Open Journal of Social Sciences
Vol.03 No.07(2015), Article ID:57982,4 pages
10.4236/jss.2015.37008
Employee Performance Appraisal in a Logistics Company
Yu-Wei Chang
Department of Air Transportation Management, Aletheia University, Tainan, Chinese Taipei
Email: uwchang@mt.au.edu.tw


Received 7 April 2015; accepted 11 July 2015; published 14 July 2015

ABSTRACT
This paper develops a multi-criteria decision making method (MCDM) method to evaluate the employee performance in a logistics company. Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is used for the weights of criteria and employees. Technique for order preference by similarity to an ideal solution (TOPSIS) is used for ranking the overall performance of the employees. Result shows that the proposed method is a generalized method and is applicable for the performance appraisal problem.
Keywords:
Performance Appraisal, AHP, TOPSIS

1. Introduction
The logistic industry is getting more and more competitive in today’s global environment due to the increasing competition of globalization and the success of the logistics industry depends on the high human productivity. Human resource management is of great importance for a logistic company. Employee performance appraisal is an important aspect of human resource management. It is designed to assess each employee’s contribution to the company. In addition, it is a periodic process that assesses an individual employee’s job performance and productivity with regard to certain established criteria and organizational objectives. Hence, it is important for a logistic company. For example, appropriate appraisals not only give the employees an opportunity to contemplate their performance at work but also provide feedback on employee job performance. Moreover, individual employees are considered as well, such as organizational accomplishments, citizenship behavior, strengths and weaknesses, potential for future improvement, etc. Overall, employee evaluations are used by a company to rate employees and decide how they perform in their positions for the purposes of adjusting their salaries.
Islam and Rasad (2006) [1] present a paper using Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) to evaluate employees’ performances based on quantity of the work, organization, commitment, teamwork, communication and external factors. Each of these criteria has been divided into 3 subcriteria. 294 employees are evaluated on the subcriteria. Overall ranking of the employees has been obtained using the absolute measurement procedure of AHP. Güngö et al. (2009) [2] proposed a personnel selection system based on Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (FAHP). The FAHP is applied to evaluate the best adequate personnel dealing with the rating of both qualitative and quantitative criteria. The result is compared with results produced by Yager’s weighted goals method. Moreover, a practical computer-based decision support system is also introduced to provide more information. Li and Li (2011) [3] investigated the evaluation problems for Chinese college teacher performance appraisal system. By utilizing some operational laws of uncertain variables, they extended the TOPSIS method to evaluation problems for Chinese college teacher performance appraisal system in uncertain setting. Xion et al. (2012) [4] proposed a model of engineering R & D staff performance appraisal model. They first consider the work characteristics of the engineering R & D staff, design performance indicators based on morality, ability, diligence, and performance, and then use AHP to determine the weight of every index; then, fuzzy evaluation method is used to design performance appraisal model, to overcome the issue of quantifying the engineering R & D performance. Empirical research demonstrates performance appraisal model that is feasible and practical.
Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is a powerful tool widely used for evaluating and ranking complex decision problems and is a multi-attribute decision making method proposed by Satty in 1971 [5]. AHP is used to deal with complex problems in system engineering. In this research, AHP is used for employee performance appraisal.
2. Methodology
2.1. Analytic Hierarchy Process
The main ideal of AHP is that it derives ratio scales by pairwise comparisons of criteria. It uses a qualitative concept to decompose a complex problem into a structured decision hierarchy and enable a decision maker to structure a MCDM problem visually in the form of an attribute hierarchy. First, one needs to decompose their decision problem into a more easily hierarchy of sub-problems, and each can be analyzed independently. After the hierarchial structure of the problem is finished, the next step is to use pairwise comparison to evaluate its elements and determine the priority. The decision maker uses a nine point scale to assess the priority score. The procedure focuses on two factors at a time and their relation to each other with the scores 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9. The score 1 refers to equal importance, 3 refers to slight more importance, 5 refers to strong more importance, 7 refers to very strong importance and 9 denotes extremely more importance. The scores of 2, 4, 6, and 8 are intermediate scores between the two judgments. If there are n attributes and m alternatives, the matrix judgment will lead to an n x m matrix and there are n ´ m (m − 1)/2 pairwise comparisons to be performed. After the pairwise comparison matrix is calculated, the contribution of each alternative to the overall goal needs to be computed. Satty (1977) [5] ustilized the maximal eigenvalue method to find the value vector of w. The exact values of w1, w2, …, wn are computed and finally normalized as follows:
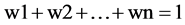 (1)
(1)
The consistency property of the matrix needs to be checked to ensure the consistency of judgments in the
pairwise comparison. Both the consistency index (C.I.) and consistency ratio (C.R.) are defined as follows:
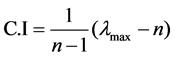 (2)
(2)
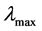 : The maximal eigenvalue;
: The maximal eigenvalue;
n: The number of items being compared in the matrix.
The closer the C.I. value is to 0, the greater the consistency and acceptable. The C.I. value less than 0.1 is general acceptable. After checking the consistency index, the consistency ratio is then examined.
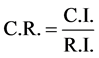 (3)
(3)
R.I. = The average consistency index.
when C.R. ≤ 0.1, the weights obtained by the eigenvalue method are acceptable.
2.2. TOPSIS
Hwang and Yoon presented the TOPSIS (technique for order preference by similarity to an ideal solution) in 1981 [6]. It is a MCDM method. Based on the technique, the most preferred alternative should not only have the shortest distance from the positive idea solution but also has the farthest distance from the negative idea solution. An ideal solution is the solution that collects the ideal levels in all considered attribute. The method is presented in the following steps (Yoon and Hwang, 1995) [7]:
1) Normalize the decision matrix.
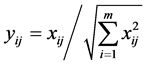 ; i = 1, 2,..., m; j = 1, 2,..., n (4)
; i = 1, 2,..., m; j = 1, 2,..., n (4)
2) Form the weighted normalized decision matrix.
3) Calculate the Positive-Ideal (PIS) and Nergative-Ideal Solution (NIS).
a+ = {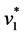 ,
, 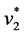 ,…,
,…, 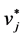 ,…,
,…, 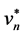 }={ (
}={ (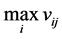 | j Î J1)}, { (
| j Î J1)}, { (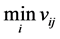 | j Î k1 )| i=1,…,m} (5)
| j Î k1 )| i=1,…,m} (5)
a− = {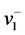 ,
,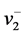 , …,
, …, 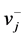 , …,
, …, 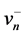 }={ (
}={ (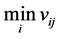 | j Î J1)},{ (
| j Î J1)},{ (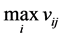 | j Î k2 )| i=1,…,m} (6)
| j Î k2 )| i=1,…,m} (6)
where k1 belongs to benefit attribute, and k2 belongs to cost attribute.
4) Calculate the distance between each alternative and PIS.


5) Calculate the distance between each alternative and NIS.


6) Calculate the similarities to PIS.

where




7) Rank the preference order.
3. Empirical Study
An employee performance evaluation has been conducted in a logistic company. In the performance evaluation problem, 10 decision makers (D1-D10) are formulated as a performance evaluation team to evaluate the performance of the employees in a logistic company. The team decides to evaluate the performance of employees based on four criteria-potential for future (A1), corporate business achievement (A2), organizational commitment (A3) and working ability (A4) are to be evaluated with 6 logistics employees (E1-E6) in the evaluate project.
The 10 decision makers compare the four criteria and 6 employees respectively by the pairwise comparisons. After each decision makers’ pairwise comparisons matrix is finished, both C.I. and C.R. are examined. Results show that both the C.I. and C.R. are acceptable. By the calculation process, we can get the weights of attributes. Table 1 shows the weights of D1-D10 with regards to 4 attributes (A1-A4) and overall weight.
After the consistency test, the weights of criteria are calculated, individual’s judgment is integrated into group judgment and the weights of attribute will be obtained. Table 2 shows the performance matrix of 6 employees.
After computing the weights of each criteria, TOPSIS is used to evaluate and compare all employees.
Firstly, the PIS (a+) and NIS (a−) are calculated:
a+ = (0.036, 0.047, 0.045, 0.100) and a− = (0.024, 0.019, 0.022, 0.036)
And the distance between each alternative and PIS and NIS are calculated:


Finally, the similarities to PIS is calculated.

Based on the results, it shows that the performance evaluation of 6 employees is E4, E5, E1, E2, E3, and E6. In the evaluation case, employee 4 (E4) has the best performance and can be a candidate to be promoted to a higher position.
Table 1. Weights of each decision maker.
Table 2. Performance matrix.
4. Conclusion
It is important to evaluate the performance of employees in a logistics company. The evaluation process is a MADM problem, since it involves a candidate employees based on multiple attributes. This paper proposes an effective and simple method that combines both AHP and TOPSIS for the logistics company for employee performance evaluation purposes. In the evaluate process, the AHP is used for the weight of attributes and performance of each employees. The TOPSIS is used for the performance order. Results show that the model can be used to evaluate the employees effectively. Future studies could apply this method to employee evaluation of different industries.
Cite this paper
Yu-Wei Chang, (2015) Employee Performance Appraisal in a Logistics Company. Open Journal of Social Sciences,03,47-50. doi: 10.4236/jss.2015.37008
References
- 1. Islama, R. and Rasad, S.B.M. (2006) Employee Performance Evaluation by the AHP: A Case Study. Asia Pacific Management Review, 11, 163-176.
- 2. Güng?r, Z., Serhadl?o?lu, G. and Kesen, S.E. (2009) A Fuzzy AHP Approach to Personnel Selection Problem. Applied Soft Computing, 9, 641-646. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2008.09.003�
- 3. Li, X. and Li, D. (2011) TOPSIS Method for Chinese College Teacher Performance Appraisal System with Uncertain Information. Advances in Information Sciences and Service Sciences, 3, 59-64. http://dx.doi.org/10.4156/aiss.vol3.issue6.7
- 4. Xiong, M.P., Zhou, X.H. and Duan, X. (2012) Modeling of Engineering R & D Staff Perform4.ance Appraisal Model Based on Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation. Systems Engineering Procedia, 4, 236-242. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sepro.2011.11.071
- 5. Saaty, T.L. (1980) The Analytic Hierarchy Process. McGraw-Hill, New York.
- 6. Hwang, C.L. and Yoon, K. (1981) Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications, A State-of-the-Art Survey. Springer-Verlag, New York. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-48318-9
- 7. Yoon, K.P. and Hwang, C.L. (1995) Multiple Attribute Decision Making: An Introduction. Sage Publication, London.


