 Open Journal of Nursing, 2012, 2, 311-326 OJN http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojn.2012.223046 Published Online November 2012 (http://www.SciRP.org/journal/ojn/) Predictors of critical care nurses’ intention to leave the unit, the hospital, and the nursing profession Claudio Giovanni Cortese Department of Psychology, University of Torino, Torino, Italy Email: claudio.cortese@unito.it Received 12 September 2012; revised 18 October 2012; accepted 30 October 2012 ABSTRACT Nursing turnover and shortage are acknowledged as worldwide issues: understanding the factors that fos- ter nurses’ intention to leave (ITL) is essential in re- taining them. The present study aims at providing in- sight into the factors influencing critical care and in- tensive care nurses’ ITL the unit, the hospital, and the nursing profession. The study was conducted in two hospitals, by a questionnaire administered to all nurses employed in critical and intensive care units. 512 questionnaires (89.4%) were returned. Results revealed that a low job satisfaction (JS) for interac- tion with physicians and nurses, seniority ≥ 20 years, and working in Emergency are related to higher ITL the unit. Low JS for work organization policies, seni- ority ≥ 11 years, working in a private hospital, and higher educational level are related to higher levels of ITL the hospital. Low JS for professional status, for pay, and for work organization policies, age ≥ 40 years, part-time schedule are related to higher ITL the nur- sing profession. The research permitted detection of various predictors of different kinds of ITL, enhan- cing the importance of regular monitoring of ITL. In order to limit ITL, it would be important to work on the relationship with physicians and colleagues, work demands, organizational policies, and acknowledge- ment of competence. Keywords: Critical Care; Intensive Care; Intention to Leave; Nurse Management; Job Satisfaction 1. INTRODUCTION In the last decade nursing shortage has been acknow- ledged as a worldwide issue. The majority of Organisa- tion for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries report nursing shortages, and in these countries unemployment of nurses appears to be marginal [1-3]. According to [4], the healthcare workforce crisis has been having an impact on many countries’ ability to fight disease and improve health. Among the causes of these situations are increasing demands of health services, ageing of the population, a diminishing workforce, lack of training courses and nurses abandoning the profession [1,5,6]. As for each single health institution, the problem of organizational leave is added, leading to personnel sub- stitutions and an increase in costs. In short, lack of nurses and nurse turnover represent a major problem for nursing and health-care in terms of the ability to care for patients [7], the quality of care [8,9] and costs [10]. When nurses leave, the quality of nursing care may decline due to the loss of expertise. In addition, novice nurses may not have the same commitment to the or- ganization or the ability, intuition, and confidence as an expert nurse [6]. Moreover, the organizations that lose workers inevitably have to face costs. [11] estimated the total turnover costs of one nurse to range from $62,000 to $67,000, depending on the service line, including the costs of recruitment, selection, orientation, training, and productivity loss. It is also worthy to note that a request to change the unit in which one works, while remaining within the same organization, results in costs, linked to the management of demands, to the training necessary for those who have changed their working unit and to diminished productivity over the period of new organiza- tional socialization. [12,13] highlighted how nursing shortages have not been institution-wide but concentrated in specialty care areas, in particular intensive care units and operating rooms. Similarly, a Study by [6] indicates that the spe- cialty areas, especially intensive care units, had the high- est nurse turnover rate (26%), and, in [14]’s words “shortage is most evident in critical care, emergency ser- vices, and perioperative care” (p. 348). Such a problem is aggravated by the fact that nurses working in these units hold specialized knowledge, skills, and experience nec- essary to safely deal with the challenges of meeting the complex needs of critically-ill patients. Research conducted in Italy has confirmed that the nursing shortage is a current problem. All of the above- OPEN ACCESS  C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 312 mentioned causes are also present in Italy: it is “esti- mated to be a structural shortage of over 70,000 nurses; insufficient numbers graduate from nursing schools and the replacement of the nursing workforce is not ensured” [15, p. 243]. In this sense, [16] mentioned “Italy’s acute nursing shortage” and Italian Nurses Federation (IPASVI) esti- mated a number of 158,000 nurses required to bring Italy in line with the average OECD member countries [17]. In addition, a high turnover rate is added: studies con- ducted in the Emilia Romagna region on a population of 23,456 nurses on duty starting from 2004 has showed how the probability of leaving was 50% at only 3 and a half years after hiring, and 60% at 5 years [18]. A solution to the nursing shortage consists of employ- ing foreign personnel. For example, more than 34,000 foreign nurses are working in Italy at present, around 10% of its total membership. In general, all Western European countries show a growing tendency to employ foreign nurses, mainly from Eastern Europe, Africa and Latin America [19]. A second solution, though very on- erous, could be to increase education and training op- portunities. Therefore, in order to contain public ex- penses as well, many authors suggest [20,21] concen- trating efforts in order to reduce organizational leave (i.e. leaving an organization for another one or becoming a freelancer) or professional leave (i.e. leaving to take up some other profession or to stop working altogether). Understanding the psychological process leading to the decision to leave the unit, the hospital and the nursing profession, detecting factors intervening in this process, is therefore crucial. The study of these factors appears unavoidable both for planning retention policies for em- ployed personnel and for attracting personnel available in the labour market [22]. The urgency is particularly no- ticeable in the Italian context, which has been object of a limited number of studies up until now [23]. 1.1. Intention to Leave The nurse turnover has been described as a withdrawal process or as chain reaction: nurses may first leave their unit, then the hospital and finally the profession [24,25]. Moreover, each of these steps is the result of a choice process originating from the intention to leave (ITL): although intention is not always followed by action, ac- tion is always preceded by intention that can manifest itself some time before (from two-three months to two- three years) actually leaving (the unit, the hospital, or the nursing profession) or the final decision to stay on [26, 27]. In this lapse of time, [28] maintains that individuals keep on working in their positions despite the fact that they feel “on the border” with the outside. For this reason ITL is presently regarded as “the most direct and imme- diate antecedent of overt turnover behaviour” [29, p. 249]. In addition, [28] continues, different predictors can be found behind ITL. Among these, work satisfaction plays a lead role: [30], for example, found that nurses who reported overall dissatisfaction with their jobs had a 65% higher probability of intending to leave than satisfied nurses. Many other studies have highlighted how per- sonal experiences characterized by dissatisfaction rela- tive to various aspects, such as the nature of the activities performed, work load, career opportunities, autonomy, training opportunities, fairness in evaluation systems, financial rewards, benefits, physical characteristics of working environment are linked to higher ITL [6,8,20,25, 29,31-36]. Many studies have consistently reported posi- tive relationships between nurses’ intention to stay on and perception of job satisfaction, including satisfaction with pay and benefits [25,37-39], scheduling [40], auto- nomy and responsibility [41], and professional develop- ment opportunities [26,42,43]. Along with work satisfaction, other variables can in- fluence ITL: personal characteristics such as gender [26, 37], age [26,31,37,44-46], education [40], professional qualification [26,37,47], years of experience [45,48,49]; context and organizational factors, such as type of or- ganization, type of units, clearness in work processes and roles [29,50], presence of threads of aggression risks and of biological risks [51]; psychosocial factors. Particularly relevant among the latter are: relationships with collea- gues [20,48,52-54], managers’ style [51,55], work-family conflict and work-life conflict [42,47,56-61]. Further predictors of ITL investigated by scholars are work-re- lated stress [62,63] and burnout [26,47]. 1.2. Job Satisfaction Job satisfaction (JS) was defined by [64] as “the extent to which people like (satisfaction) or dislike (dissatisfaction) their jobs” (p. 2). Different dimensions or facets of satis- faction have also been described, e.g. nature of the work, job conditions, supervision, co-workers, career, training opportunities, pay and benefits [65,66]. To date, no com- plete classification of the factors of JS as perceived by nurses exists. Various questionnaires cover various fac- tors but there is no consistency between factors covered by questionnaires and those highlighted through qualita- tive studies [67]. Relevance of JS, attested by the great number of stud- ies employing it as an independent variable, lies not only on its relation to ITL, but to many other variables as well. It is important to mention here that JS is related to ab- senteeism, work performance, patient-satisfaction and service quality: all of these are elements that, together, can compromise the overall results of an organization [8,35,68-74]. In addition, JS appears to be an antecedent to life satisfaction [75]. Copyright © 2012 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS  C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 313 According to the literature, although personality fac- tors can influence an employee’s work satisfaction [76, 77], the characteristics of the organization and of work activities have a crucial impact on JS [44,64,78-83]. There- fore, a person’s JS can change throughout his/her profes- sional career depending on the different contexts, depart- ments, supervisors, co-workers, duties, etc. progressively encountered [83,84]. The characteristics of the organiza- tion that can influence JS are, among others, role ambi- guity, work load, communication, recognition, routiniza- tion and care setting [85,86]. The unbalance between work and personal life is associated with a lower JS as well [87-89]. 1.3. Study Objective The OECD report on nursing shortages concluded that policies designed to reduce the flow of nurses out of the workforce are still relatively underdeveloped in many OECD countries [2]. Understanding the reasons why nur- ses consider leaving their unit, hospital or profession is essential in order to keep them in nursing. Moreover, if the nursing community gained a better understanding of the reasons why nurses have developed an ITL, there might be more possibilities of attracting leavers back [1]. The aim of this study was to identify the factors influ- encing critical care and intensive care nurses’ ITL while taking into account personal characteristics, context cha- racteristics and JS factors. As literature suggests [24,25], three different kinds of ITL have been determined: ITL the unit, ITL the hospital, ITL the nursing profession. Even if it represents a research field essential to steer policies acting against turnover and professional leave, few studies have been conducted within the Italian con- text as of yet. Among these, the Nurses’ Early Exit (NEXT) Study [61] highlighted how Italian nurses show a desire to leave their profession more frequently com- pared to those in other European countries; [23] Study emphasised the role of supervising and organizational supports in the relationship between nurses’ perceptions of care adequacy, JS, and turnover intention; [33] Study highlighted that the tendency to leave the profession was associated with job dissatisfaction, burnout symptoms and the labour market situation; [87] Study stressed the role of work-life conflict as an antecedent of JS, moder- ated by support on the part of colleagues and supervisors. It is important to note that no research carried out in Italy as of yet has detected the ITL the unit, ITL the hospital, and the ITL the nursing profession simultaneously. 2. METHOD 2.1. Subjects The present study was conducted in two large hospitals —one public, the other private—in a big city in Northern Italy. The research instrument was a self-completed structured questionnaire, which was administered to all nurses employed in the critical care and intensive care units of both hospitals. Upon approval of the hospitals’ Boards of Directors, nurse coordinators of each unit were asked for authori- zation to administer the questionnaire to nurses. All nurse coordinators consented and the questionnaire was ad- ministered in 12 critical and intensive care units (six in the public hospital and six in the private one). Each nurse received the questionnaire from his/her coordinator with a letter by the head of the study (explaining the research aim, underlying voluntary participation and ensuring anonymous collection and processing of data) and a blank envelope to return the questionnaire in. The ques- tionnaires were returned into a box located in the unit meeting room. 573 questionnaires were distributed, of which 512 (89.4% response rate) were returned com- pletely filled-in (Table 1). 2.2. Study Questionnaire The questionnaire consisted of four sections. Personal characteristics: age (≤29; 30 - 39; 40 - 49; ≥50), gender (woman; man), marital status (single; mar- ried or in cohabitation), educational level (degree or university master/specialization; diploma), role (nurse coordinator; nurse), work schedule (full-time; part-time), work experience (≤5; 6 - 10; 11 - 20; ≥20 years). Context characteristics: hospital (public; private), type of unit (cardiology; emergency; medicine; obstetrics/neo- natal; paediatrics; surgery). JS was detected through 44 items of Work Satisfaction Index section B [77, adapted by 67]. The items are mea- sured on a 7-point Likert scale from 1 (strongly disagree) to 7 (strongly agree). The questionnaire includes seven factors: autonomy (9 items), professional status (7 items), pay (6 items), job requirements (6 items), work organi- zation policies (6 items), interaction with physicians (5 items), interaction with nurses (5 items). ITL was detected through 3 items placed at the end of the questionnaire which could be answered yes, no, don’t know. The “don’t know” answers have not been included in the study. These three items refer to the three ITL kinds described above: “Do you intend to change the unit where you work, remaining in the same hospital?”; “Do you intend to change the hospital where you work?”; “Do you intend to give up the nursing profession?” A similar question, on the same response scale, was used by [90] in a Study on ITL the nursing profession. 2.3. Ethical Considerations The study was approved by the Board of Directors of the Copyright © 2012 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS 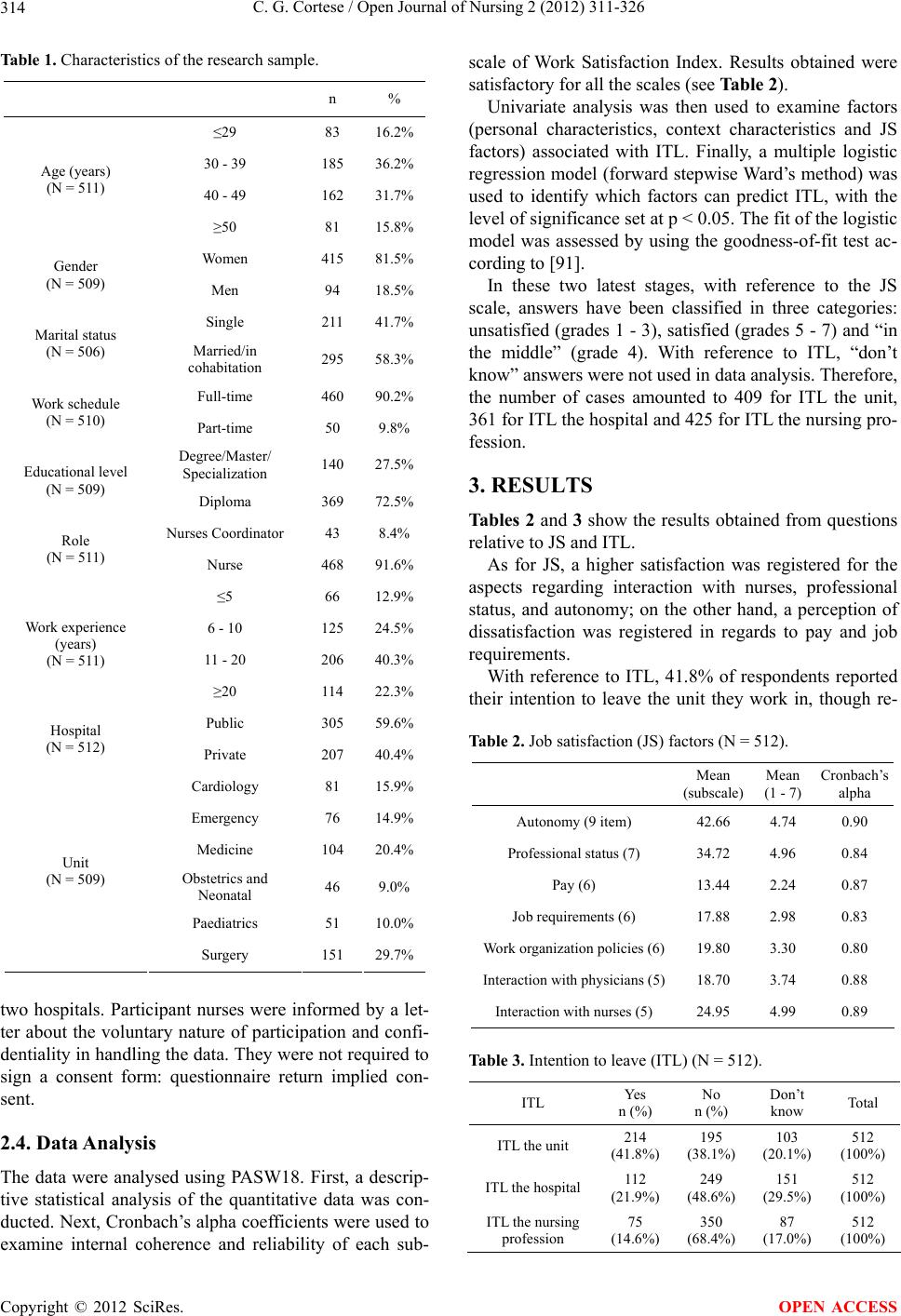 C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 314 Table 1. Characteristics of the research sample. n % ≤29 83 16.2% 30 - 39 185 36.2% 40 - 49 162 31.7% Age (years) (N = 511) ≥50 81 15.8% Women 415 81.5% Gender (N = 509) Men 94 18.5% Single 211 41.7% Marital status (N = 506) Married/in cohabitation 295 58.3% Full-time 460 90.2% Work schedule (N = 510) Part-time 50 9.8% Degree/Master/ Specialization 140 27.5% Educational level (N = 509) Diploma 369 72.5% Nurses Coordinator 43 8.4% Role (N = 511) Nurse 468 91.6% ≤5 66 12.9% 6 - 10 125 24.5% 11 - 20 206 40.3% Work experience (years) (N = 511) ≥20 114 22.3% Public 305 59.6% Hospital (N = 512) Private 207 40.4% Cardiology 81 15.9% Emergency 76 14.9% Medicine 104 20.4% Obstetrics and Neonatal 46 9.0% Paediatrics 51 10.0% Unit (N = 509) Surgery 151 29.7% two hospitals. Participant nurses were informed by a let- ter about the voluntary nature of participation and confi- dentiality in handling the data. They were not required to sign a consent form: questionnaire return implied con- sent. 2.4. Data Analysis The data were analysed using PASW18. First, a descrip- tive statistical analysis of the quantitative data was con- ducted. Next, Cronbach’s alpha coefficients were used to examine internal coherence and reliability of each sub- scale of Work Satisfaction Index. Results obtained were satisfactory for all the scales (see Table 2). Univariate analysis was then used to examine factors (personal characteristics, context characteristics and JS factors) associated with ITL. Finally, a multiple logistic regression model (forward stepwise Ward’s method) was used to identify which factors can predict ITL, with the level of significance set at p < 0.05. The fit of the logistic model was assessed by using the goodness-of-fit test ac- cording to [91]. In these two latest stages, with reference to the JS scale, answers have been classified in three categories: unsatisfied (grades 1 - 3), satisfied (grades 5 - 7) and “in the middle” (grade 4). With reference to ITL, “don’t know” answers were not used in data analysis. Therefore, the number of cases amounted to 409 for ITL the unit, 361 for ITL the hospital and 425 for ITL the nursing pro- fession. 3. RESULTS Tables 2 and 3 show the results obtained from questions relative to JS and ITL. As for JS, a higher satisfaction was registered for the aspects regarding interaction with nurses, professional status, and autonomy; on the other hand, a perception of dissatisfaction was registered in regards to pay and job requirements. With reference to ITL, 41.8% of respondents reported their intention to leave the unit they work in, though re- Table 2. Job satisfaction (JS) factors (N = 512). Mean (subscale) Mean (1 - 7) Cronbach’s alpha Autonomy (9 item) 42.66 4.74 0.90 Professional status (7) 34.72 4.96 0.84 Pay (6) 13.44 2.24 0.87 Job requirements (6) 17.88 2.98 0.83 Work organization policies (6)19.80 3.30 0.80 Interaction with physicians (5)18.70 3.74 0.88 Interaction with nurses (5) 24.95 4.99 0.89 Table 3. Intention to leave (ITL) (N = 512). ITL Yes n (%) No n (%) Don’t know Total ITL the unit 214 (41.8%) 195 (38.1%) 103 (20.1%) 512 (100%) ITL the hospital 112 (21.9%) 249 (48.6%) 151 (29.5%) 512 (100%) ITL the nursing profession 75 (14.6%) 350 (68.4%) 87 (17.0%) 512 (100%) Copyright © 2012 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS 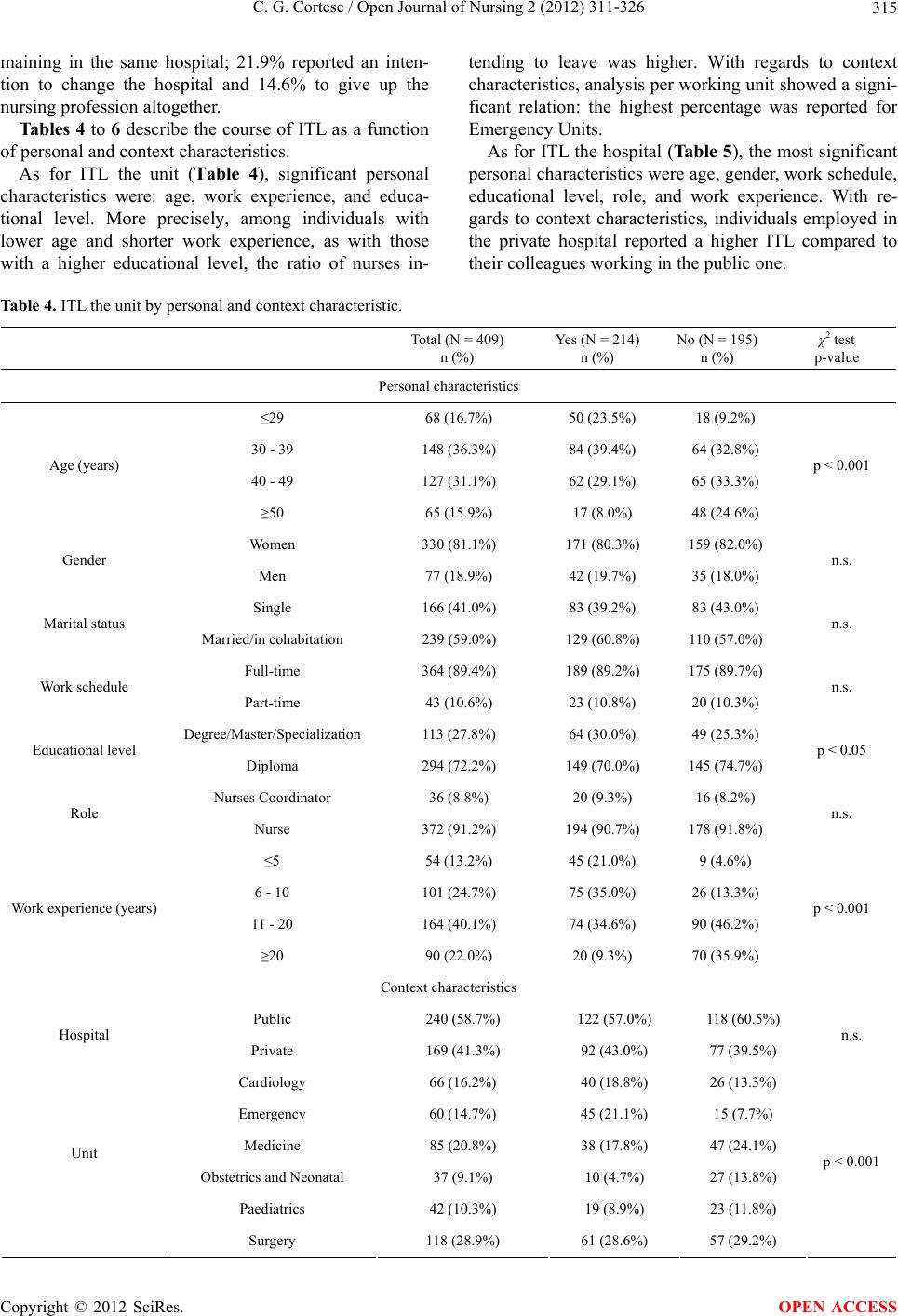 C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 Copyright © 2012 SciRes. 315 OPEN ACCESS maining in the same hospital; 21.9% reported an inten- tion to change the hospital and 14.6% to give up the nursing profession altogether. Tables 4 to 6 describe the course of ITL as a function of personal and context characteristics. As for ITL the unit (Table 4), significant personal characteristics were: age, work experience, and educa- tional level. More precisely, among individuals with lower age and shorter work experience, as with those with a higher educational level, the ratio of nurses in- tending to leave was higher. With regards to context characteristics, analysis per working unit showed a signi- ficant relation: the highest percentage was reported for Emergency Units. As for ITL the hospital (Table 5), the most significant personal characteristics were age, gender, work schedule, educational level, role, and work experience. With re- gards to context characteristics, individuals employed in the private hospital reported a higher ITL compared to their colleagues working in the public one. Table 4. ITL the unit by personal and context characteristic. Total (N = 409) n (%) Yes (N = 214) n (%) No (N = 195) n (%) χ2 test p-value Personal characteristics ≤29 68 (16.7%) 50 (23.5%) 18 (9.2%) 30 - 39 148 (36.3%) 84 (39.4%) 64 (32.8%) 40 - 49 127 (31.1%) 62 (29.1%) 65 (33.3%) Age (years) ≥50 65 (15.9%) 17 (8.0%) 48 (24.6%) p < 0.001 Women 330 (81.1%) 171 (80.3%) 159 (82.0%) Gender Men 77 (18.9%) 42 (19.7%) 35 (18.0%) n.s. Single 166 (41.0%) 83 (39.2%) 83 (43.0%) Marital status Married/in cohabitation 239 (59.0%) 129 (60.8%) 110 (57.0%) n.s. Full-time 364 (89.4%) 189 (89.2%) 175 (89.7%) Work schedule Part-time 43 (10.6%) 23 (10.8%) 20 (10.3%) n.s. Degree/Master/Specialization 113 (27.8%) 64 (30.0%) 49 (25.3%) Educational level Diploma 294 (72.2%) 149 (70.0%) 145 (74.7%) p < 0.05 Nurses Coordinator 36 (8.8%) 20 (9.3%) 16 (8.2%) Role Nurse 372 (91.2%) 194 (90.7%) 178 (91.8%) n.s. ≤5 54 (13.2%) 45 (21.0%) 9 (4.6%) 6 - 10 101 (24.7%) 75 (35.0%) 26 (13.3%) 11 - 20 164 (40.1%) 74 (34.6%) 90 (46.2%) Work experience (years) ≥20 90 (22.0%) 20 (9.3%) 70 (35.9%) p < 0.001 Context characteristics Public 240 (58.7%) 122 (57.0%) 118 (60.5%) Hospital Private 169 (41.3%) 92 (43.0%) 77 (39.5%) n.s. Cardiology 66 (16.2%) 40 (18.8%) 26 (13.3%) Emergency 60 (14.7%) 45 (21.1%) 15 (7.7%) Medicine 85 (20.8%) 38 (17.8%) 47 (24.1%) Obstetrics and Neonatal 37 (9.1%) 10 (4.7%) 27 (13.8%) Paediatrics 42 (10.3%) 19 (8.9%) 23 (11.8%) Unit Surgery 118 (28.9%) 61 (28.6%) 57 (29.2%) p < 0.001 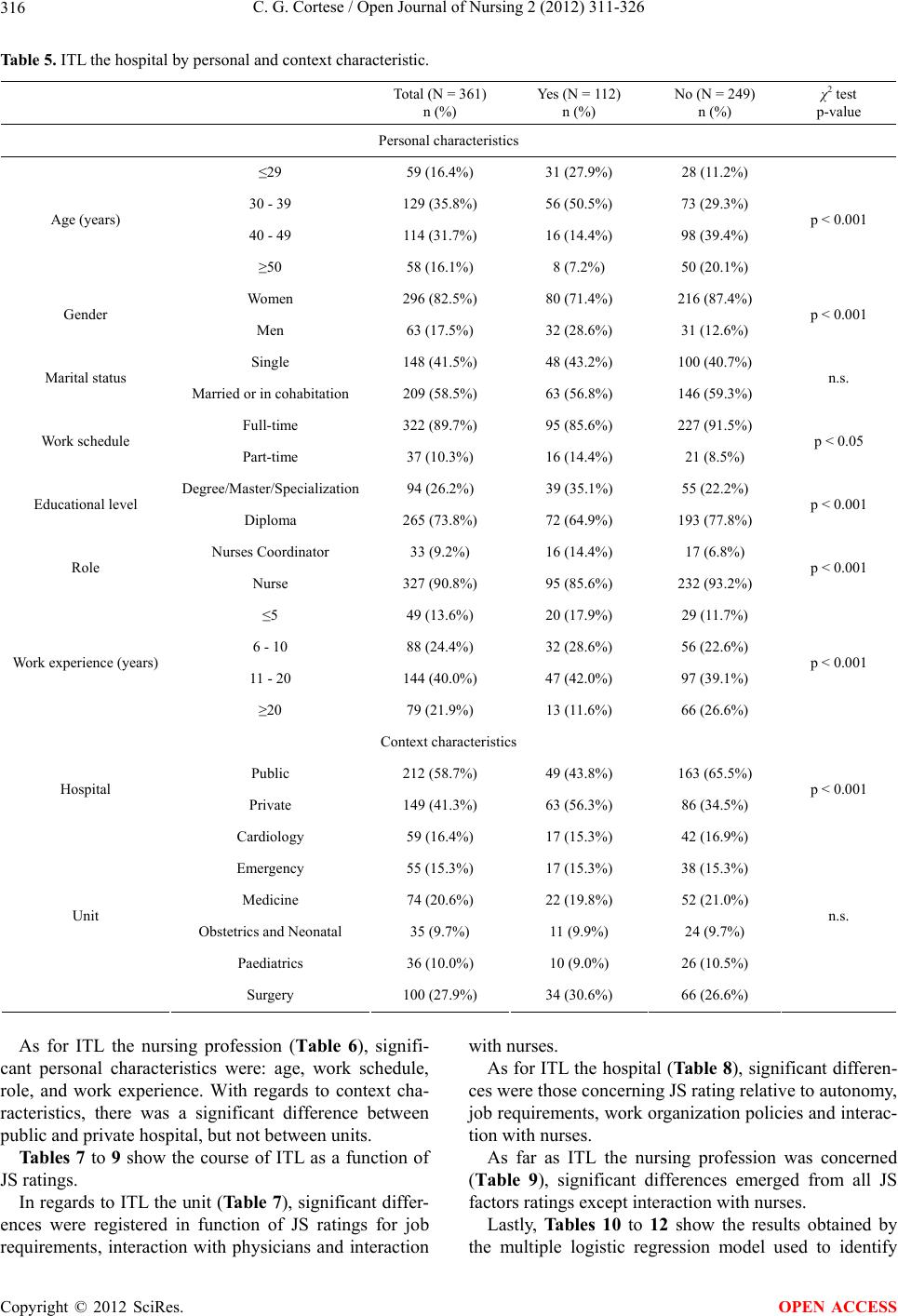 C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 316 Table 5. ITL the hospital by personal and context characteristic. Total (N = 361) n (%) Yes (N = 112) n (%) No (N = 249) n (%) χ2 test p-value Personal characteristics ≤29 59 (16.4%) 31 (27.9%) 28 (11.2%) 30 - 39 129 (35.8%) 56 (50.5%) 73 (29.3%) 40 - 49 114 (31.7%) 16 (14.4%) 98 (39.4%) Age (years) ≥50 58 (16.1%) 8 (7.2%) 50 (20.1%) p < 0.001 Women 296 (82.5%) 80 (71.4%) 216 (87.4%) Gender Men 63 (17.5%) 32 (28.6%) 31 (12.6%) p < 0.001 Single 148 (41.5%) 48 (43.2%) 100 (40.7%) Marital status Married or in cohabitation 209 (58.5%) 63 (56.8%) 146 (59.3%) n.s. Full-time 322 (89.7%) 95 (85.6%) 227 (91.5%) Work schedule Part-time 37 (10.3%) 16 (14.4%) 21 (8.5%) p < 0.05 Degree/Master/Specialization94 (26.2%) 39 (35.1%) 55 (22.2%) Educational level Diploma 265 (73.8%) 72 (64.9%) 193 (77.8%) p < 0.001 Nurses Coordinator 33 (9.2%) 16 (14.4%) 17 (6.8%) Role Nurse 327 (90.8%) 95 (85.6%) 232 (93.2%) p < 0.001 ≤5 49 (13.6%) 20 (17.9%) 29 (11.7%) 6 - 10 88 (24.4%) 32 (28.6%) 56 (22.6%) 11 - 20 144 (40.0%) 47 (42.0%) 97 (39.1%) Work experience (years) ≥20 79 (21.9%) 13 (11.6%) 66 (26.6%) p < 0.001 Context characteristics Public 212 (58.7%) 49 (43.8%) 163 (65.5%) Hospital Private 149 (41.3%) 63 (56.3%) 86 (34.5%) p < 0.001 Cardiology 59 (16.4%) 17 (15.3%) 42 (16.9%) Emergency 55 (15.3%) 17 (15.3%) 38 (15.3%) Medicine 74 (20.6%) 22 (19.8%) 52 (21.0%) Obstetrics and Neonatal 35 (9.7%) 11 (9.9%) 24 (9.7%) Paediatrics 36 (10.0%) 10 (9.0%) 26 (10.5%) Unit Surgery 100 (27.9%) 34 (30.6%) 66 (26.6%) n.s. As for ITL the nursing profession (Table 6), signifi- cant personal characteristics were: age, work schedule, role, and work experience. With regards to context cha- racteristics, there was a significant difference between public and private hospital, but not between units. Tables 7 to 9 show the course of ITL as a function of JS ratings. In regards to ITL the unit (Table 7), significant differ- ences were registered in function of JS ratings for job requirements, interaction with physicians and interaction with nurses. As for ITL the hospital (Table 8), significant differen- ces were those concerning JS rating relative to autonomy, job requirements, work organization policies and interac- tion with nurses. As far as ITL the nursing profession was concerned (Table 9), significant differences emerged from all JS factors ratings except interaction with nurses. Lastly, Tables 10 to 12 show the results obtained by the multiple logistic regression model used to identify Copyright © 2012 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS 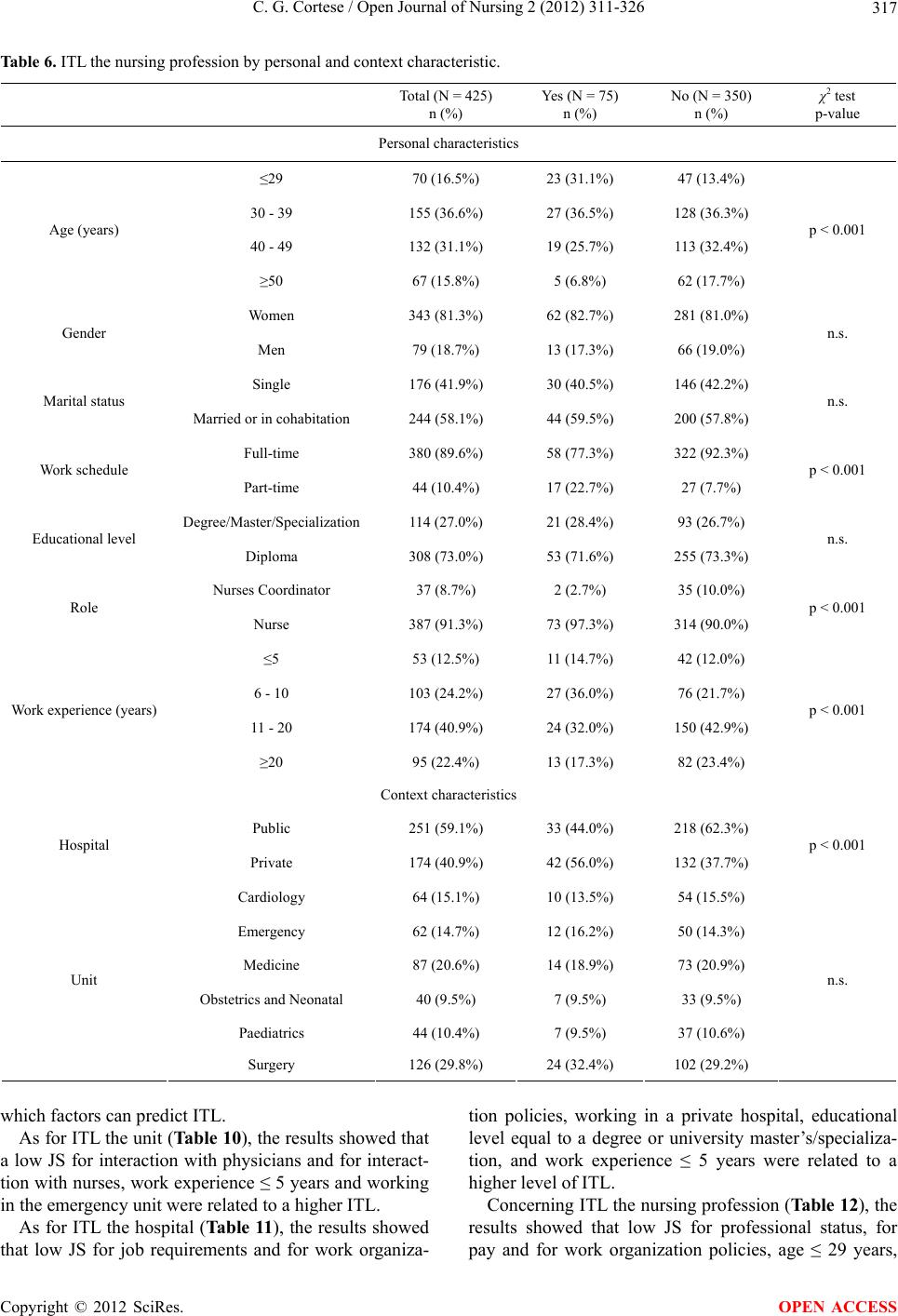 C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 317 Table 6. ITL the nursing profession by personal and context characteristic. Total (N = 425) n (%) Yes (N = 75) n (%) No (N = 350) n (%) χ2 test p-value Personal characteristics ≤29 70 (16.5%) 23 (31.1%) 47 (13.4%) 30 - 39 155 (36.6%) 27 (36.5%) 128 (36.3%) 40 - 49 132 (31.1%) 19 (25.7%) 113 (32.4%) Age (years) ≥50 67 (15.8%) 5 (6.8%) 62 (17.7%) p < 0.001 Women 343 (81.3%) 62 (82.7%) 281 (81.0%) Gender Men 79 (18.7%) 13 (17.3%) 66 (19.0%) n.s. Single 176 (41.9%) 30 (40.5%) 146 (42.2%) Marital status Married or in cohabitation 244 (58.1%) 44 (59.5%) 200 (57.8%) n.s. Full-time 380 (89.6%) 58 (77.3%) 322 (92.3%) Work schedule Part-time 44 (10.4%) 17 (22.7%) 27 (7.7%) p < 0.001 Degree/Master/Specialization 114 (27.0%) 21 (28.4%) 93 (26.7%) Educational level Diploma 308 (73.0%) 53 (71.6%) 255 (73.3%) n.s. Nurses Coordinator 37 (8.7%) 2 (2.7%) 35 (10.0%) Role Nurse 387 (91.3%) 73 (97.3%) 314 (90.0%) p < 0.001 ≤5 53 (12.5%) 11 (14.7%) 42 (12.0%) 6 - 10 103 (24.2%) 27 (36.0%) 76 (21.7%) 11 - 20 174 (40.9%) 24 (32.0%) 150 (42.9%) Work experience (years) ≥20 95 (22.4%) 13 (17.3%) 82 (23.4%) p < 0.001 Context characteristics Public 251 (59.1%) 33 (44.0%) 218 (62.3%) Hospital Private 174 (40.9%) 42 (56.0%) 132 (37.7%) p < 0.001 Cardiology 64 (15.1%) 10 (13.5%) 54 (15.5%) Emergency 62 (14.7%) 12 (16.2%) 50 (14.3%) Medicine 87 (20.6%) 14 (18.9%) 73 (20.9%) Obstetrics and Neonatal 40 (9.5%) 7 (9.5%) 33 (9.5%) Paediatrics 44 (10.4%) 7 (9.5%) 37 (10.6%) Unit Surgery 126 (29.8%) 24 (32.4%) 102 (29.2%) n.s. which factors can predict ITL. As for ITL the unit (Table 10), the results showed that a low JS for interaction with physicians and for interact- tion with nurses, work experience ≤ 5 years and working in the emergency unit were related to a higher ITL. As for ITL the hospital (Table 11), the results showed that low JS for job requirements and for work organiza- tion policies, working in a private hospital, educational level equal to a degree or university master’s/specializa- tion, and work experience ≤ 5 years were related to a higher level of ITL. Concerning ITL the nursing profession (Table 12), the results showed that low JS for professional status, for pay and for work organization policies, age ≤ 29 years, Copyright © 2012 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS 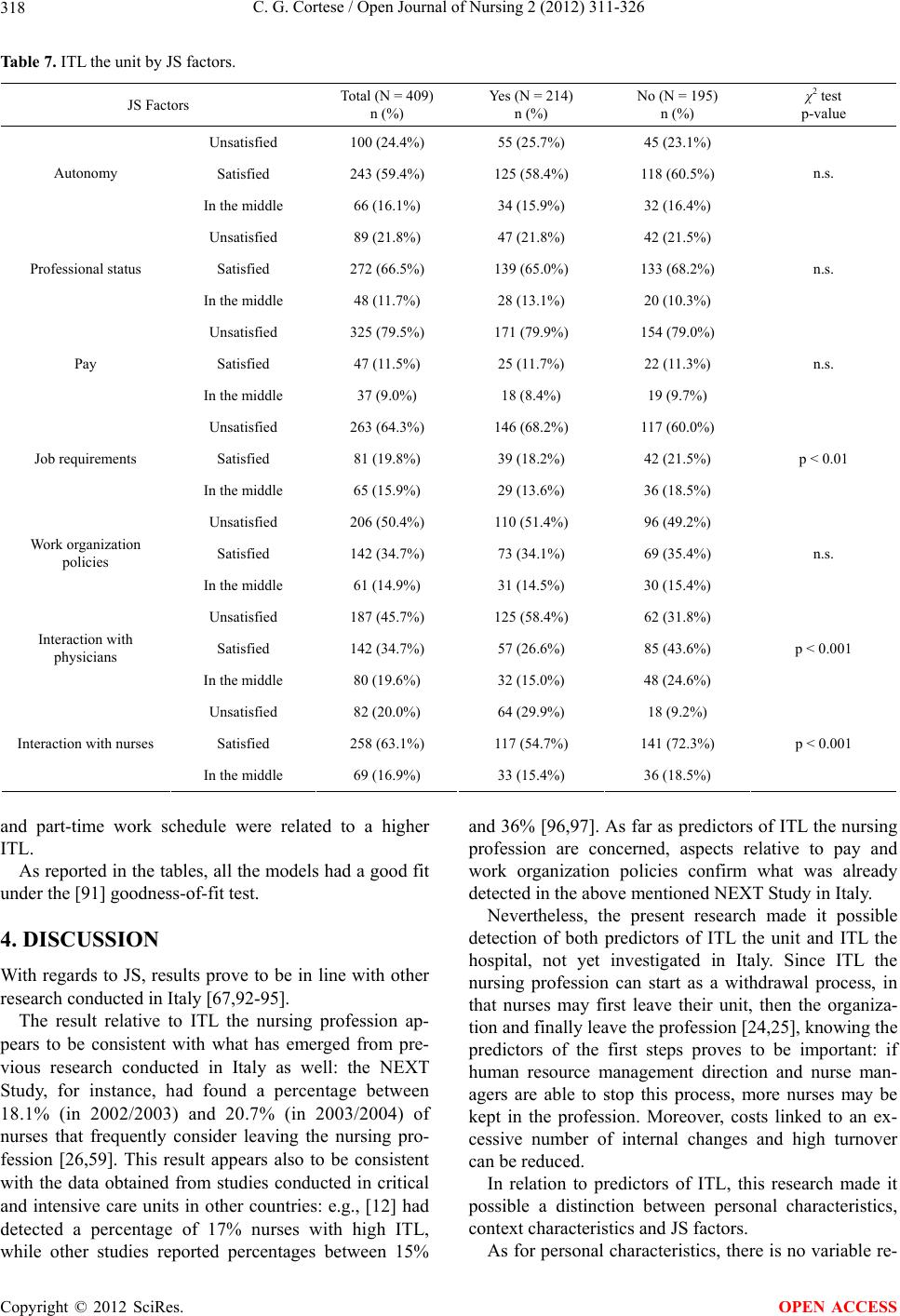 C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 318 Table 7. ITL the unit by JS factors. JS Factors Total (N = 409) n (%) Yes (N = 214) n (%) No (N = 195) n (%) χ2 test p-value Unsatisfied 100 (24.4%) 55 (25.7%) 45 (23.1%) Satisfied 243 (59.4%) 125 (58.4%) 118 (60.5%) Autonomy In the middle 66 (16.1%) 34 (15.9%) 32 (16.4%) n.s. Unsatisfied 89 (21.8%) 47 (21.8%) 42 (21.5%) Satisfied 272 (66.5%) 139 (65.0%) 133 (68.2%) Professional status In the middle 48 (11.7%) 28 (13.1%) 20 (10.3%) n.s. Unsatisfied 325 (79.5%) 171 (79.9%) 154 (79.0%) Satisfied 47 (11.5%) 25 (11.7%) 22 (11.3%) Pay In the middle 37 (9.0%) 18 (8.4%) 19 (9.7%) n.s. Unsatisfied 263 (64.3%) 146 (68.2%) 117 (60.0%) Satisfied 81 (19.8%) 39 (18.2%) 42 (21.5%) Job requirements In the middle 65 (15.9%) 29 (13.6%) 36 (18.5%) p < 0.01 Unsatisfied 206 (50.4%) 110 (51.4%) 96 (49.2%) Satisfied 142 (34.7%) 73 (34.1%) 69 (35.4%) Work organization policies In the middle 61 (14.9%) 31 (14.5%) 30 (15.4%) n.s. Unsatisfied 187 (45.7%) 125 (58.4%) 62 (31.8%) Satisfied 142 (34.7%) 57 (26.6%) 85 (43.6%) Interaction with physicians In the middle 80 (19.6%) 32 (15.0%) 48 (24.6%) p < 0.001 Unsatisfied 82 (20.0%) 64 (29.9%) 18 (9.2%) Satisfied 258 (63.1%) 117 (54.7%) 141 (72.3%) Interaction with nurses In the middle 69 (16.9%) 33 (15.4%) 36 (18.5%) p < 0.001 and part-time work schedule were related to a higher ITL. As reported in the tables, all the models had a good fit under the [91] goodness-of-fit test. 4. DISCUSSION With regards to JS, results prove to be in line with other research conducted in Italy [67,92-95]. The result relative to ITL the nursing profession ap- pears to be consistent with what has emerged from pre- vious research conducted in Italy as well: the NEXT Study, for instance, had found a percentage between 18.1% (in 2002/2003) and 20.7% (in 2003/2004) of nurses that frequently consider leaving the nursing pro- fession [26,59]. This result appears also to be consistent with the data obtained from studies conducted in critical and intensive care units in other countries: e.g., [12] had detected a percentage of 17% nurses with high ITL, while other studies reported percentages between 15% and 36% [96,97]. As far as predictors of ITL the nursing profession are concerned, aspects relative to pay and work organization policies confirm what was already detected in the above mentioned NEXT Study in Italy. Nevertheless, the present research made it possible detection of both predictors of ITL the unit and ITL the hospital, not yet investigated in Italy. Since ITL the nursing profession can start as a withdrawal process, in that nurses may first leave their unit, then the organiza- tion and finally leave the profession [24,25], knowing the predictors of the first steps proves to be important: if human resource management direction and nurse man- agers are able to stop this process, more nurses may be kept in the profession. Moreover, costs linked to an ex- cessive number of internal changes and high turnover can be reduced. In relation to predictors of ITL, this research made it possible a distinction between personal characteristics, context characteristics and JS factors. As for personal characteristics, there is no variable re- Copyright © 2012 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS 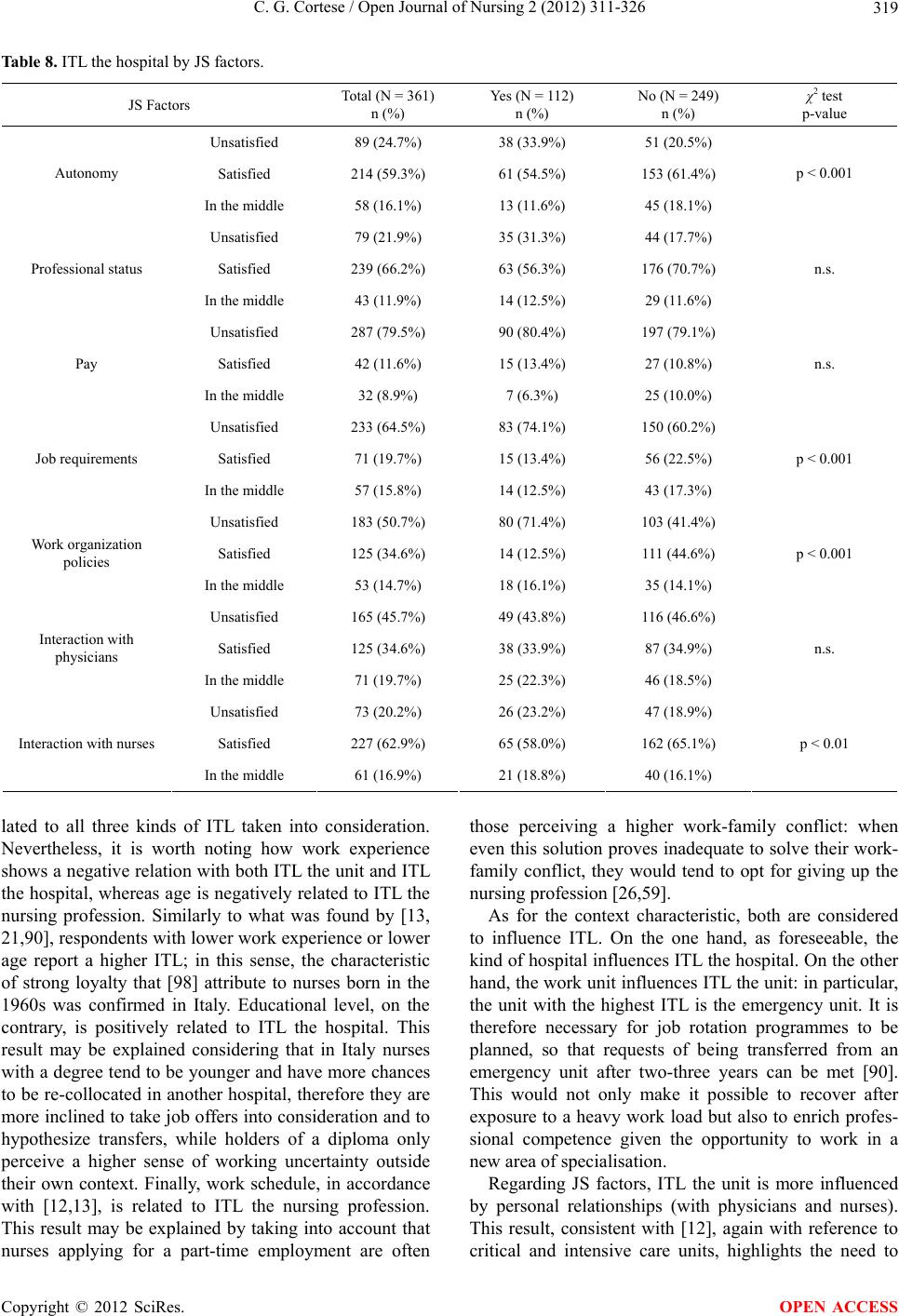 C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 319 Table 8. ITL the hospital by JS factors. JS Factors Total (N = 361) n (%) Yes (N = 112) n (%) No (N = 249) n (%) χ2 test p-value Unsatisfied 89 (24.7%) 38 (33.9%) 51 (20.5%) Satisfied 214 (59.3%) 61 (54.5%) 153 (61.4%) Autonomy In the middle 58 (16.1%) 13 (11.6%) 45 (18.1%) p < 0.001 Unsatisfied 79 (21.9%) 35 (31.3%) 44 (17.7%) Satisfied 239 (66.2%) 63 (56.3%) 176 (70.7%) Professional status In the middle 43 (11.9%) 14 (12.5%) 29 (11.6%) n.s. Unsatisfied 287 (79.5%) 90 (80.4%) 197 (79.1%) Satisfied 42 (11.6%) 15 (13.4%) 27 (10.8%) Pay In the middle 32 (8.9%) 7 (6.3%) 25 (10.0%) n.s. Unsatisfied 233 (64.5%) 83 (74.1%) 150 (60.2%) Satisfied 71 (19.7%) 15 (13.4%) 56 (22.5%) Job requirements In the middle 57 (15.8%) 14 (12.5%) 43 (17.3%) p < 0.001 Unsatisfied 183 (50.7%) 80 (71.4%) 103 (41.4%) Satisfied 125 (34.6%) 14 (12.5%) 111 (44.6%) Work organization policies In the middle 53 (14.7%) 18 (16.1%) 35 (14.1%) p < 0.001 Unsatisfied 165 (45.7%) 49 (43.8%) 116 (46.6%) Satisfied 125 (34.6%) 38 (33.9%) 87 (34.9%) Interaction with physicians In the middle 71 (19.7%) 25 (22.3%) 46 (18.5%) n.s. Unsatisfied 73 (20.2%) 26 (23.2%) 47 (18.9%) Satisfied 227 (62.9%) 65 (58.0%) 162 (65.1%) Interaction with nurses In the middle 61 (16.9%) 21 (18.8%) 40 (16.1%) p < 0.01 lated to all three kinds of ITL taken into consideration. Nevertheless, it is worth noting how work experience shows a negative relation with both ITL the unit and ITL the hospital, whereas age is negatively related to ITL the nursing profession. Similarly to what was found by [13, 21,90], respondents with lower work experience or lower age report a higher ITL; in this sense, the characteristic of strong loyalty that [98] attribute to nurses born in the 1960s was confirmed in Italy. Educational level, on the contrary, is positively related to ITL the hospital. This result may be explained considering that in Italy nurses with a degree tend to be younger and have more chances to be re-collocated in another hospital, therefore they are more inclined to take job offers into consideration and to hypothesize transfers, while holders of a diploma only perceive a higher sense of working uncertainty outside their own context. Finally, work schedule, in accordance with [12,13], is related to ITL the nursing profession. This result may be explained by taking into account that nurses applying for a part-time employment are often those perceiving a higher work-family conflict: when even this solution proves inadequate to solve their work- family conflict, they would tend to opt for giving up the nursing profession [26,59]. As for the context characteristic, both are considered to influence ITL. On the one hand, as foreseeable, the kind of hospital influences ITL the hospital. On the other hand, the work unit influences ITL the unit: in particular, the unit with the highest ITL is the emergency unit. It is therefore necessary for job rotation programmes to be planned, so that requests of being transferred from an emergency unit after two-three years can be met [90]. This would not only make it possible to recover after exposure to a heavy work load but also to enrich profes- sional competence given the opportunity to work in a new area of specialisation. Regarding JS factors, ITL the unit is more influenced by personal relationships (with physicians and nurses). This result, consistent with [12], again with reference to critical and intensive care units, highlights the need to Copyright © 2012 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS 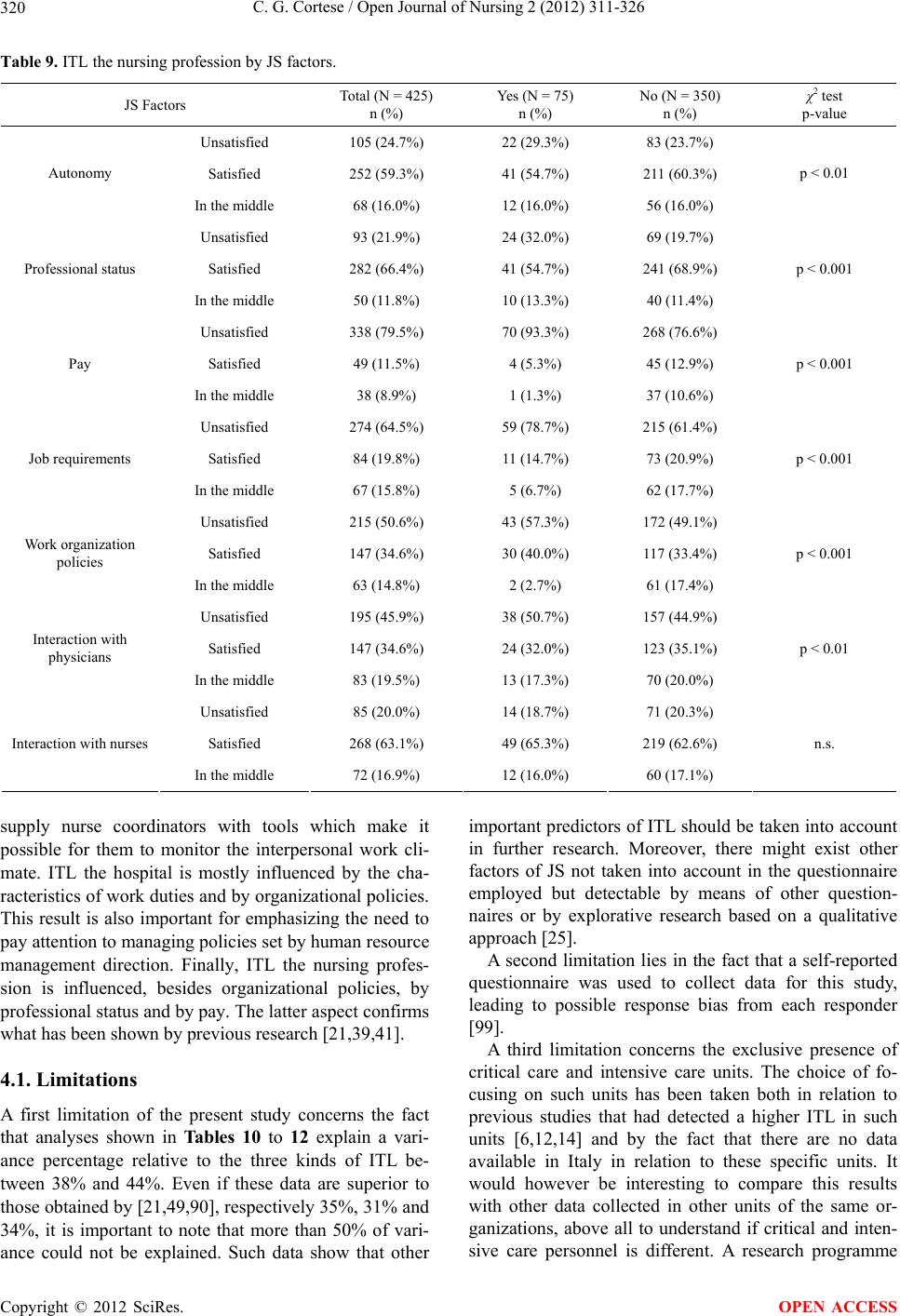 C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 320 Table 9. ITL the nursing profession by JS factors. JS Factors Total (N = 425) n (%) Yes (N = 75) n (%) No (N = 350) n (%) χ2 test p-value Unsatisfied 105 (24.7%) 22 (29.3%) 83 (23.7%) Satisfied 252 (59.3%) 41 (54.7%) 211 (60.3%) Autonomy In the middle 68 (16.0%) 12 (16.0%) 56 (16.0%) p < 0.01 Unsatisfied 93 (21.9%) 24 (32.0%) 69 (19.7%) Satisfied 282 (66.4%) 41 (54.7%) 241 (68.9%) Professional status In the middle 50 (11.8%) 10 (13.3%) 40 (11.4%) p < 0.001 Unsatisfied 338 (79.5%) 70 (93.3%) 268 (76.6%) Satisfied 49 (11.5%) 4 (5.3%) 45 (12.9%) Pay In the middle 38 (8.9%) 1 (1.3%) 37 (10.6%) p < 0.001 Unsatisfied 274 (64.5%) 59 (78.7%) 215 (61.4%) Satisfied 84 (19.8%) 11 (14.7%) 73 (20.9%) Job requirements In the middle 67 (15.8%) 5 (6.7%) 62 (17.7%) p < 0.001 Unsatisfied 215 (50.6%) 43 (57.3%) 172 (49.1%) Satisfied 147 (34.6%) 30 (40.0%) 117 (33.4%) Work organization policies In the middle 63 (14.8%) 2 (2.7%) 61 (17.4%) p < 0.001 Unsatisfied 195 (45.9%) 38 (50.7%) 157 (44.9%) Satisfied 147 (34.6%) 24 (32.0%) 123 (35.1%) Interaction with physicians In the middle 83 (19.5%) 13 (17.3%) 70 (20.0%) p < 0.01 Unsatisfied 85 (20.0%) 14 (18.7%) 71 (20.3%) Satisfied 268 (63.1%) 49 (65.3%) 219 (62.6%) Interaction with nurses In the middle 72 (16.9%) 12 (16.0%) 60 (17.1%) n.s. supply nurse coordinators with tools which make it possible for them to monitor the interpersonal work cli- mate. ITL the hospital is mostly influenced by the cha- racteristics of work duties and by organizational policies. This result is also important for emphasizing the need to pay attention to managing policies set by human resource management direction. Finally, ITL the nursing profes- sion is influenced, besides organizational policies, by professional status and by pay. The latter aspect confirms what has been shown by previous research [21,39,41]. 4.1. Limitations A first limitation of the present study concerns the fact that analyses shown in Tables 10 to 12 explain a vari- ance percentage relative to the three kinds of ITL be- tween 38% and 44%. Even if these data are superior to those obtained by [21,49,90], respectively 35%, 31% and 34%, it is important to note that more than 50% of vari- ance could not be explained. Such data show that other important predictors of ITL should be taken into account in further research. Moreover, there might exist other factors of JS not taken into account in the questionnaire employed but detectable by means of other question- naires or by explorative research based on a qualitative approach [25]. A second limitation lies in the fact that a self-reported questionnaire was used to collect data for this study, leading to possible response bias from each responder [99]. A third limitation concerns the exclusive presence of critical care and intensive care units. The choice of fo- cusing on such units has been taken both in relation to previous studies that had detected a higher ITL in such units [6,12,14] and by the fact that there are no data available in Italy in relation to these specific units. It would however be interesting to compare this results with other data collected in other units of the same or- ganizations, above all to understand if critical and inten- sive care personnel is different. A research programme Copyright © 2012 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS 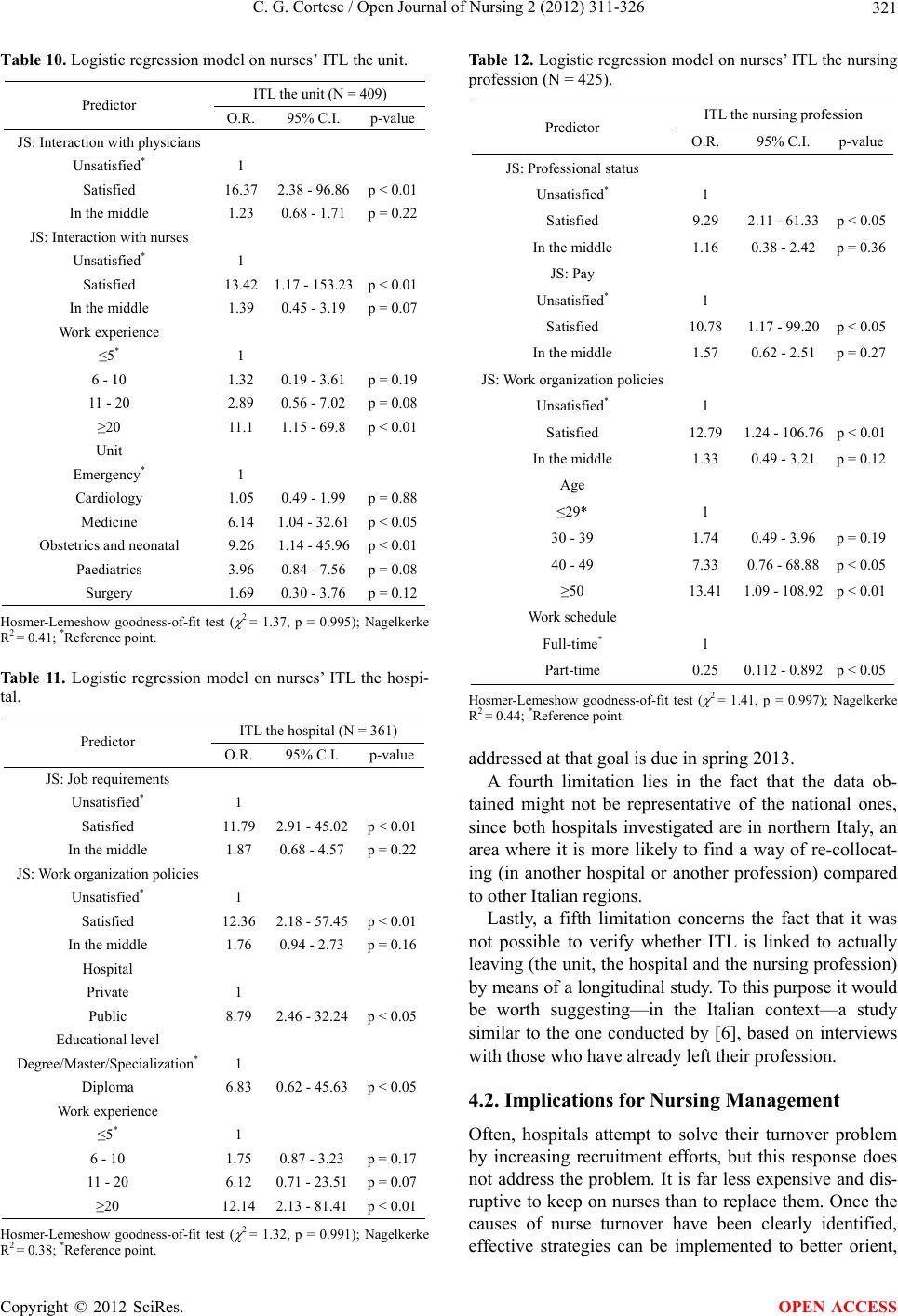 C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 321 Table 10. Logistic regression model on nurses’ ITL the unit. ITL the unit (N = 409) Predictor O.R. 95% C.I. p-value JS: Interaction with physicians Unsatisfied* 1 Satisfied 16.37 2.38 - 96.86 p < 0.01 In the middle 1.23 0.68 - 1.71 p = 0.22 JS: Interaction with nurses Unsatisfied* 1 Satisfied 13.42 1.17 - 153.23p < 0.01 In the middle 1.39 0.45 - 3.19 p = 0.07 Work experience ≤5* 1 6 - 10 1.32 0.19 - 3.61 p = 0.19 11 - 20 2.89 0.56 - 7.02 p = 0.08 ≥20 11.1 1.15 - 69.8 p < 0.01 Unit Emergency* 1 Cardiology 1.05 0.49 - 1.99 p = 0.88 Medicine 6.14 1.04 - 32.61 p < 0.05 Obstetrics and neonatal 9.26 1.14 - 45.96 p < 0.01 Paediatrics 3.96 0.84 - 7.56 p = 0.08 Surgery 1.69 0.30 - 3.76 p = 0.12 Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test ( 2 = 1.37, p = 0.995); Nagelkerke R2 = 0.41; *Reference point. Table 11. Logistic regression model on nurses’ ITL the hospi- tal. ITL the hospital (N = 361) Predictor O.R. 95% C.I. p-value JS: Job requirements Unsatisfied* 1 Satisfied 11.79 2.91 - 45.02 p < 0.01 In the middle 1.87 0.68 - 4.57 p = 0.22 JS: Work organization policies Unsatisfied* 1 Satisfied 12.36 2.18 - 57.45 p < 0.01 In the middle 1.76 0.94 - 2.73 p = 0.16 Hospital Private 1 Public 8.79 2.46 - 32.24 p < 0.05 Educational level Degree/Master/Specialization* 1 Diploma 6.83 0.62 - 45.63 p < 0.05 Work experience ≤5* 1 6 - 10 1.75 0.87 - 3.23 p = 0.17 11 - 20 6.12 0.71 - 23.51 p = 0.07 ≥20 12.14 2.13 - 81.41 p < 0.01 Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test ( 2 = 1.32, p = 0.991); Nagelkerke R2 = 0.38; *Reference point. Table 12. Logistic regression model on nurses’ ITL the nursing profession (N = 425). ITL the nursing profession Predictor O.R. 95% C.I. p-value JS: Professional status Unsatisfied* 1 Satisfied 9.29 2.11 - 61.33p < 0.05 In the middle 1.16 0.38 - 2.42p = 0.36 JS: Pay Unsatisfied* 1 Satisfied 10.78 1.17 - 99.20p < 0.05 In the middle 1.57 0.62 - 2.51p = 0.27 JS: Work organization policies Unsatisfied* 1 Satisfied 12.79 1.24 - 106.76p < 0.01 In the middle 1.33 0.49 - 3.21p = 0.12 Age ≤29* 1 30 - 39 1.74 0.49 - 3.96p = 0.19 40 - 49 7.33 0.76 - 68.88p < 0.05 ≥50 13.41 1.09 - 108.92p < 0.01 Work schedule Full-time* 1 Part-time 0.25 0.112 - 0.892p < 0.05 Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test ( 2 = 1.41, p = 0.997); Nagelkerke R2 = 0.44; *Reference point. addressed at that goal is due in spring 2013. A fourth limitation lies in the fact that the data ob- tained might not be representative of the national ones, since both hospitals investigated are in northern Italy, an area where it is more likely to find a way of re-collocat- ing (in another hospital or another profession) compared to other Italian regions. Lastly, a fifth limitation concerns the fact that it was not possible to verify whether ITL is linked to actually leaving (the unit, the hospital and the nursing profession) by means of a longitudinal study. To this purpose it would be worth suggesting—in the Italian context—a study similar to the one conducted by [6], based on interviews with those who have already left their profession. 4.2. Implications for Nursing Management Often, hospitals attempt to solve their turnover problem by increasing recruitment efforts, but this response does not address the problem. It is far less expensive and dis- ruptive to keep on nurses than to replace them. Once the causes of nurse turnover have been clearly identified, effective strategies can be implemented to better orient, Copyright © 2012 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS  C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 322 educate, satisfy, motivate, and keep on quality nursing staff [6]. In light of this remark some interventions are suggested. In general terms, nurse managers should regularly mo- nitor ITL the unit, the hospital, and the nursing profes- sion in their organizations (e.g. with survey question- naires or as a part of developmental discussions) because a period of consideration (even two-three years) has been detected before nurses make the final decision to leave [26,27]. In addition, according to [100], interviews with nurses leaving the hospital or the nursing profession should also be performed to find out why they have made the final decision to leave: such information would be useful in limiting the number of nurses from leaving in the future. It would also be relevant to plan actions aimed at favouring organizational socialization in order to foster efficacy of new personnel’s integration, particu- larly in units showing a higher turnover. Other interventions could focus on the variables that have proved to be predictors of ITL. In order to limit ITL the unit, the quality of the rela- tionship with physicians and colleagues should be im- proved, favouring, for instance, meeting opportunities, even informal, for the unit staff, or offering people in charge (head physicians and nurse coordinators) training or counselling programmes aimed at acquiring better competence in group management. It would also be im- portant to offer the possibility to change units, even re- maining within critical care and intensive care units, to nurses who show a desire to do so, in order to reduce the likelihood of the development of ITL the hospital or the nursing profession. To reduce ITL the hospital it would be important to focus on working demands and on organizational po- licies. In particular, after examining our research results, de-bureaucratizing activities and better managing shifts and schedules. As for the latter, the solution suggested by [6] could be considered: giving nurses wishing to the possibility to chose the weekend package, catching up hours on other weekdays. This would allow other nurses to work fewer weekends. Moreover, in order to limit ITL the hospital, competence of graduated nurses should be acknowledged by verifying that attributions of responsi- bilities and career promotions are based truly on merit. In order to lessen ITL the nursing profession, [6]’s advice relative to autonomy and acknowledgement could be followed: staff nurses are encouraged to participate in nursing committees, assume leadership roles, and be- come decision-makers. Moreover, the organization should reconsider its performance evaluation system in order to recognize clinical excellence in nursing. As for pay, on the other hand, commitment should be undertaken by the IPASVI Federation to negotiate a National collective agreement adequate to the professionalism shown by nurses working in Italian hospitals. REFERENCES [1] Flinkman, M., Leino-Kilpi, H. and Salanterä, S. (2010) Nurses’ intention to leave the profession: Integrative re- view. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 66, 1422-1434. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2010.05322.x [2] Simoens, S., Villeneuve, M. and Hurst, J. (2005) Tackling nurse shortages in OECD Countries. OECD Health Wor- king Papers, 19. http://www.oecd.org/health/healthpoliciesanddata/345713 65.pdf [3] World Health Organization (2008) The world health re- port 2008—Now more than ever. http://www.who.int/whr/2008/whr08_en.pdf [4] Oulton, J.A. (2006) The global nursing shortage: An over- view of Issues and Actions. Policy Politics Nursing Pra- ctice, 7, 34S-39S. doi:10.1177/1527154406293968 [5] Dubois, C.-A., McKee, M. and Rechel, B. (2006) Critical challenges facing the health care workforce in Europe. In: Rechel, B., Dubois, C.-A. and McKee, M., Eds, World Health Organization, on Behalf of the European Obser- vatory on Heath Systems and Policies, The Cromwell Press, Trowbridge, 1-18. http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0008/914 75/E89156.pdf [6] Strachota, E., Normandin, P., O’Brien, N., Clary, M. and Krukow, B. (2003) Reasons registered nurses leave or change employment status. Journal of Nursing Admini- stration, 33, 111-117. http://journals.lww.com/jonajournal/Fulltext/2003/02000/ Reasons_Registered_Nurses_Leave_or_Change.8.aspx [7] Clarke, S. and Aiken, L. (2003) Failure to rescue: Need- less deaths are prime examples of the need for more nur- ses at the bedside. American Journal of Nursing, 103, 42- 47. http://www.uic.edu/depts/oce/OCEweb/04FA/ClarkeAike n.pdf [8] Aiken, L.H., Clarke, S.P., Sloane, D.M., Sochalski, J.A. and Silber, J.H. (2002) Hospital nurse staffing and patient mortality, nurse burnout, and job dissatisfaction. Journal of the American Medical Association, 288, 1987-1993. doi:10.1001/jama.288.16.1987. [9] Wagner, C.M. (2010) Predicting nursing turnover with catastrophe theory. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 66, 2071- 2084. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2010.05388.x [10] Rivers, P.A., Tsai, K.-L. and Munchus, G. (2005) The fi- nancial impacts of the nursing shortage. Journal of Health Care Finance, 31, 52-64. http://content.ebscohost.com/pdf9/pdf/2005/HLT/01Mar0 5/16946431.pdf [11] Jones, C.B. (2005) The costs of nurse turnover, part 2: Application of the nursing turnover cost calculation me- thodology. Journal of Nursing Administration, 35, 41-49. http://journals.lww.com/jonajournal/Abstract/2005/01000 /The_Costs_of_Nurse_Turnover,_Part_2__Application.1 4.aspx Copyright © 2012 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS  C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 323 [12] Stone, P.W., Larson, E.L., Mooney-Kane, C., Smolowitz, J., Lin, S.X. and Dick, A. (2009) Organizational climate and intensive care unit nurses’ intention to leave. Journal of Nursing Administration, 39, S37-S42. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000218411.53557.29 [13] van Dam, K., Meewis, M. and van der Heijden, B.I. (2012) Securing intensive care: towards a better understanding of intensive care nurses’ perceived work pressure and turn- over intention. Journal of Advanced Nursing, in press. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2012.05981.x. [14] Odom, J. (2000) Nursing shortage: Impending doom or challenging opportunity. Journal Perianesthesia Nursing, 15, 348-349. doi:10.1053/jpan.2000.18206 [15] Bertinato, L., Glinos, I.A., Boscolo, E. and Ciato, L. (2009) Oversupplying doctors but seeking carers: Italy’s demo- graphic challenges and health professional mobility. Health Professional Mobility and Health Systems Observatory Studies, 23, 243-262. http://www.sfes.info/IMG/pdf/Health_professional_mobil ity_and_Health_systems.pdf#page=276 [16] Chaloff, J. (2008) Mismatches in the formal sector, ex- pansion of the informal sector: Immigration of health pro- fessionals to Italy. Organisation for Economic Co-opera- tion and Development Health Working Papers, Paris, 34. http://www.oecd.org/italy/41431698.pdf [17] Ghizzoni, A.M. and Avenati, L. (2010) La professione in- fermieristica, una scelta che paga. L’infermiere, 1, 18-23. [18] Regione Emilia Romagna (2011) Dinamiche del perso- nale infermieristico nelle Aziende sanitarie. Permanenza in servizio e mobilità in uscita. http://asr.regione.emilia-romagna.it/wcm/asr/collana_dos sier/doss100.htm [19] Wismar, M., Maier, C.B., Glinos, I.A., Dussault, G. and Figueras, J. (2011) Health professional mobility and health systems. Evidence from 17 European countries. http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0017/152 324/e95812.pdf [20] Sourdif, J. (2004) Predictors of nurses’ intent to stay at work in a university health center. Nursing and Health Sciences, 6, 59-68. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2018.2003.00174.x [21] Tourangeau, A.E. and Cranley, L.A. (2006) Nurse inten- tion to remain employed: Understanding and strengthen- ing determinants. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 55, 497- 509. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2006.03934.x [22] Beecroft, P.C., Dorey, F. and Wenten, M. (2008) Turno- ver intention in new graduate nurses: A multivariate ana- lysis. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 62, 41-52. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2007.04570.x [23] Galletta, M., Portoghese, I., Penna, M.P., Battistelli, A. and Saiani, L. (2011) Turnover intention among Italian nurses: The moderating roles of supervisor support and organizational support. Nursing & Health Sciences, 13, 184-191. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2018.2011.00596.x [24] Krausz, M., Koslowsky, M., Shalom, N. and Elyakim, N. (1995) Predictors of intentions to leave the ward, the hos- pital, and the nursing profession: An longitudinal study. Journal of Organizational Behaviour, 16, 277-288. doi:10.1002/job.4030160308 [25] Morrell, K. (2005) Towards a typology of nursing turn- over: The role of shocks in nurses’ decisions to leave. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 49, 315-322. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2004.03290.x [26] Hasselhorn, H.-M., Muller, B.H., Tackenberg, P., Witten- berg, J., Kuemmerling, A., Simon, M. and the NEXT Stu- dy Group (2005) Nursing in Europe: Intention to leave the nursing profession. In: Hasselhorn, H.-M., Muller, B.H. and Tackenberg, P., Eds., NEXT Scientific Report, Elanders Gotab AB, Vallingby, 17-24. [27] Lum, L., Kervin, J., Clark, K., Reid, F. and Sirola, W. (1998) Explaining nursing turnover intent: Job satisfac- tion, pay satisfaction, on organizational commitment? Journal of Organizational Behaviour, 19, 305-320. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1379(199805) [28] Tham, P. (2007) Why are they leaving? Factors affecting intention to leave among social workers in child welfare. British Journal of Social Work, 37, 1225-1246. doi:10.1093/bjsw/bcl054 [29] McCarthy, G., Tyrrel, M.P. and Lehane, E. (2007) Inten- tion to “leave” or “stay” in nursing. Journal of Nursing Management, 15, 248-255. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2834.2007.00648.x [30] Shields, M.A. and Ward, M. (2001) Improving nurse retention in the National Health Service in England: The impact of job satisfaction on intention to quit. Journal of Health Economics, 20, 677-701. doi:10.1016/S0167-6296(01)00092-3 [31] Borda, B. and Norman, I. (1997) Factors influencing turn- over and absence of nurses: A research review. Interna- tional Journal of Nursing Studies, 34, 385-394. doi:10.1016/S0020-7489(97)00031-X, [32] Cowin, L. (2002) The effects of nurses’ job satisfaction on retention: An Australian perspective. Journal of Nurs- ing Administration, 32, 283-291. http://journals.lww.com/jonajournal/Abstract/2002/05000 /The_Effects_of_Nurses__Job_Satisfaction_on.8.aspx [33] Destrebecq, A., Terzoni, S., Colosso, C., Neri, L. and Brambilla, G. (2009) Intention to leave nursing in a major Milan hospital: Current situation and future perspectives. La medicina del Lavoro, 100, 109-119. [34] Hsiao, Y. and Lu, M. (1996) A study of organizational commitment, organizational retention and professional retention of clinical nurses? Nursing Research, 4, 137- 150. [35] Ingersoll, G.L., Olsan, T., Drew-Cates, J., DeVinney, B.C. and Davies, J. (2002) Nurses’ job satisfaction, organiza- tional commitment and career intent. Journal of Nursing Administration, 32, 250-263. http://journals.lww.com/jonajournal/Abstract/2002/05000 /Nurses__Job_Satisfaction,_Organizational.5.aspx [36] Price, J.L. (2004) The development of a causal model of voluntary turnover. In: Griffeth and Hom, P., Eds, Inno- vative Theory and Empirical Research on Employee Turnover, Information Age Publishing, Charlotte, 3-32. [37] Barron, D. and West, A.E. (2005) Leaving nursing: An event-history analysis of nurses’ career. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy, 10, 105-157. [38] Lacey, L.M. (2003) Called into question: What nurses Copyright © 2012 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS  C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 324 want? Nursing Management, 34, 25-26. [39] Santos, S.R. and Cox, K. (2000) Workplace adjustment and intergenerational differences between nurses, boom- ers and Xers. Nursing Economics, 18, 7-13. [40] Roberts, B.J., Jones, C. and Lynn, M. (2004) Job satisfac- tion of new baccalaureate nurses. Journal of Nursing Ad- ministration, 34, 428-435. http://journals.lww.com/jonajournal/Fulltext/2004/09000/ Job_Satisfaction_of_New_Baccalaureate_Nurses.9.aspx [41] Larrabee, J.H., Janney, M.A., Ostrow, C.L., Withrow, M.L., Hobbs, G.R. and Burant, C. (2003) Predicting reg- istered nurse job satisfaction and intent to leave. Journal of Nursing Administration, 33, 271-283. http://journals.lww.com/jonajournal/Fulltext/2003/05000/ Predicting_Registered_Nurse_Job_Satisfaction_and.3.a s px [42] Flinkman, M., Laine, M., Leino-Kilpi, H., Hasselohorn, H.-M. and Salanterä, S. (2008) Explaining young regis- tred Finnish nurses’ intention to leave the profession: A questionnaire survey. International Journal of Nursing Study, 45, 727-739. doi:10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2006.12.006 [43] Joshua-Amadi, M. (2002) Recruitment and retention: A study in motivation. Nursing Management, 9, 17-21. http://nursingmanagement.rcnpublishing.co.uk/archive/art icle-recruitment-and-retention-a-study-in-motivation [44] Blegen, M.A. (1993) Nurses’ job satisfaction: A meta- analysis of related variables. Nursing Research, 42, 36-41. doi:10.1097/00006199-199301000-00007 [45] Hu, J., Herrick, C. and Allard, H.K. (2004) Managing the multigenerational nursing team. The Health Care Man- ager, 23, 334-340. http://journals.lww.com/healthcaremanagerjournal/Abstra ct/2004/10000/Managing_the_Multigenerational_Nursing _Team.8.aspx [46] Kuokkanen, L., Leino-Kilpi, H. and Katajisto, J. (2003) Nurse empowerment, job-related satisfaction, and organ- izational commitment. Journal of Nursing Care Quality, 18, 184-193. [47] Laine, M. (2005) Hoitajana huomennakin. Hoitajien tyo- paikkaan ja ammattiin sitoutuminen/Organizational and professional commitment of nurses. Finnish Institute of Occupational Health. University of Turku, Scripta lingua Finnica edita 0082-6995. [48] Chan, E. and Morrison, P. (2000) Factors influencing the retention and turnover intentions of registered nurses in a Singapore hospital. Nursing and Health Sciences, 2, 113- 121. doi:10.1046/j.1442-2018.2000.00046.x [49] Shader, K., Broome, M.E., Broome, C.D., West, M.E. and Nash, M. (2001) Factors influencing satisfaction and an- ticipated turnover for nurses in an academic medical cen- ter. Journal of Nursing Administration, 31, 210-217. http://journals.lww.com/jonajournal/Fulltext/2001/04000/ Factors_Influencing_Satisfaction_and_Anticipated.10. as px [50] Takase, M., Maude, P. and Manias, E. (2006) The impact of role discrepancy on nurses’ intention to quit their jobs. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 15, 1071-1080. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2702.2005.01508.x [51] Ito, H., Eisen, S.V., Sederer, L.I., Yamada, O. and Tachi- mori, H. (2001) Factors affecting psychiatric nurses’ in- tention to leave their current job. Psychiatric Services, 52, 232-234. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.52.2.232 [52] Acker, G.M. (2004) The effect of organizational condi- tions (role conflict, role ambiguity, opportunities for pro- fessional development, and social support) on job satis- faction and intention to leave among social workers in mental health care. Community Mental Health Journal, 40, 65-73. doi:10.1023/B:COMH.0000015218.12111.26 [53] Adams, A. and Bond, S. (2000) Hospital nurses’ job sat- isfaction, individual and organizational characteristics. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 32, 536-543. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2648.2000.01513.x. [54] Hemingway, M.A. and Smith, C.S. (1999) Organizational climate and occupational stressors as predictors of with- drawal behaviours and injuries in nurse. Journal of Oc- cupational and Organizational Psychology, 72, 285-299. doi:10.1348/096317999166680 [55] AbuAlRub, R.F. and Al-Zaru, I.M. (2008) Job stress, re- cognition, job performance and intention to stay at work among Jordanian hospital nurses. The Journal of Nursing Management, 16, 227-236. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2834.2007.00810.x [56] Barnett, R.C., Gareis, K.C. and Carr, P.L. (2005) Career satisfaction and retention of women physicians who work reduced hours. Journal of Women’s Health, 14, 146-153. doi:10.1089/jwh.2005.14.146. [57] Camerino, D., Conway, P.M., van der Heijden, B.I.J.M., Estryn-Béhar, M., Costa, G. and Hasselhorn, H.-M. (2008) Age-dependent relationship between work ability, think- ing of quitting the job, and actual leaving among Italian nurse: A longitudinal study. International Journal of Nurs- ing Studies, 45, 1645-1659. doi:10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2008.03.002 [58] Estryn-Be’har, Van der Heijden, B.I., Oginska, H., Came- rino, D., Le Nèzet, O., Conway, P.M., Fry, C., Hassel- horn, H.-M. and NEXT Study Group (2007) The impact of social work environment, teamwork characteristics, burnout, and personal factors upon intent to leave among European nurse. Medical Care, 45, 939-950. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e31806728d8 [59] Hasselhorn, H.-M., Muller, B.H. and Tackenberg, P. (2005) NEXT Scientific Report. http://www.econbiz.de/archiv1/2008/53602_nurses_work _europe.pdf [60] Hasselhorn, H.M., Tackenberg, P. and Müller, B.H. (2003) Working conditions and intent to leave the profession among nursing staff in Europe. SALTSA—Joint Program- me for Working Life Research in Europe Report No 7, 7. http://nile.lub.lu.se/arbarch/saltsa/2003/wlr2003_07.pdf [61] Simon, M., Kummerling, A., Hasselhorn, H.M. and NEXT Study Group (2004) Work-home conflict in the European nursing profession. International Journal of Occupatio- nal Environmental Health, 10, 384-391. [62] Balloch, S., Pahl, J. and McLean, J. (1998) Working in the social services: Job satisfaction, stress and violence. British Journal of Social Work, 28, 329-350. http://bjsw.oxfordjournals.org/content/28/3/329.short Copyright © 2012 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS  C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 325 [63] Zeytinoglu, I.U., Denton, M., Davies, S., Baumann, A., Blythe, J. and Boos, L. (2006) Retaining nurses in their employing hospitals and in the profession: Effects of job preference, unpaid overtime, importance of earnings and stress. Health Policy, 79, 57-72. doi:10.1016/j.healthpol.2005.12.004 [64] Spector, P.E. (1997) Job satisfaction. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks. [65] Weiss, H.M. (2002) Deconstructing job satisfaction: Sep- arating evaluations, beliefs and affective experiences. Hu- man Resource Management Review, 12, 173-194. doi:10.1016/S1053-4822(02)00045-1 [66] Williams, J. (2004) Job satisfaction and organizational commitment, a Sloan Work and Family Encyclopedia en- try. http://wfnetwork.bc.edu/encyclopedia_entry.php?id=244 &area=academics [67] Cortese, C.G. (2007) Job satisfaction of Italian nurses: An exploratory study. Journal of Nursing Management, 15, 303-312. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2834.2007.00694.x [68] Aiken, L.H., Clarke, S.P. and Sloane, D.M. (2000) Hos- pital restructuring: does it adversely affect care and out- comes? The Journal of Nursing Administration, 30, 457- 465. http://journals.lww.com/jonajournal/Abstract/2000/10000 /Hospital_Restructuring__Does_It_Adversely_Affect.3.a spx [69] Aiken, L.H., Smith, H.L. and Lake, E.T. (1994) Lower medicare mortality among a set of hospitals known for good nursing care. Medical care, 32, 771-787. http://www.jstor.org/discover/10.2307/3766652?uid=373 8296&uid=2&uid=4&sid=21101282535247 [70] Hellman, C.M. (1997) Job satisfaction and the intent to leave. Journal of Social Psychology, 137, 677-689. doi:10.1080/00224549709595491 [71] Kramer, M. and Schmalenberg, C. (1991) Job satisfaction and retention. Insight for the 90’s. Nursing, 21, 50-55. [72] Ruggiero, J.S. (2005) Health, work variables, and job sa- tisfaction among nurses. Journal of Nursing Administra- tion, 35, 254-263. http://journals.lww.com/jonajournal/Fulltext/2005/05000/ Health,_Work_Variables,_and_Job_Satisfaction_Among. 9.aspx [73] Sochalski, J. (2001) Nursing’s valued resources: Critical issues in economics and nursing care. The Canadian Jour- nal of Nursing Research, 33, 11-18. [74] Tzeng, H.M. (2002) Satisfying nurses on job factors they care about. A Taiwanese perspective. Journal of Nursing Administration, 32, 306-309. http://journals.lww.com/jonajournal/Fulltext/2002/06000/ Satisfying_Nurses_on_Job_Factors_They_Care_About.5. aspx [75] Bowling, N.A., Eschleman, K.J. and Wang, Q. (2010) A meta-analytic examination of the relationship between job satisfaction and subjective well-being. Journal of Oc- cupational and Organizational Psychology, 83, 915-934. doi:10.1348/096317909X478557 [76] Jenkins, J.M. (1993) Self monitoring and turnover: The impact of personality on intent to leave. Journal of Orga- nizational Behaviour, 14, 83-91. doi:10.1002/job.4030140108 [77] Stamps, P.L. (1997) Nurses and work satisfaction: An in- dex for measurement. Healt Administration Press, Chi- cago. [78] Adams, A., Bond, S. and Hale, C.A. (1998) Nursing orga- nizational practice and its relationship with other features of ward organization and job satisfaction. Journal of Ad- vanced Nursing, 27, 1212-1222. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2648.1998.00657.x [79] Irvine, D.M. and Evans, M.G. (1995) Job-satisfaction and turnover among nurses—Integrating research findings across studies. Nursing Research, 44, 246-253. doi:10.1097/00006199-199507000-00010 [80] Kangas, S., Kee, C.C. and McKee-Waddle, R. (1999) Or- ganizational factors, nurses’ job satisfaction, and patient satisfaction with nursing care. Journal of Nursing Admi- nistration, 29, 32-42. http://journals.lww.com/jonajourn al/Fulltext/199 9/0100 0/O rganizational_Factors,_Nurses__Job_Satisfaction,.6.asp x [81] Mäkinen, A., Kivimäki, M., Elovainio, M., Virtanen, M. and Bond, S. (2003) Organization of nursing care as a deter- minant of job satisfaction among hospital nurses. Journal of Nursing Management, 11, 299-306. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2834.2003.00399.x [82] Mills, A. and Blaesing, S. (2000) A lesson from the last nursing shortage. Journal of Nursing Administration, 30, 309-315. http://journals.lww.com/jonajourn al/Fulltext/200 0/0600 0/A _Lesson_from_the_Last_Nursi ng_Sh ortage__The. 9.aspx [83] Tovey, E.J. and Adams, A.E. (1999) The changing nature of nurses’ job satisfaction: An exploration of sources of satisfaction in the 1990s. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 30, 150-158. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2648.1999.01059.x [84] Cavanagh, S.J. (1992) Job satisfaction of nursing staff working in hospitals. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 17, 704-711. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.1992.tb01968.x [85] Best, M.F. and Thurston, N.E. (2004) Measuring nursing job satisfaction. Journal of Nurcing Administration, 34, 283-290. http://journals.lww.com/jonajournal/Abstract/2004/06000 /Measuring_Nurse_Job_Satisfaction.7.aspx [86] Ma, C.C., Samuels, M.E. and Alexander, J.W. (2003) Fac- tors that influence nurses’ job satisfaction. Journal of Nursing Administration, 33, 293-299. http://journals.lww.com/jonajournal/Abstract/2003/05000 /Factors_That_Influence_Nurses__Job_Satisfaction.5.aspx [87] Cortese, C.G., Colombo, L. and Ghislieri, C. (2010) De- terminants of nurses’ job satisfaction: The role of work- family conflict, job demand, emotional charge and social support. Journal of Nursing Management, 18, 35-43. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2834.2009.01064.x [88] Ganster, D.C. and Schaubroeck, J. (1991) Work stress and employee health. Journal of Management, 17, 235- 271. doi:10.1177/014920639101700202 [89] Netemeyer, R.G., McMurrian, R. and Boles, J.S. (1996) Development and validation of work-family conflict and Copyright © 2012 SciRes. OPEN ACCESS  C. G. Cortese / Open Journal of Nursing 2 (2012) 311-326 Copyright © 2012 SciRes. 326 OPEN ACCESS family-work conflict scales. Journal of Applied Psychol- ogy, 81, 400-410. doi:10.1037/0021-9010.81.4.400 [90] Chan, M.F., Luk, A.L., Leong, S.M., Yeung, S.M. and Van, I.K. (2008) Factors influencing Macao nurses’ in- tention to leave current employment. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 18, 893-901. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2702.2008.02463.x [91] Hosmer, D. W. and Lemeshow, S. (2000) Applied logis- tic regression. Wiley, New York. [92] Camerino, D., Conway, P.M. and Lusignani, M. (2005) Condizioni di lavoro e intenzione di cambiare: Risultati dello studio europeo NEXT in Italia. Giornale Italiano di Scienze Infermieristiche, 1, 12-25. http://air.unimi.it/handle/2434/5427 [93] Camerino, D., Lusignani, M., Conway, P., Bertazzi, P.A. and Gruppo NEXT (2004) L’intenzione di lasciare la professione infermieristica. La Medicina del Lavoro, 95, 354-364. http://www.lamedicinadellavoro.it/summary/2004/vol_95 _05/02_vol_95_05.pdf [94] Ferrari, F. (2010) The nurse job satisfaction. Comparison between ideal job and organizational reality: A prelimi- nary study. Munich Personal RePEc Archive Paper. http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/24798/ [95] Tabolli, S., Ianni, A., Renzi, C., Di Pietro, C. and Puddu, P. (2006) Job satisfaction, burnout and stress amongst nursing staff: A survey in two hospitals in Rome. Gior- nale Italiano di Medicina del Lavoro ed Ergonomia, 28, 49-52. http://gimle.fsm.it/28/1s_psi/07.pdf [96] Steel, R.P. (2002) Turnover theory at the empirical in- terface: Problem of fit and function. Academic of Man- agement Review, 27, 346-360. http://www.jstor.org/discover/10.2307/4134383?uid=373 8296&uid=2&uid=4&sid=21101293632717 [97] Tai, T.W., Bame, S.I. and Robinson, C.D. (1998) Review of nursing turnover research, 1977-1996. Social Science & Medicine, 47, 1905-1924. doi:10.1016/S0277-9536(98)00333-5 [98] Wilson, B., Squires, M., Widger, K., Cranley, L. and Tou- rangeau, A. (2008) Job satisfaction among a multigenera- tional nursing workforce. Journal of Nursing Manage- ment, 16, 716-723. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2834.2008.00874.x [99] Polit, D.F. and Beck, C.T. (2004) Nursing research: Prin- ciples and methods. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Phi- ladelphia. [100] O’Brien-Pallas, L., Griffin, P., Shamion, J., Buchan, L., Duffield, C., Hughes, F., et al. (2006) The impact of nurse turnover on patient, nurse, and system outcomes: A pilot study and focus for a multicenter international study. Po- licy, Politics, & Nursing Practice, 7, 169-179. doi:10.1177/1527154406291936
|