Health
Vol.5 No.3A(2013), Article ID:29578,7 pages DOI:10.4236/health.2013.53A075
Study of family environmental factor on only-children’s personality*
![]()
1Mental Health Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China; #Corresponding Author: mhq99666@sina.com,
2Department of Clinical Medicine, Chongqing Medical and Pharmaceutical College, Chongqing, China
3Chongqing Ninth People Hospital, Chongqing, China
4Mental Health Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China;#Corresponding Author: xuntao26@hotmail.com
5Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
Received 13 January 2013; revised 17 February 2013; accepted 25 February 2013
Keywords: Only-Children; Personality; Family Environment
ABSTRACT
Objective: To analyze the impact of family environment on only-children’s personality. Methods: Using cross-sectional design to recruit onlychildren aged 6 - 16 years old; using EPQ to evaluate the children’s personality. The general questionnaire, PSDQ (Parenting Styles and Dimensions Questionnaire), FAD-GFS (The General Functioning Scale of MacMaster family activity device), SLE (Stressful Life Events), FSQ (Family Stresses Questionnaire), FLQ (Family Life Questionnaire), EFQ (Everyday Feelings Questionnaire) were used to collect information about family environment from parents. Results: In only-child family, standardized regression equations of family environment influence on children personality include: 1) EPQ-p = 0.087 × SLE + 0.207 × father autocratic parenting + 0.131 × education of father + 0.110 × family type − 0.110 × role of discipline − 0.080 × parental attitude + 0.087 × family adaptability; 2) EPQ-e = 0.105 × EFQ − 0.088 × SLE − 0.101 × family income; 3) EPQ-n = 0.143 × SLE − 0.090 × family cohesion + 0.089 × family income + 0.117 × the orderly’s attitude − 0.138 × the child’s role experience of FLQ − 0.101 × parents shaping the behavior of children of FLQ and 4) EPQ − l = −0.136× SLE − 0.093 × relationship between parents − 0.155 × attitude of the old. Conclusion: It is important for children to develop personality normally if the father doesn’t choose autocratic parent style. Children tend to be optimistic if the parent can feel happy. The stressful life events are a double-blade sword depending on the parent’s handling. The difference of the parenting style can influence the lie-personality of children
1. INTRODUCTION
Children aged 6 - 16 years old are at a critical period of physical and mental development, an important period of formation of perfect personality as well as a high risk period of personality disorder occurring and further development of personality disorder, schizophrenia, depressive disorder, etc. in adulthood [1]. The key to promote the healthy and balanced development of children’s personality is to grasp the reasons for the formation of personality. Some domestic surveys on personality are in allusion to a related factor and some researches only focus on the partial environmental factors such as parental education. For example, Wang J.Y. [2] argues that father’s severe punishment, excessive interference and protection are the important factors to affect the performance of emotional stability. Currently, the research to comprehensively discuss the impact of family environment as an object on personality is still in blank. Most foreign researches [3] tend to explore the personality assessment tools, or consider the personality as the research objective (such as the relation between personality and behavior or diseases [4]), or focus on morbid personality or comorbidity of personality and other diseases, but there are few researches on personality as a single research object. Therefore, it is important to focus on the personality of children aged 6 - 16 years old and comprehensively discuss the ways of family environmental impact on personality.
The policy of birth control was carried out in China at the end of 1970s. So far, the accumulated number of only-children is nearly 0.1 billion [5]. The only-children born after 1990 s is experiencing the period of shaping of personality, psychology and social behaviors. Due to the tremendous influence from foreign cultures, co-existence of various outlooks of value as well as changes of family concepts, the impact of environment on shaping of Children’s personality has great particularity. Therefore, it is necessary to pay special attention to the personality characteristics of this group of children and related factors.
Currently, most psychological researches are on those only-children who are adults, college students at school and engage in specific occupations, but pay less attention to personality. Besides, among the researches on onlychildren at school age, few discuss the only-children’s intelligence, personal relationship and personality, etc, but most of them discuss the only-children’s psychological development born in 1980s and 1970s at the end of 1990s in the last century. The subjects are only-children themselves and the information is not collected from their parents, but the interference from the perspective of parents is most intuitive, therefore, it is necessary to acquaint the impact of family environment from the perspective of parents.
The development of personality is from the family, which play the earliest and important role as the first school. The family is the basic unit of social life and the starting point of individual socialization. The personality is influenced by family environment through the whole life, especially in children stage, therefore, this study focuses on the family environmental.
Family environment include material entity and psychological environment. Material entity contains all kinds of family characteristic index, such as family income, parents’ educational level, occupation, family type and so on. Family psychological environment include educational style of parents, the consistency and communication of family members, family activity plan, independent members behavior and attitude and so on, therefore, in this study, we choose the general questionnaire, PSDQ (Parenting Styles and Dimensions Questionnaire), FAD-GFS (The General Functioning Scale of MacMaster family activity device), SLE (Stressful Life Events), FSQ (Family Stresses Questionnaire), FLQ (Family Life Questionnaire), EFQ (Everyday Feelings Questionnaire) as tools to explore family information.
So, this research, taking the parents as the information source, focuses on the only-children’s personality and acquaints the impact of related family factors on personality.
2. OBJECTIVE AND METHODS
2.1. Objective
Only-children aged 6 - 16 years old in Chongqing were selected based on the demographic data from school enrollment system of Chongqing education committee. EPQ (including p, e, n, l) was used to assess the children’s personality: The General Questionnaire, PSDQ (Parenting Styles and Dimensions Questionnaire), FAD-GFS (The General Functioning Scale of MacMaster family activity device), SLE (Stressful Life Events), FSQ (Family Stresses Questionnaire), FLQ (Family Life Questionnaire), EFQ (Everyday Feelings Questionnaire) were used to acquire the various information of family environment from the parents.
Inclusion criteria: student aged 6 - 16 who study in general school and their parents with normal reading and writing ability. Exclusion criteria: children with mental retardation or studying in special school and their parents without normal reading and writing ability or who is illiterate person or refused to take part in this study.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Assessment tool of Personality
Children’s version of Eysenck Personality Inventory (Eysenck Personality questionnaire, EPQ [6]) revised by Gong Yaoxian was used to assess the children’s personality characteristics. Four sub scales were used to assess 4 characteristics: N subscale was used to assess the stability of emotion; E subscale was used to assess the tendency of extraversion and introversion; P subscale was used to assess the subjects’ psychiatric characteristics and L subscale was used as the validity scale.
2.2.2. Related Assessment Tool of Family Environmnet
Parenting Styles and Dimensions Questionnaire (PSDQ) [7], developed by Robinson and Mandleco in 1995, are internationally known as a tool to assess the parenting style with the parents as the subject and is verified to have good reliability and validity. Parenting styles in this scale are divided into three types: authoritative parenting style, authoritarian parenting style and permissive parenting style. This research uses father’s (mother’s) score in authority, authoritarian and permission to express the tendency of attitude to the parenting styles respectively.
The General Functioning Scale of the MacMaster Family Activity Device (FAD-GFS [8]) was developed by Fristad in 1989. It is mainly used to know general family functions, including activity plans, crisis support, mutual trust, etc. The higher the score is, the worse the family functions will be.
Stressful Life Events (SLE) [9] was developed by Goodyer in 1990. It is mainly used to know general family functions, including activity plans, crisis support, mutual trust, etc. The higher the score is, the worse the family functions will be (Repeating the above paragraph).
Family Stresses Questionnaire provided by Institute of Mental Health of Huaxi Hospital of Sichuan University was used to mainly acquaint the family members’ job, life and economic income, psychological and physiological health, and sensed pressure from the communication with external world. The higher the score is, the larger the pressure will be.
Family Life Questionnaire provided by Institute of Mental Health of Huaxi Hospital of Sichuan University was used to mainly acquaint the behavioral mode among the family members and the rules of encouragement and punishment. This scale includes three factors: children’s role experience in the family, impact of family on individual’s behavior shaping, and children’s dependence and self-determination. The higher score reveals that the family atmosphere that the children percept is more harmonious, children’s emotion is easier to be paid attention to, the children as the independent individuals participate in the family decision making and the family has a clear definition of the children’s behaviors, etc.
Everyday Feelings Questionnaire [10] provided by Institute of Mental Health of Huaxi Hospital of Sichuan University, with a duplicate copy, was used to assess the subject and the spouse. The higher the score is, the better the subject’s feeling will be.
General Condition Questionnaire includes the children’s gender, age, the subject children’s parents’ education level and occupation, parents’ monthly economic situation, parents’ habits such as smoking, drinking and playing mahjong, mother’s age of procreation, types of family, parents’ relationship, family attitude to the education, etc.
2.2.3. Statistical Method
SPSS15.0 statistical analysis software was used to analyze the data
3. RESULTS
3.1. Sample Composition
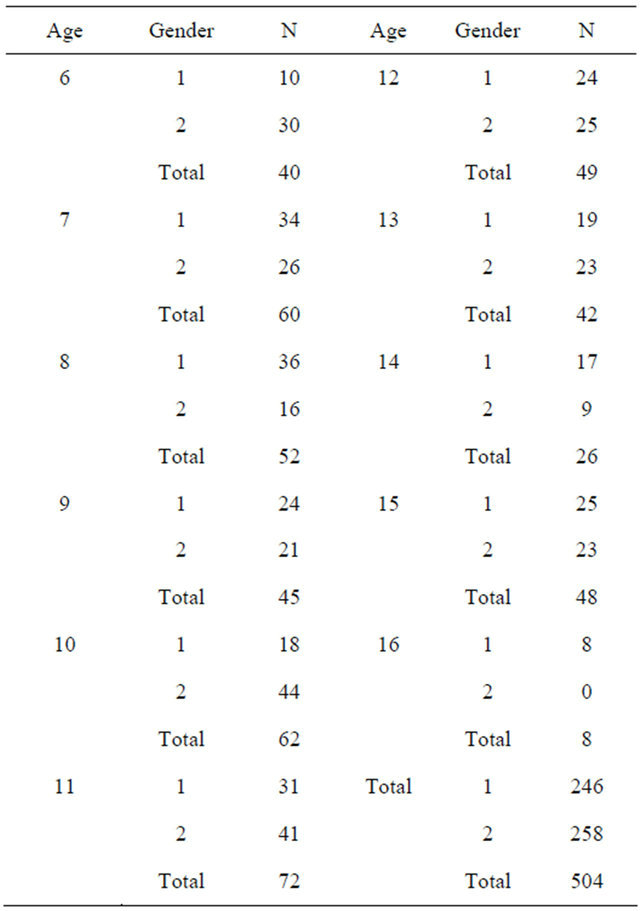
The age and gender of the only-children aged 6 - 16 years old in this research is listed in Table 1.
3.2. Statistic Description of Basic Characteristics of Group Samples
The education range of children’s parents in the sample is from illiteracy to master, and their occupations include manager, worker, farmer, etc. Family types and family income, the parents and the elderly’s attitude to the children’s education and the person in charge of the children’s education are different. Specific distribution sees Table 2.
Table 1. Distribution of age and gender of sample (1: male; 2: female).
3.3. Statistics Description of Children’s Personality
The personality characteristics of EPQ of the group sample include 4 dimensions: epq_p, epq_n, epq_e, epq_l (stand for psychotism, neuroticism, extraversion and lie respectively) and the statistics description sees Table 3.
3.4. Multi-Factor Analysis of Family Environmental Impact on Only-Children’s Personality
Multivariate stepwise regression analysis method is used to analyze the dependent variable-four dimensions of children’s personality and the independent variablegeneral family information and children’s stressful event in General Condition Questionnaire and family environment such as family function, family life, parents’ pressure and daily feeling, family cohesion and adaptability, parenting style.
In order to bring into more factors, the average value of variables selection and screening level into the model is 0.15. The repression analysis of four dimensions of personality and 6 dimensions of psychological health see Tables 4-7.
Table 2. Basic family characteristics and ranked variable assignment of subject.
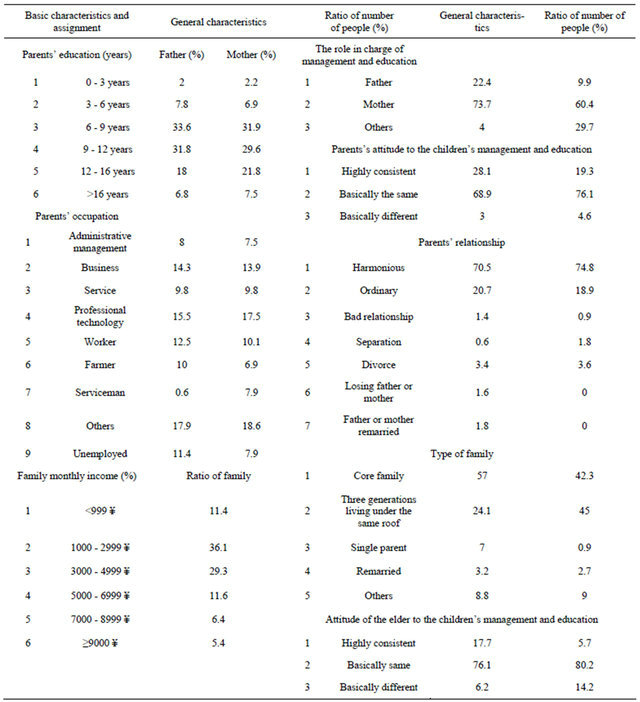
Table 3. Statistical description of EPQ in children.
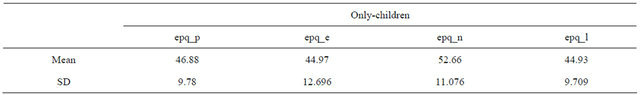
Table 4. Regression analysis on P-factor personality and family environment.
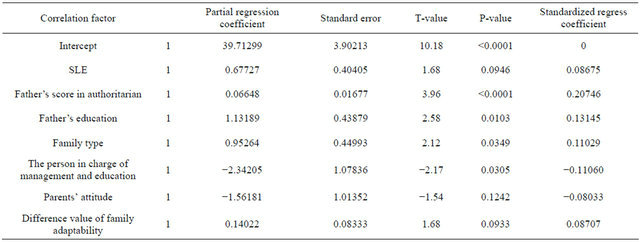
Table 5. Regression analysis on E-factor personality and family environment.
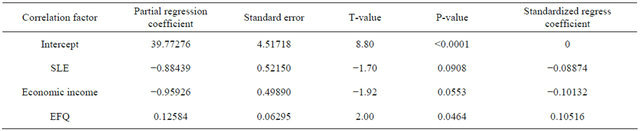
Table 6. Regression analysis on N-factor personality and family environment.
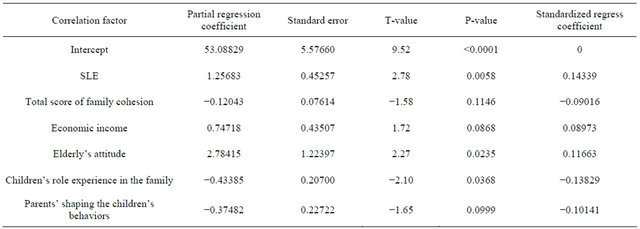
Table 7. Regression analysis on L-factor personality and family environment.
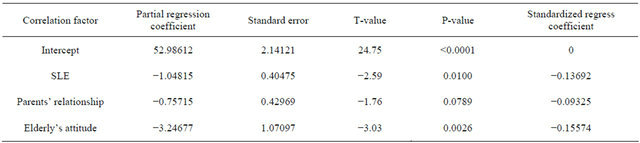
4. DISCUSSION
This research, with the only-children born after 1990 s as the research subject, firstly used the relatively new quantitative assessment tool and carried out multiple regression analysis with various factors related to family fully considered from the perspective of parents.
As for the impact of family environment on the children’s personality, studies have shown that formation of children’s personality is significantly affected by family environmental factors such as family structure, parents’ education level and family income [11], and family atmosphere and parenting style [12], and parents’ ability of perception, negative emotion, guardian’s education level have impact on the children’s development [13]. Therefore, the above contents were brought into this research when discussing the impact of related family environmental factors on children’s personality.
This research indicated that the father’s role is especially important to the normal development of children’s personality.
Father is the core role in the family. In the only-children family, parents’ full energy is concentrated on the only offspring. If the child is treated with corporal punishment and mandatory means to require the children to obey, the educatee as an only-child without communication with other brothers or sisters will forms strange, eccentric and cold characteristics more easily. The higher the father’s education level is, the more obvious the opinions to the matters and the more accurate the restrictions to children’s behaviors will be. If the growing children with strong sense of question to the matters receive too much concepts and frames from the parents and can not communicate with other fellows, their ability of self thinking will be weaken and they can not harmonize and combine the external matters with internal experience, thus, habitual behaviors such as intense reaction to problems, no good communication with others and indifference will appear, which are the reasons why the father’s education level significantly affects the children’s psychoticism in this research.
This result suggests that father should avoid oppressive and autocratic education way and use few fixed outlooks of value and concepts to interfere the children’s understanding of the world, which is beneficial for the healthy development of children’s personality.
As for children’s characteristics of introversion and extroversion, the result in this research suggests that: parent’s status of emotion and attitude to the life directly affect children’s personality of introversion and extroversion. If the parents hold an optimistic attitude to the future and enjoy the life commendably, the children will form the personality of extroversion more easily, while the stressful event has positive impact on children’s personality of introversion and extroversion, probably because children’s ability to bear frustration is inspired by the stressful event and they convert the negative events into positive perceptual evaluation, thus children’s personality of introversion and extroversion is easily cultivated.
This also suggests that if the parents hope that the children are optimistic and easy to communicate with the outside world, the parents themselves should firstly experience the joy of living and enjoy the life, thus the children can be influenced by close association; while it is not a necessarily bad thing for a child to experience negative life, and the child will be easier to have the personality of extroversion if correcting the cognition positively and rightly.
Parents all expect that the children’s personality tends to be stable, while the result of this research suggests that the stressful event is the main factor to shape children’s stable personality.
Similar to the previous results of research, if the children experience stressful event and their coping style is still not mature, they are easy to be confound, and emotional, behavioral and physiological reactions will be over expressed, and these behavioral habits will remain to influence the stability of personality. Therefore, stressful event can not be belittled, but we should also be aware of that stressful event is a good opportunity to the children’s growth, thus the parents may evaluate and guide it positively and family support system should handle the impact of stressful event on the children’s personality as much as possible and even make it play the positive role.
In order to explore the personality, this research suggests that the consistency of parenting styles between the elderly and parents is the main influencing factors. The elderly and parents belong to different roles of householder. When their opinions vary, the children are easy to keep their own behavior mode which may be possibly emended based on one party’s opinions so that their inherent character will be widely known, without the necessary of palliation. Palliation embodies the degree of socialization, without difference of goodness and badness, so it is not necessary for the parents to cultivate, but be aware of that children’s behavior of palliation is the reflection of self growth or the compensation of self closeness.
REFERENCES
- Fanous, A.H. and Kendler, K.S. (2004) The genetic relationship of personality to major depression and schizophrenia. Neurotoxicity Research, 6, 43-50. doi:10.1007/BF03033295
- Wang, J.Y. (2006) Comparison study of Personality characteristic and parental rearing style between male Gongdu students and common male students. China Journal of Health Psychology, 14,147-149.
- Meijer, R.R., Egberink, I.J., Emons. W.H., et al. (2008) Detection and validation of unscalable item score patterns using item response theory: An illustration with Harter’s self-perception profile for children. Journal of Personality Assessment, 90, 227-238. doi:10.1080/00223890701884921
- Sansone, R.A. and Sansone, L.A. (2007) Childhood trauma, borderline personality, and eating disorders: A developmental cascade. Eating Disorders: The Journal of Treatment & Prevention, 15, 333-334. doi:10.1080/10640260701454345
- Chen, X. and Du J. Z. (2006) The relationship between parenting style and implicit aggression. Psychological Science, 29, 798-801.
- Gong Y.X. (1986) Manual of Eysenck personality questionnaire. Hunan Medical University, Changsha, 2-49.
- Robinson, C.C., Mandleco, B., Olsen, S.F. and Hart, C. H. (2001) The parenting styles and dimension questionnaire (PSDQ). In: Touliatos, J. and Perlmutter, B., Eds., Handbook of Family Measurement Techniques (2nd Edition), Sage, Thousand Oaks.
- Byles, J., Byrne, C., Boyle, M.H., et al. (1988) Ontario child health study: reliability and validity of the general functioning scale of the MacMaster family assessment device. Family Process, 30, 116-123.
- Goodyer, I.M. (1990) Life experiences, development and childhood psychopathology. Wiley, Chichester, 10-11.
- Phillips, M.R., et al. (1991) Preliminary evaluation of Chinese version of FACES II and FES: Comparison of normal families and families of schizophrenic patients. Chinese Mental Health Journal, 5, 198-202.
- Wang, Y., Liu, Y.H. and Li, Y.M. (2004) Personality types and influencing factors of juvenile aged 10 to 14 years old in Beijing. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation, 8, 7481-7483.
- Zhu, L.J., Sun, Y., Zhang, H.L., et al. (2011) Relationship between bad childhood home environment and personality for depressed patients. China Journal of Health Psychology, 6, 43-45.
- David, S.B., Margaret B., et al. (2005) Antecedents of emotion knowledge: Preditors of individual differences in young children. Cognition and Emotion, 19, 375.
NOTES
*Grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81101025).

