29 p.
- Niamien-Ebrottié, J.E. (2010) Composition et distribution spatio-temporelle des peuplements d’algues de quatre rivières du Sud-Est de la Côte d’Ivoire (Soumié, Éholié, Éhania et Noé). Thèse de Doctorat Unique, Université d’Abobo-Adjamé, Abidjan, 146 p.
- Aminot, A. and Chaussepied, M. (1983) Manuel des analyses chimiques en milieu marin. Éditions Jouve, CNEXO, Paris, 395 p.
- Murphy, J. and Riley, J.P. (1962) A Modified Single Solution Method for the Determination of Phosphorus in Natural Waters. Analytica Chimica Acta, 27, 31-36.
- Da, K.P. (2007) Étude taxinomique du phytoplancton dulçaquicole des masses d’eau lentiques et lotiques de quelques sites au Sud de la Côte d’Ivoire, entre les fleuves Bandama et Bia: Apports de la microscopie électronique à balayage. Thèse d’État ès Sciences Naturelles, Université de Cocody, Abidjan, 402 p.
- De Oliveira, C.J. (2000) Le phytoplancton estuarien de deux fleuves de Guyane française (l’Iracoubo et le Sinnamary): Caractérisation du milieu, composition et diversité spécifique. Thèse de Doctorat de l’Université Paris 6, Paris, 258 p.
- Iltis, A. and Lévêque, C. (1982) Caractéristiques physico-chimiques des rivières de Côte d’Ivoire. Revue d’Hydrobiologie tropicale, 15, 115-130.
- Bremond, R. and Vuichard, R. (1973) Paramètres de la qualité des eaux. Documentation Française, Paris, 178 p.
- Diomandé, D. (2001) Macrofaune benthique et stratégies alimentaires de Synodontis bastiani et S. schall en milieu fluvio-lacustre (Bassins Bia et Agnébi, Côte d’Ivoire). Thèse de Doctorat, Université d’Abobo-Adjamé, Abidjan, 260 p.
- Dietoa, Y.M. (2002) Entomofaune et stratégies alimentaires des poissons du genre Brycinus (Characidae) en milieux fluviatiles et lacustre (Bassins Bia et Agnéby, Côte d’Ivoire). Thèse de Doctorat, Université d’Abobo-Adjamé, Abidjan, 261 p.
- Bamba, S.B., Ouffoue, S., Ble, M.C., Metongo, S.B. and Bakayoko, S. (2008) Etat de l’environnement lagunaire de l’ile vitre (grand-bassam, cote d’ivoire): Aspects physiques, chimiques et biologiques. Revue Ivoirienne des Sciences et Technologie, 12, 77-92.
- Andresen Leitao, A. (1984) Aspects du phytoplancton d’un bassin de rétention: Relations avec quelques paramètres physico-chimiques du milieu. Thèse de Doctorat 3è cycle. Toxicologie, Université Paris V, Paris, 165 p.
- Mainstone, C.P. and Parr, W. (2002) Phosphorus in Rivers—Ecology and Management. Science of the Total Environment, 282-283, 25-47. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00937-8
- Pagès, J., Lemasson, L. and Dufour, P. (1979) Éléments nutritifs et production primaire dans les lagunes de Côte d’Ivoire: Cycle annuel. Archives Scientifiques, Centre de Recherches Océanographiques, Abidjan, 5, 1-60.
- Salla, M., Da Kouhete, P., Koffi, S.O. and Traore, D. (2011) Cyanobactéries des rivières Boubo et Mé dans le Sud côtier de la Côte d’Ivoire. International Journal of Biological and Chemical Sciences, 5, 1365-1373.
- Chapman, D. (1992) Water Quality Assessment: A Guide to the Use of Biota, Sediment and Water in Environmental Monitoring. WHO, Geneva, 585 p.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.






