Paper Menu >>
Journal Menu >>
 International Journal of Clean Coal and Energy, 2013, 2, 8-12 doi:10.4236/ijcce.2013.22B002 Published Online May 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcce) Solar Energy and Residential Building Integration Technology and Application Ding Ma, Yi-bing Xue Department of Architecture and Urban Planning.Shandong Jianzhu University, Jinan, China Email: mading.1989@163.com Received 2013 ABSTRACT Building energy saving needs solar energy, but the promotion of solar energy has to be integrated with the constructions. Through analyzing the energy-saving significance of solar energy, and the status and features of it, this paper has dis- cussed the solar energy and building integration technology and application in the residential building, and explored a new way and thinking for the close combination of the solar technology and residence. Keywords: Solar Energy; Residential Building; Integration Technology and Application 1. Introduction With the improvement of China’s economic construction and people’s living standards, the energy crisis and en- vironmental degradation are also growing, we are facing the dual pressures of resources and environmental pro- tection. Building energy consumption accounts for 25% to 40% of the total energy consumption, together with transportation and industry as the three major energy- consuming households, building energy efficiency plays an important role in the national energy conservation strategies. As the large construction number of residen- tial buildings energy-saving or not, will no doubt have positive practical significance to realization of building energy conservation and environmental protection. 2. Status and Features of Solar Energy and Building Integration Technology 2.1. Status of Solar Energy and Building Integration Technology As the building renewable energy, solar energy is clean, non-polluting and easy to get, more and more people of all ages. Solar energy resource in China is extremely rich, and the total annual solar radiation amount is more than 5.02 million KJ/m2, annual sunshine hours over 2200h areas accounted for more than two-thirds of the land area, so there is great potential in the use of solar energy[1]. Currently, the use of solar energy in our country has made gratifying achievements, but the degree of realiza- tion of solar energy and building integration technologies is not high. Firstly, the development of solar thermal and photovoltaic is uneven, from the Renewables 2012 global Status Report can see that China ranks the world’s first in solar water heaters in 2011, while the development of solar photovoltaic is relatively slow[2]. Secondly, there exist many problems in the use of solar water heater, such as the water heaters rank highly on the roof, placed very messy, not only destroy the architectural aesthetics, but also affect the image of the city. The aim of imple- menting solar energy and building integrated technolo- gies is to change the disjointed, fragmented status quo of each branch and link, incorporate the use of solar energy into the over all design of the environment, make archi- tecture, technologies and aesthetics be in harmony as an organic whole, and make solar facilities to be part of the building. 2.2. Features of Solar Energy and Building Integration Technology The main features of solar energy and building integra- tion technology are: ● Involving a wide range To achieve the application of solar energy and build- ing integration technology need the coordination and joint effort of several departments, such as national poli- cies and regulations department, component construction department, solar manufacturers, property developers, designing institution and construction enterprises. ● High technical content Solar energy and building integration technology is a comprehensive technical which combines multiple disci- plines such as optical, thermal, electronic, fluid mechan- ics and architecture, etc. ● Complicated construction Copyright © 2013 SciRes. IJCCE  D. MA, Y.-B. XUE 9 Solar energy and building integration technology also requires the integration of construction process and technology, in addition to the conventional construction, there also need to conduct the complex construction of waterway and circuit and to complete the installation and debugging tasks of solar equipments . ● High initial investment Due to the increased solar equipments, pipeline and appliances, as well as the corresponding structural and construction detail handing, the initial investment of so- lar energy and building integration technology is high, and the construction cost is also high[3]. But with the use of solar energy, the economic benefits that generate from its energy conservation, environmental protection, safe and efficient will become increasingly apparent. 3. Application of Solar Energy and Building Integration Technology in Residential Building The application of solar energy and building integration technology in residential buildings, mainly has three as- pect: solar thermal technology, solar photovoltaic tech- nology, solar optical technology, and mainly set on roofs, balconies, exterior walls and somewhere with ample sunshine. 3.1. Solar Thermal Technology Solar thermal is mainly used to supply domestic hot wa- ter, heating and refrigeration. In designing the integration of solar hot water system and residential buildings, not only need to consider the layout of solar hot water sys- tem, but need to further improve the form of the system itself. Traditional solar hot water system with vacuum tube can not meet the needs of the ever-changing layout and style of the residential buildings, beyond that, it have other deficiencies, such as the installation is very diffi- cult, easy to destroy the waterproof layer of the roof, have security risks if the lightning protection and drought exclusion device not in place, vacuum tube belongs to quick-wear part and the maintenance ratio is high, water pipes are exposed to the outdoor cause large heat loss, etc. In short, the traditional solar hot water system with vacuum tube can not meet the need of integration of so- lar energy and building either in quality or in perform- ance. Now, the flat plate solar collector system is gradu- ally replacing the solar hot water system with vacuum tube, for it has higher adaptability, and the installation of it can better achieve the perfect combination with the construction[4]. Solar collector system mainly operate on the split double-cycle under pressure, the hot water tank can located in the basement, attic, staircase, balcony and other hidden parts, and not occupy the indoor space, avoiding the load-bearing of roofs, balconies and exterior walls; water tank can use single tank, double tank and even a multi-tank, so as to achieve a larger holding tank capacity, when the tank capacity is increased, the instal- lation area is correspondingly increased to meet the hot water needs; hot water is not just use for bath, but also used for heating and supplying domestic water, the water quality should keep clean to meet the drinking water standards. Integrating solar collector with the roofs, balcony rails of the south façade, bay windows and walls, can make the appearance of residential buildings be overall unified, and have rich hierarchies[5] (Figure 1). When installed on (a) combined with the roof (b) combined with the balcony (c) combined with the exterior wall Figure 1. Ways of the solar collector combined with the residential building. C opyright © 2013 SciRes. IJCCE  D. MA, Y.-B. XUE Copyright © 2013 SciRes. IJCCE 10 the sloping roof, the solar collector can be embedded in the roof like a sunroof or flat out on the roof, integrating with the construction to increase the building beauty. When installed on the flat roof, the flat-plate solar col- lector can act as roof covering or insulation layer, not only conforms to the residential modeling requirements, but also avoids the repeated investment and reduce the cost. In addition, the flat-plate solar collector can be combined with balconies, bay windows, outside walls of residential buildings, to maximize the use of solar energy and provide new ways and means to the residential fa- çade design, and achieve the aim of multi-purpose as well (Figure 2). new concept for the application of solar power, in short, installing the solar photovoltaic phalanx on the surface of the maintenance structure of the building to provide electricity[6]. Photovoltaic arrays do not take up addi- tional floor space when integrate with the construction, and is the best installation way of photovoltaic genera- tion system, thus attracting much attention. BIPV can be divided into two categories according to the forms that photovoltaic array integrated with the buildings[7]. One is the combination of photovoltaic array with building, installing the PV array on the build- ing, and the building play a supporting role as a photo- voltaic carrier (Figure 3). The other is the integration of photovoltaic array with building, PV modules appear as the building material, and the photovoltaic array become the integral part of the construction, such as photoelectric tile roof, photoelectric curtain wall and photoelectric lighting roof, etc (Figure 4). 3.2. Solar Photovoltaic Technology Solar photovoltaic technology applying in residential buildings is mainly used for photovoltaic conversion and lighting. BIPV (Building Integrated Photovoltaic) is a Figure 2. Construction node design of the solar collector combined with the residential building. 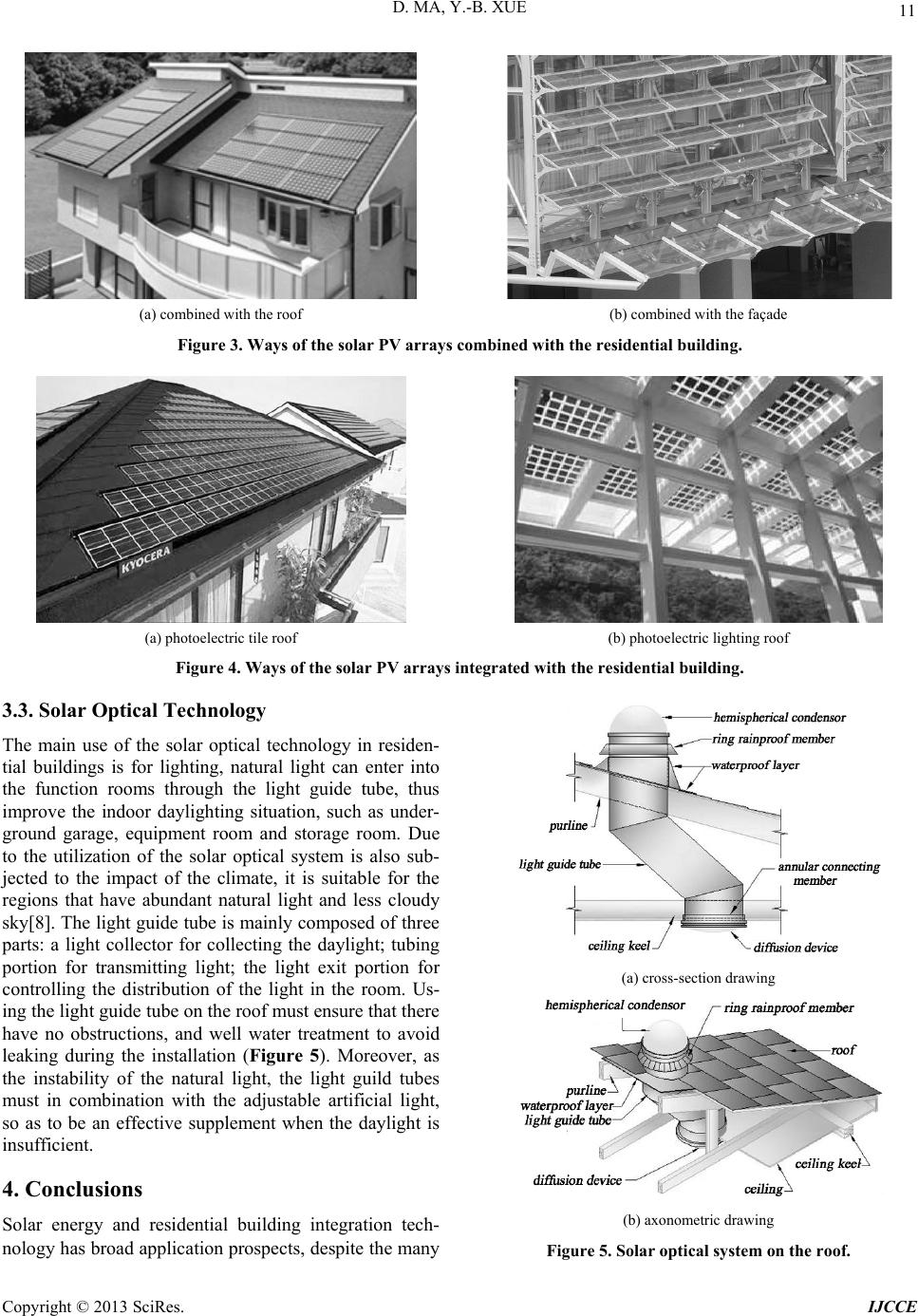 D. MA, Y.-B. XUE 11 (a) combined with the roof (b) combined with the façade Figure 3. Ways of the solar PV arrays combined with the residential building. (a) photoelectric tile roof (b) photoelectric lighting roof Figure 4. Ways of the solar PV arrays integrated with the residential building. 3.3. Solar Optical Technology The main use of the solar optical technology in residen- tial buildings is for lighting, natural light can enter into the function rooms through the light guide tube, thus improve the indoor daylighting situation, such as under- ground garage, equipment room and storage room. Due to the utilization of the solar optical system is also sub- jected to the impact of the climate, it is suitable for the regions that have abundant natural light and less cloudy sky[8]. The light guide tube is mainly composed of three parts: a light collector for collecting the daylight; tubing portion for transmitting light; the light exit portion for controlling the distribution of the light in the room. Us- ing the light guide tube on the roof must ensure that there have no obstructions, and well water treatment to avoid leaking during the installation (Figure 5). Moreover, as the instability of the natural light, the light guild tubes must in combination with the adjustable artificial light, so as to be an effective supplement when the daylight is insufficient. 4. Conclusions Solar energy and residential building integration tech- nology has broad application prospects, despite the many (a) cross-section drawing (b) axonometric drawing Figure 5. Solar optical system on the roof. C opyright © 2013 SciRes. IJCCE  12 D. MA, Y.-B. XUE problems, such as the integration degree of solar water heating system and building is not high, solar photo- voltaic industry is lack of technological breakthroughs, and the production cost is high, etc. But with the intro- duction of the “Renewable Energy Law” and the detru- sion of a series of policies and measures that encouraging the use of renewable energy, is bound to promote peo- ple’s enthusiasm toward the use of renewable energy, increase the technology innovation and development efforts, make the building integrated solar technologies become more mature, and make the solar energy and building integration technology more closely combined with residential and broader development prospects. 5. Acknowledgements This research was partially co-funded by the National Natural Science Foundation (51078223), We would like to thank the Key Laboratory of Renewable Energy Utili- zation Technologies in Buildings of the National Educa- tion Ministry and the Key Laboratory of energy-saving technology of Shandong Province for providing us with historical data of solar energy, integration technology and application etc. We also thank Professor Wang Chong-jie, a specialist on the solar energy and building integration technology, for his valuable advice. REFERENCES [1] C. J. Wang and Y. B. Xue, “Solar Building Design,” Bei- jing: China Architecture & Building Press, 1st Edition, 2007, pp. 87-90. [2] S. N. Wang, “The Development of Solar Building Tech- nology in Domestic and Foreign,” Journal of New Build- ing Materials, No. 10, 2008, pp. 44-46. [3] T. S. Xin and C. M. Yang, “Application of Solar Energy Technology to Congregated House,” Journal of Archi- tecture, No. 8, 2006, pp. 22-25. [4] Y. H. Wang, “Design of solar Residential Building Inte- gration,” Journal of Building Energy Efficiency, Vol. 38, No. 1, 2010, pp.53-55. [5] C. H. Xu and M. L. Qin, “The Application of Solar En- ergy and Building Integrated Multi-technology,” Journal of Construction Science and Technology, No. 5, 2012, pp.69-71. [6] L. R. Zhang, “The Application of Motor Control Unit in the Cement,” Journal of Equipment Manufacturing Technology, No. 8, 2011, pp. 208-209. [7] W. Jin, “Application of Building Integrated Photovoltaic (BIPV) in Green Buildings,” Journal of Architecture Technology, Vol. 42, No. 10, 2011, pp. 907-908. [8] A. Y. Wang and G. Shi, “New Process of Daylighting Technology,” Journal of Architecture, No. 3, 2003, pp. 64-66. C opyright © 2013 SciRes. IJCCE |

