Creative Education
Vol.06 No.20(2015), Article ID:61381,8 pages
10.4236/ce.2015.620219
Analysis on the Effectiveness of Preschool Education Teachers Construction in Western China
―An Empirical Investigation Based on Shaanxi Province
Youlong Zhang1,2, Yaoyang Han1, Xiaoping Yang1
1Faculty of Education, Southwest University, Chongqing, China
2Teachers College, Guizhou University of Engineering Science, Bijie, China

Copyright © 2015 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).


Received 1 June 2015; accepted 29 June 2015; published 23 November 2015

ABSTRACT
Using a purposive sampling technique, this research chooses Shaanxi Province as the sample area to analyze the implementation effect of the Program Outline in three aspects which include the scale, quality and resource allocation of preschool education teachers. It is found that teachers’ construction has achieved remarkable effects illustrated by population explosion, more training opportunities, growing education qualification rate, and gradually increasing teachers’ salary. However, there are still some shortcomings need to be improved, which mainly include the lack and instability of teachers, irrational structure, low-level professionalization and imbalance of resource allocation. Therefore, it is suggested that the government should make the policy of listing out the kindergarten teachers’ position, and reconstruct a scientific model of teachers’ position according to the workload; add up teachers by all approaches and establish long-term mechanism to supplement teachers; strictly control entrance of teachers’ enrollment and implement the “Double Entry Mechanism”; strengthen the target of training and highlight the subjectivity of teachers; integrate all kinds of resources to establish the county-level training center, and play the radiation role of the demonstrated kindergartens or town central-kindergartens; improve and implement teachers’ salary in kindergarten, and perfect the social security system for teachers in rural areas and private kindergartens.
Keywords:
Preschool Teacher, Analysis on Effectiveness, Scale, Quality, Resource Allocation

1. Introduction
Preschool Education is the “root” of education and the key factor of high-quality preschool education is high- quality teachers. Chinese government has enacted the State Medium and Long Term Program on Education Reform and Development (2010-2020) (hereinafter referred to as Program), and clearly came up with the development demands of “strictly carrying out the standard of kindergarten teachers qualification, strengthen and cultivate kindergarten teachers, engage in training programs, and improve kindergarten teachers’ comprehensive qualities”. At the same year, another regulation named as Several Proposals on Development of Current Preschool Education from the State Council (hereinafter referred to as “National Ten”) was issued. The central government requires local government by county to make and implement “Three-Year Action Plan of Preschool Education (2011-2013)” and strongly promotes the development of preschool education. Program and “National Ten” have already carried out for five years and it is necessary to make an objective and comprehensive evaluation on the effectiveness of implementation. The study mainly focuses on the levels from preschool education teachers’ construction to summarize the effectiveness of the Program, analyze existing problems and put forward some targeted countermeasures and suggestions.
Scholars have researched the implementation effect of the first phase Preschool Education Three-year Action Plan in China, which the result has shown that the number of kindergarten is being considerably increased, the qualification rate of education is being constantly raised, and more training opportunities are being emerged. However, researchers have also pointed out that there are still many problems such as lack of teachers, poor complementary channels, irrational teachers’ structure and low-level professionalization. And there are deep differences in different regions and urban-rural areas. The teachers’ salary is quite low. The status of private kindergarten teachers and public non-authorized teachers of kindergarten is lower than public authorized teachers of kindergarten (Zheng, 2014; Li & Cheng, 2015; Hong & Ma, 2015) . At the same time, the scholars have put forward many relevant countermeasures and suggestions which include expanding the scale of professional enrollment, paying more attention to the pre-career training, having more teacher complementary channels, strictly strengthening the standard of teachers who enter the school, strengthening the teachers’ training on breadth and depth, and gradually coming true teachers on private kindergarten giving the same work and reward as public teachers (Shen & Li, 2013; Li & Cheng, 2015) . Although the current researches have involved in the overall effectiveness analysis on preschool teachers construction nationwide, there are few special studies for poverty-stricken areas of western China. Meanwhile, many studies have mainly aimed at the implementation effect of the Three-year Action Plan. Therefore, this paper aims to study the effectiveness of preschool education teachers construction in western China based on five-year Program implementation.
2. Research Methods
2.1. Sampling
Using a purposive sampling technique, Shaanxi province has been chosen as the sample area, and then three Cities (X, Y and W City) with the high (secondary, inferior) level of the economic development in Shaanxi province have been chosen as samples. Preschool administrative staffs have been interviewed at three different levels: provincial, municipal and county levels, and the data collection table of the basic information of preschool education development has been filled in by them (see Table 1). In addition, some of data come from statistical bulletin of the educational development in Shaanxi province in the corresponding years.
2.2. Tool
A series of research tools have been made to evaluate the preschool educational implementation effect of the State Medium and Long Term Program on Education Reform and Development by authoritative experts from over ten famous Normal Universities in China. Tools adopted in this research are some of these tools. One tool
Table 1. Number of interview to preschool administrative staffs.
is “the outline of interview to preschool administrative staffs”, which concerns 5 areas: teachers’ position, salaries, preferential policy, teaching researcher and teachers training. Another tool is “the data collection table of the basic information of preschool education development”, which consists of five dimensions. The first part is basic situation of economic and social development. The second part is gross enrollment rate. The third part is the expansion of preschool education resources. The fourth part is fund investment. The fifth part is the main parts, which is about preschool education teachers construction, including number of preschool administrative staffs and teaching researchers, qualified license number of teachers and health-care doctors, the salary of preschool teachers, the basic situation of preschool teachers in rural areas, and number of kindergarten teachers attending training.
3. Research Results
3.1. The Overall Development Situation of Preschool Education Teachers
3.1.1. Numbers of Full-Time Teachers
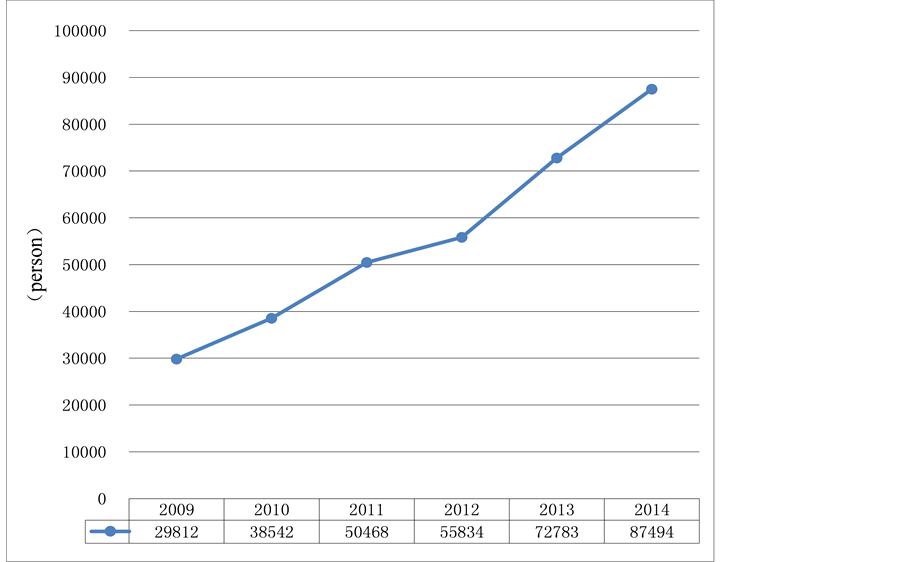
To meet the rapid development of kindergarten, the number of kindergarten teachers has rapidly increased. The number of full-time preschool teachers reached 87,494 persons in 2014 compared with 2009, and it has increased 57,682 persons and the growth of rate was 193.5% (see Figure 1).
3.1.2. Teacher-Child Ratio
The ratio between teachers and children in Shaanxi province was increased from 1:19.76 in 2009 to 1:15.26 in 2014 (see Table 2). Therefore the situation of having lack of teachers in preschool education has effectively improved.
3.1.3. Teachers Training
Under the guidance of the national policies about child-teacher training, it has constructed province, city, county and kindergarten four training networks in Shaanxi province in accordance with the requirements of the training. The number of participants attending the training was increased year by year from 1800 participants in 2009 to 18,128 participants in 2014 (see Table 3). It has raised nearly more than 10 times.
Figure 1. Number of full-time teachers in kindergarten in 2009-2014.
Table 2. Teacher-child ratio of kindergarten.
Table 3. Number of kindergarten teachers attending training.
3.1.4. Teachers’ Structure
According to incomplete survey statistics for 6 Cities, the ratio of kindergarten teacher who have acquired college or above education degree raised from 60.97% to 75.04% (see Table 4). With the cooperation of many new teachers, the number of non-profession grades teachers in rural areas basically accounts for about half. Meanwhile, the total number of having senior middle or primary school profession preschool education basically remained the same (see Table 5), so the overall level of visible rural preschool teachers needs to be improved.
3.2. Differences of Preschool Education Teachers’ Development in Shaanxi Province
3.2.1. Regional Difference
Although the number of kindergarten teachers rapidly increases in recent years, the developmental speed of district is different. The highest increasing rate in number of full-time teachers is X City, and the rate of increasing is 136.3%; and Y City and W City are 131.8% and 127.4% respectively. From the teacher-children ratio, the city with the biggest increasing rate is W City, it has increased to 10%; and X City is secondary, it has improved 3%; and Y City has basically not changed (see Table 6).
3.2.2. Differences between Urban and Rural Areas
Although the number of full-time preschool teachers in urban and rural areas is expanding year by year, there is still a big gap on the scale between urban and rural areas. For example in 2014, the number of public kindergarten full-time teachers in town is 37,791, however the number is 5524 in rural areas. The full-time teachers in town accounts for 87.25% and it is more than in rural areas (see Table 7).
3.2.3. The Nature of the Kindergarten and Teachers’ Identity Difference
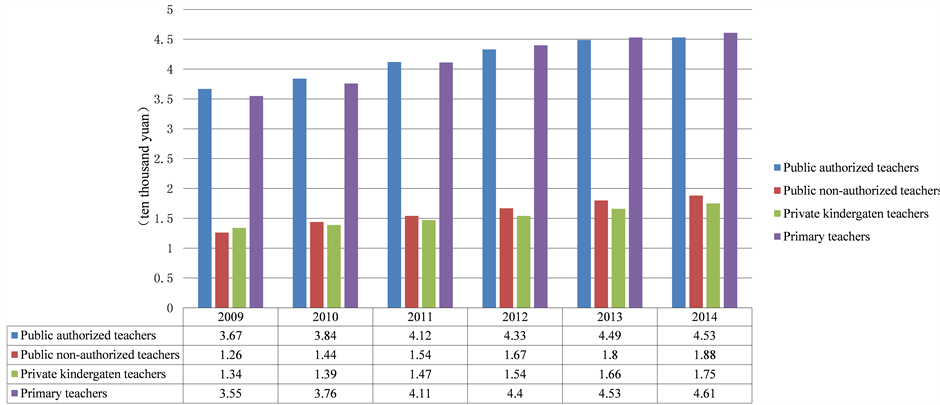
Although the kindergarten teachers’ salary is increasing year by year, there is still a big gap in terms of wages between public and private kindergartens and so is the authorized and non-authorized teachers in public kindergartens. According to incomplete survey statistics for six Cities, the teachers’ average income in private kindergarten in 2014 is 17,500 yuan that is lower than non-authorized teachers in public kindergarten, much lower than authorized teachers in public kindergarten. The difference of their salary is 27,800 yuan (see Figure 2).
Table 4. The structure of kindergarten teachers’ qualification in rural areas.
Note: incomplete survey statistics, including Xi’an, Baoji, Tongchuan, Yuling, Ankang and Shangluo six cities.
Table 5. The structure of teachers’ professional.
Note: incomplete survey statistics, including Xi’an, Baoji, Tongchuan, Yuling, Ankang and Shangluo six cities.
Table 6. Number of full-time teachers and teacher-child ratio in 3 cities.
Table 7. Comparison of teachers in public kindergarten between urban and rural areas.
Figure 2. The average salary of kindergarten teachers. Note: incomplete survey statistics, including Xi’an, Baoji, Tongchuan, Yuling, Ankang and Shangluo six cities.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Scale of Preschool Education Teachers
With the rapid increase in the number of kindergartens, the number of preschool teacher is increasing year by year through an open recruitment, the transfer from the surplus primary and middle school teachers and temporary appointment of kindergarten teachers, etc. in Shaanxi Province. Overall, however, the growth of kindergarten teachers doesn’t keep up with the speed of construction of kindergartens, and preschool teachers in the gap remains large and unstable.
First, there is a lack of urban public kindergarten teachers. Recently with the pace of urbanization accelerated, a large number of school-aged children entering the city have the need for education, but most parents believe that the quality of public kindergarten is guaranteed and they more want their children to learn in public kindergartens. However, because of the limited number of teachers in public kindergartens and the limited growth of the enrollment of preschool teachers, the needs for current development in kindergarten can’t be met. Second, there is a great need from the newly constructed, renovated and expanded kindergartens, especially rural public kindergartens and the kindergartens affiliated elementary school. Because there is no preparation or served by the re-oriented teachers after the integration of school resources, basically a class has a teacher and the demands for kindergarten teachers is most prominent and rigid. Third, the temporary teachers of some private and public kindergarten prefer to transfer from other schools. The salaries of private preschool teachers are lower, and teachers’ honor, titles, insurance and other implementation don’t reach the designated level. These made teachers generalized that the basic living cannot be guaranteed. As a result, many people give up the job as preschool teachers and do other works. Although the monthly salary of private kindergarten teachers will be slightly higher than some public kindergarten compared with public school teachers, private preschool teachers can’t enter the formal teacher preparation, status is very difficult to change, and same work with different pay makes the private preschool teachers have a strong sense of inferiority. Most temporary teachers don’t tend to view preschool teachers as a lifelong career, but choose to solve the existing problems. These teachers will not be hesitated to leave when they meet better job opportunities.
4.2. The Quality of Preschool Education Teachers
Since “the National Education Plan” has implemented for the past five years, Shaanxi preschool education teachers greatly enhanced the overall quality, full-time teachers education qualification rate increased year by year, the structure of professional title also improved, and teachers’ training opportunities obviously increased. But overall, the structure of teachers is unreasonable and professional level needs to be improved. Because the supply of the kindergarten constantly expanded everywhere, and recruited a large number of new teachers, as well as the basic requirement for recruiting is college education, not limiting the professional background, so that the new kindergarten teachers’ education levels have improved but the proportions of the teachers with the preschool education background is low, along with having large percentage job-transfer teachers, appearing the widespread phenomenon that the educational levels are qualified but the specialty is not corresponding. The non-preschool education background of the teachers is not only poor in adaptability, but also not high-sense of identity for the preschool education work. At the same time, a large number of new teachers becomes the preschool teachers, and it is difficult for them to achieve regional rules of professional title evaluation criteria in a short time with the restriction of the their professional background, combined with the professional title ratio affects the enthusiasm of the teachers title evaluation and identity of title to assess fairness. This caused that the number of teachers without professional title is rising apparently and the number of teachers with senior professional titles is falling.
As the number of new teachers increases, as well as the old teachers’ education ideas, knowledge structure and professional development also needed to be improved and optimized, teachers’ training has become an important measure to improve the professional quality of teachers. In recent years, more and more preschool teachers participate in the training, but training mainly concentrated on the national and provincial training, leading to less local training opportunities and low training ability of kindergartens. In addition, lacking of goals or practical training content, interviewed teachers often said: “the trainers have little or no contact with the kindergarten, and only talk profound theory, not being a good guide to the practical teaching, as well as low training effect, small harvest, and they can’t dramatically improve their own ability.” In general, training is given priority to the class teaching, and yet the interaction, case analysis as well as field guide between teachers and students or between students are relatively small.
4.3. The Rationality of Preschool Education Teacher Resources Allocation
The teacher-child ratio is an important reflection to the number allocation index of preschool teachers. From 2010 to 2013, the child-teacher ratio fluctuates from 1:16.82 to 1:20.53 in Shaanxi province, otherwise the national teacher-child ratio is from 1:23.41 to1:26.03. This proved that Shaanxi province is strongly hosting kindergarten, and strive to complement teachers, so that the teacher-child ratio remains at reasonable level, and ensure the quality of preschool education. From 3 sample Cities in 2014, the economic and social development level and the teacher-child ratio can be known, the 3 Cities’ GDP per capital from the highest to lowest is X, Y and W, and the teacher-child ratio from the highest to the lowest is X, Y and W (see Table 8). It can be seen that the level of economic and social development directly affected the arrangement of teachers in preschool education institutions. At the same time, although X City and W City gross enrollment rate have reached 98%, but the teachers-child ratio in X City is higher up to 10% than W City. The reason is probably that X City is the developed provincial capital city and full-time preschool teachers’ wages, benefits, working environment and personal development space are more ideal, attracts the inflow of large amount of the province and high-quality early childhood teachers.
Through comparing between public and private, urban and rural full-time preschool teacher’s educational background and professional title, condition of the preschool teachers’ configuration can be analyzed and evaluated them rationally. The survey found that the proportion of public kindergarten teachers with college education and above is much higher than that of private kindergarten teachers, the proportion of urban kindergarten teachers with higher education (undergraduate and master) is higher than that of rural kindergarten teachers, and the rural preschool teachers with a high school education still accounts for a certain proportion; the proportion of private kindergarten teachers without the title of a technical post is higher than public kindergarten teachers, the proportion of rural teachers without the title is higher than urban teachers and the proportion of urban teachers
Table 8. Comparison of teacher-child ratio, GDP per capital, and gross enrollment rate in 3 cities.
with senior professional titles is higher than that of rural teachers. In the interview, many private kindergartens’ principal said: “some teachers spend a lot of cost to go to public kindergarten, because public kindergarten is relaxed and salary is better… Although the kindergartens have to buy their pension insurance, but still cannot stay them, because the gap between public and private is too big.”
Based on the above, we can see the reasons that cause the uneven allocation of teacher resources in kindergartens, in addition to being mainly restricted by the level of economic and social development, but also by the admission rate, the kindergarten types and differences between urban and rural areas and so on.
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
After the implementation of Program for five years, the contradictions of western China preschool education teachers in “quantity” and “quality” has been alleviated, and the number of teachers, teacher training opportunities, increasing the qualification rate and the growing rate of teachers’ salaries have been improved. However, there are still some problems and the urgent needs to be strengthened, which mainly include that the gap of the teachers is still very large and unstable, the structure is irrational, the level of specialization needs to improve and the allocation of resources is imbalanced as well as other aspects.
Teachers’ team construction is the key to improve the quality of preschool education, and in order to effectively promote the rapid and balanced development of preschool education in China and to construct an adequate, relatively stable, and with a higher professional and comprehensive quality of the kindergarten teachers, the following suggestions should be put forward. First, make the policy of listing out the kindergarten teachers’ position and according to the actual teaching needs to complement the needed teachers and to view the students getting equalized public education services as the basic value orientation, meanwhile, on the basis of the workload of teachers to build a scientific teacher preparation calculation model. Second, add up teachers by all approaches and establish long-term mechanism to supplement teachers; give priority to expand the scale of rural teachers as well as newly registered teachers firstly enter kindergartens in rural areas through multi-channel such as directional training, special post plan and entrusted cultivation. Also, strictly control entrance of teachers’ enrollment, and implement the “Double Entry Mechanism”, namely the qualified and professional counterparts; further strengthen training of transfer teachers and non-professionals, and training should be based on the practical problems in kindergarten education to enhance the professional ability and to focus on subjectivity of teachers; integrate all kinds of resources to establish the county-level training center, and play the radiation role of the demonstrated kindergartens or town central-kindergartens. Finally, improve and implement teachers’ salary in kindergarten, and perfect the social security system for teachers in rural areas and private kindergartens. To attract talented people to teach in rural areas needs to enhance the work offers of rural teachers (wages, good opportunities of development, etc.), occupational health forces (establishment, medical insurance, swing, etc.) and social actuation force, and to explore beneficial incentives helping to attract talents “come in”, to create an opportunity structure to “retain” the rural teachers, and to implement “well done” the micro-environment improvement mechanisms for rural teachers (Wu, 2014) .
Fund
This research was supported by a grant “Problems and Countermeasures on the Preschool Education Teachers Construction in Poor Mountainous Rural Areas of Western China” (Grant No.: SWU1409224) from “the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities”.
Cite this paper
YoulongZhang,YaoyangHan,XiaopingYang, (2015) Analysis on the Effectiveness of Preschool Education Teachers Construction in Western China —An Empirical Investigation Based on Shaanxi Province. Creative Education,06,2152-2159. doi: 10.4236/ce.2015.620219
References
- 1. Hong, X. M., & Ma, Q. (2015). Evaluation of the Implementation Effect of the Early Childhood Education Three-Year Action Plan: Perspectives of Internal Stakeholders. Journal of Educational Studies, 1, 115-126.
- 2. Li, M. Y., & Cheng, X. (2015). Analysis on the Predicament and Breakout of Teachers Supply in China: Data Analysis of the First Phase of Three-Year Action Plan. China Education Journal, 4, 65-69.
- 3. Shen, J. Z., & Li, L. F. (2013). On the Implementation of the Three-Year Developmental Project of Preschool Education of Gansu Province. Studies in Preschool Education, 12, 11-20.
- 4. Wu, Z. H. (2014). How to Improve the Attraction of Teacher Profession in Rural Areas. Guangming Daily, 2 September, 11.
- 5. Zheng, M. (2014). On the Three Years’ Project for Preschool Education. Studies in Early Childhood Education, 8, 34-43.