iBusiness
Vol. 4 No. 2 (2012) , Article ID: 19980 , 8 pages DOI:10.4236/ib.2012.42023
Research on the Mobile Electronic Delivery Platform for Iron and Steel Sales Logistics Based on 3G Netbook
![]()
1Institute of Systems Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China; 2Logistics Management Company, Wuhan Iron and Steel (Group) Corporation, Wuhan, China.
Email: shizg@uestc.edu.cn
Received February 27th, 2012; revised March 9th, 2012; accepted March 19th, 2012
Keywords: 3G Netbook; Iron and Steel Enterprise; Sales Logistics; Mobile Electronic Delivery Platform
ABSTRACT
According to the situation of sales logistics transportation management in an iron and steel enterprise and the possible logistics risks, the architecture of mobile electronic delivery platform for iron and steel sales logistics based on 3G netbook is proposed. The delivery process based on 3G netbook is analyzed. The three-tier C/S-based platform framework is also proposed, including database server, application server and clients. The function design of the platform is given. Finally, the key technologies of the platform are discussed.
1. Introduction
Goods delivery, as an important link in a sail logistics, is referred to carry goods to the destination and be endorsed by the consignee according to a transportation contract [1]. In the present transportation logistics of a Chinese iron and steel enterprise, delivery information (e.g., goods type, quantity, quality) are mostly recorded in a written documentation form called quality delivery bill. The disadvantages of this form are that the information about each link is isolated and the transportation process is short of effectively real-time monitoring, which will result in higher logistics risk. Although the advantages of GPS monitoring system had been taken by most Chinese large-scale iron and steel enterprises to achieve real-time carriers (such as vehicles and vessels) positioning, tracking and scheduling, there is still lacking of intelligent management and control in transit. Delivery information is usually delayed, not detailed, and difficultly inquired. Thus, the communication between an iron and steel enterprise and its customers will be backward and not unblocked.
As the continuous development of electronic computer and Internet, its application is increasing popular since the 20th century. In the field of economy and trade, it appears various kinds of commercial trading activities realized by electronic means. A mass of electronic tools (such as cell phones, PDA, etc.) and network (such as the current GMS, GPRS, CDMA 1X and developing 3G wireless wan technologies, etc.) have been used systematically, which makes the commodity exchange higher efficiency and lower cost. It is the inevitable trend that delivery means will be electronic and mobile. The inquiring system based on PDA has been widely used in present express industry [1]. The integrated application of PDA, GPRS, GPS and GIS which is popularized in public security industry is an ideal solution for mobile police [2]. The application system using intelligent PDA phone as the terminal is playing a major role in flood contact as well [3]. Electronic delivery system and method for integrating global financial services has been studied in United States [4]. In order to reduce the logistics risk of unforeseen events during the distribution process, some scholars believe that improvement opportunities still lie in the area of real-time distribution management [5]. On the basis of technologies and information systems allowing for seamless mobile and wireless connectivity between delivery vehicles and distribution facilities, a system architecture for urban distribution and real-time event-driven vehicle management has been proposed, and the on-board truck computer is discussed to be used as a carrier [6].
Mobile electronic delivery is referred to running electronic delivery procedures on mobile computer such as 3G netbook. The real-time information about each transportation link can be collected and sent to the controlling center. The electronic data loading specific information instead of traditional paper document is applied to transmit information, so as to realize the easy, fast and effective monitoring of the transportation and delivery process [7]. Electronic payment [8] has been widely used in communication, bank [9] and express industries now. In the sales logistics of iron and steel enterprises, the primitive method of recording delivery information can be altered by using mobile electronic delivery. The management of delivery information will be improved. Compared to PDA, netbook has the advantages as big operation interface, cheap, easy to use (similar to the general notebook computer operation) etc. Because of the advantage of 3G wireless networks, it has been gradually used in various fields (especially communications, logistics industry, etc).
In this paper, the framework of mobile electronic delivery platform for iron and steel sales logistics based on 3G netbook is studied. The paper is organized in the following way. Delivery process design is given in Section 2. Software architecture is proposed in Section 3. Function design is analyzed in Section 4. Key technology in realization is discussed in Section 5. Conclusions are given in Section 6.
2. Iron and Steel Sales Logistics Delivery Process Based on 3G Netbook
Mobile electronic delivery platform is designed to realize the real-time acquisition of delivery information, which can help to achieve effective management of the whole process of logistics delivery. The logistics systematic level and logistics management level can be improved. The main thought of this platform is organized as follows: Mobile electronic delivery platform is built with 3G wireless networks. The real-time delivery information will be mastered by installing the platform on vehicles and vessels, which can help to make management more convenient. The carriers can be supervised, too.
On the basis of the different modes of transportation, the delivery ways of iron and steel logistics mainly include highway delivery and waterway delivery. The assignment sheet loaded is used as delivery receipt in highway delivery, which is generated with goods leaving warehouse. It is issued by the warehouse manager to highway carriers, and endorsed by the single corresponding consignee at destination. The assignment sheet on board which is issued by dock outgoing group is used in waterway delivery. They are sent group to waterway carriers when vessels leave the port. To be different with the highway delivery, the assignment sheet on board is consisted of one or more assignment sheets loaded and corresponded to more than one consignee. The carrier mission can not be finished until the assignment sheet on board is endorsed by the consignees one by one. Therefore, the design of mobile electronic delivery platform should be combined with the different delivery ways.
According to the above design concept, the whole transport process can be divided into several node types: carriage node, transit node (emergency prevention) and delivery node based on a large-scale iron and steel enterprise. The mobile electronic delivery platform is designed to do the real-time management of these logistics nodes. A whole transport process is consisted of one outbound carriage, one receiving delivery and zero or more times of transit delivery and transit carriage. The transit delivery information must be filled in when outbound carriage cannot be finished by one time. The fuses may be vehicles’ own fault, traffic accidents, or natural causes (e.g., weather, damaged roads). One transit carriage must be corresponded to one transit delivery. They must be in pairs. The delivery process is only finished after the assignment sheet has gone through receiving delivery. That is to say, carriage information should be filled in by the user of the mobile electronic delivery platform based on 3G netbook before beginning outbound carriage (off-port carriage). Then transfer delivery information must be submitted to record transfer details and interim reasons if any abnormality. In the end, the receiving delivery information confirmed by consignee is submitted to complete the transportation process.
The operation schematic of mobile electronic delivery platform based on 3G netbook for iron and steel sales logistics is shown in Figure 1. The netbook is taken along with the carries (including vehicles and vessels). The delivery information can be submitted at any time everywhere and transmitted to application server in time. Then the data will be processed at application server and sent back in order to reduce the user’s workload of inputting them manually. The design of mobile delivery platform is completed with the technology of assignment sheet tracked [10]. The status of carriage and delivery is updated and sent to the monitoring center by the carrier timely. Therefore, the whole delivery process can be followed.
3. Software Architecture
C/S (Client/Server) architecture and B/S (Browser/Server) architecture are the mainstreams of development models. Compared with B/S architecture, C/S architecture system can allocate tasks more reasonably by deploying client programs to many computers. The pressure of the server can be reduced effectively. The utilization of the client computers is increased. Friendly man-machine interface is provided. The cost of the whole system is reduced. And enterprise internal resources are reliably protected. For this reason, C/S software architectural model is adopted to design mobile electronic delivery platform in this paper.
The design of this platform is on account of the intranet and public network in order to protect the enterprise security. ERP database is used to provide the upstream
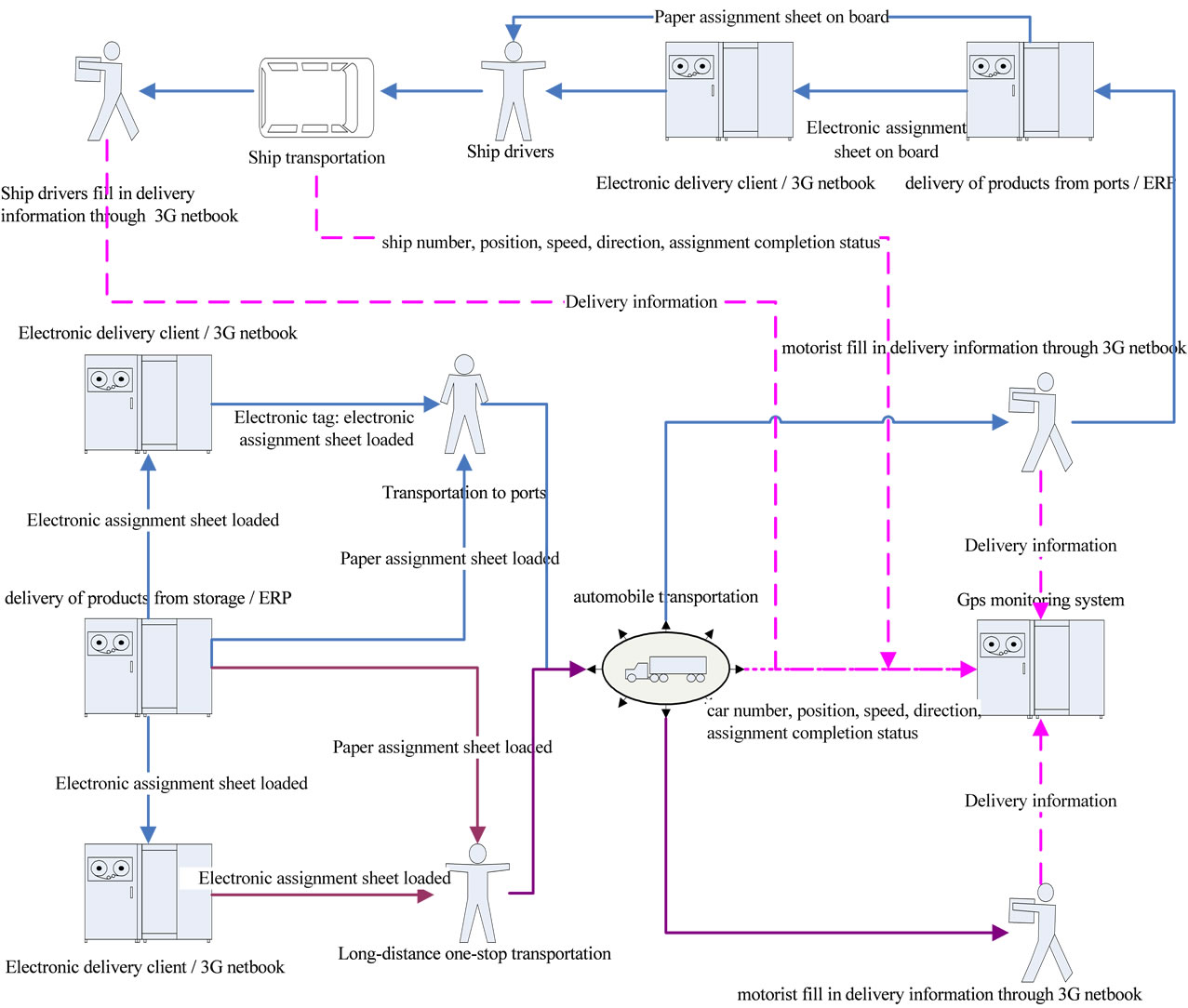
Figure 1. The run chart of 3G netbook based mobile delivery platform for iron and steel sales logistics.
data sources. The data is sent to electronic delivery database server gone through data exchange server. The threetier C/S-based framework consisted of the client layer, the application layer and the data layer is adopted for the platform. The transmission and sharing of data is realized via the mutual interaction among them.
The architecture of logistics electronic delivery platform based on netbook/3G technology and GPRS communication technology is shown in Figure 2. The delivery information can be submitted at any time anywhere by the netbook installed on carriage vehicles and vessels. This real-time information will be sent to the application server by 3G networks. The administrators can also inquiry the information on the platform to achieve the target to trace the whole sales logistics process. Visual C++ 6.0 development environment is used to develop the client and application server procedures of the platform. Oracle 10 g is used to implement the database management system. The 3G netbook is used as a carrier to run the client procedure. The communication of the client and application server is based on TCP/IP protocol which can make data transmission security and reliability. Data analysis and data transmission are completed at application server. Data storage and data transmission are achieved by the interaction of both the database server and the application server.
The real-time data flow diagram is shown in Figure 3. A request can be sent to the application server according to users’ needs. The server returns the information required by retrieving data from the database. The transfer state of the assignment sheet is updated in the client by users. Then the real-time data will be sent to the server. The corresponding records in database will be refreshed at the same time. The whole process of the transportation and delivery is being monitored by operation of the client. Thus, the problems of the logistics process can be found
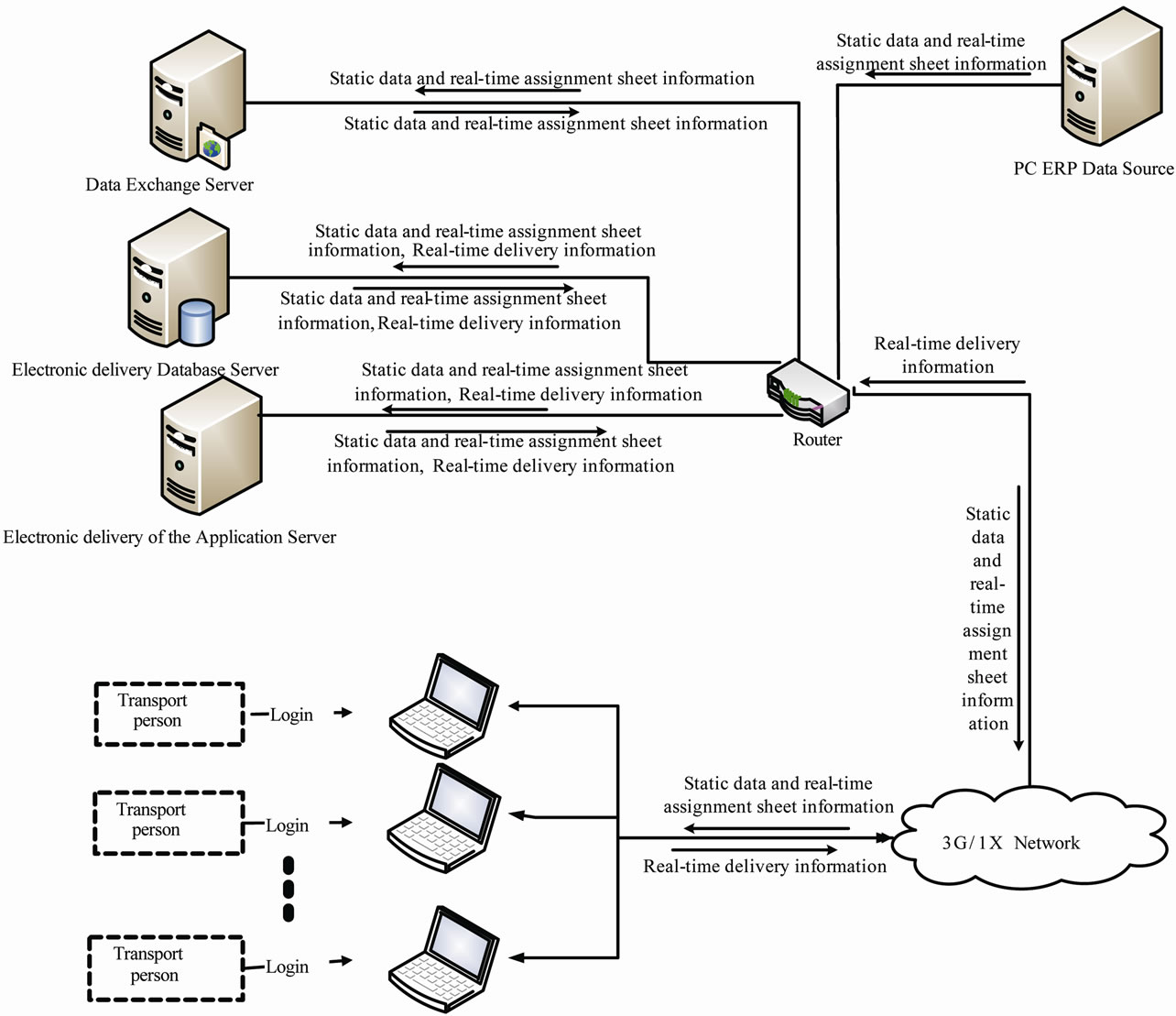
Figure 2. Platform chart.
easily.
4. System Function
According to the previous data flow analysis, the entire platform is divided into three parts: the server, the client for vehicles and the client for vessels. The function of the server is consisted of the following parts:
1) Receiving client connections Accept the connection request from clients. Process the business requisitions submitted, and store them into database. Return the results of the user’s requirements. Achieve functions of business logic layer.
2) Recording client requisitions Record the business requisitions submitted by different clients. Display them in server interface and store them in log files in order to facilitate information maintenance.
3) Receiving and processing electronic delivery information Receive requests from the client, and return the current information of the assignment sheet according to the database records. Then the user can facilitate to do the next step. Objection photos can be appended as instruction.
4) Modifying electronic delivery information Support the modification of the delivery information which has been submitted. Update the corresponding database records.
5) Querying electronic delivery information Get delivery information, details and objection photos of each logistics node by entering the assignment sheet loaded, or ship assignment sheet on board, or tag No., or order No.. Achieve the target to control the whole process. Return data to the client for display.
6) Fast delivery
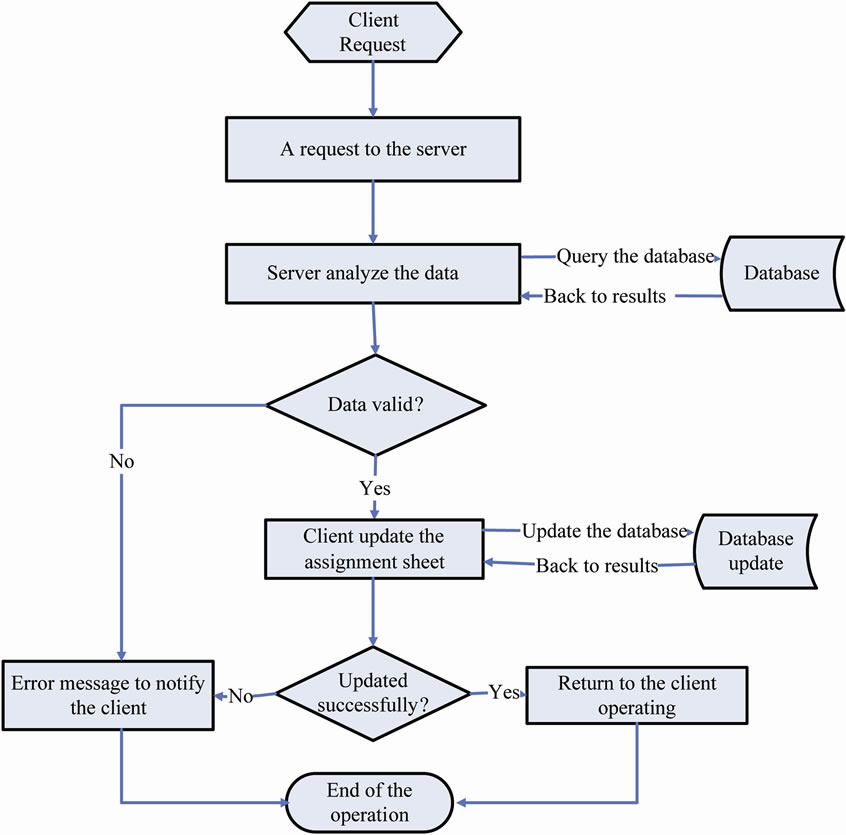
Figure 3. Real-time data flow diagram.
Automatically calculate the transport stage of the assignment sheet selected, which can help the user to submit delivery information in a quickly and easily way when the delivery information has been completely filled in. Store the submitted information into the database.
The client procedures are divided into the client for vehicles and the client for vessels. The structure is shown in Figure 4.
The structure of the client platform module is showed in Figure 4. According to the actual demand and the practical application background, the functions of each client including user management, electronic delivery information inputting, information querying and changing is proposed.
1) Electronic delivery information input Transfer type (outbound carrier, transit delivery, transit carrier and receiving delivery) of the assignment sheet will be pointed out when it is selected. Execute the submitting operation after the transfer state (No objection or Disagree) has been verified correctly and the information has been filled in completely. The addition photos can be appended if there are objections to the transport node.
2) Electronic delivery information change The information which had been submitted can be modified.
3) Electronic delivery information query
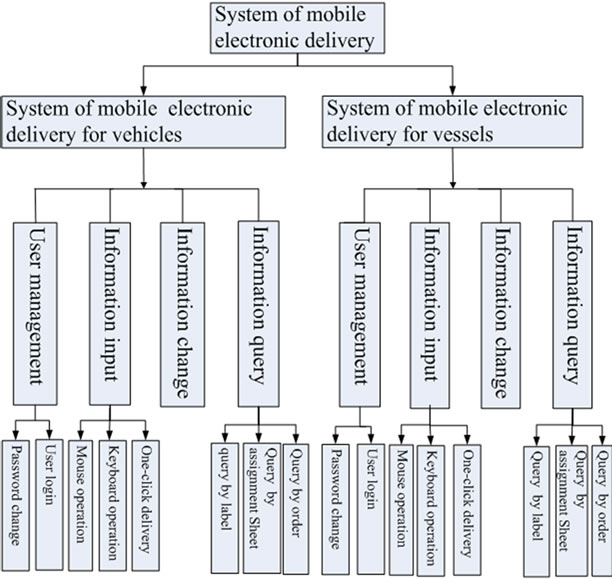
Figure 4. Structure of client platform module.
Get delivery information, details and objection photos of each logistics node by entering the assignment sheet loaded, or ship assignment sheet on board, or tag No., or order No., which can help to trace the quality of the whole process.
4) User management User rights management, user information revising and user passwords maintenance are included.
5) Keyboard operation and fast delivery All operations can be done by the keyboard. The transport stage of the assignment sheet can be calculated automatically. The delivery information can be quickly and easily submitted by the button of one-click delivery when the assignment sheet loaded is selected.
5. Key Realization Technology
The following key technologies have been used to realize the functions of the mobile electronic delivery platform.
1) 3G network communication technology TCP/IP network communication based on C/S has been put to use in this platform. The client connects to the server forwardly. Multi-thread communication and three-tier C/S-based platform framework (the appearance layer, business logic layer, database layer) are used in the application server to synchronize data exchange.
2) Photo access technology The photo reading and writing techniques based on MFC development framework and Oracle database are applied for the platform comprehensively. ActiveX Data Object is adopted. Its functions such as AppendChunk() and GetChunk() are being used to access large object data of BLOB type.
3) Photo transmission technology The multi-threaded file transmission based on the socket is used to transfer photos. The special-purpose thread which had a separate port is being used to realize the transmission of large files and other instructions synchronously.
4) Fully keyboard operation technology The keyboard overloaded technology based on MFC development framework is made extensive use in this platform. The submission of transport information can be completed with keyboard absolutely. For example, the cursor can be captured automatically, and the focus of the controls can be determined intelligently. Therefore, delivery information can be submitted quickly and easily.
The real effect of this mobile electronic delivery platform is shown in Figures 5 and 6.
The main interface of client is shown in Figure 5. The tab pages of delivery information inputting, delivery information querying and password changing is shown in the left part in order of priority. The first tab page is default to display after successful logon. As shown in Figure 5, the list of the assignment sheets based on travel No. and its receiving customer list are given in the left. The corresponding receiving customer can be selected automatically when the assignment sheet has been clicked.
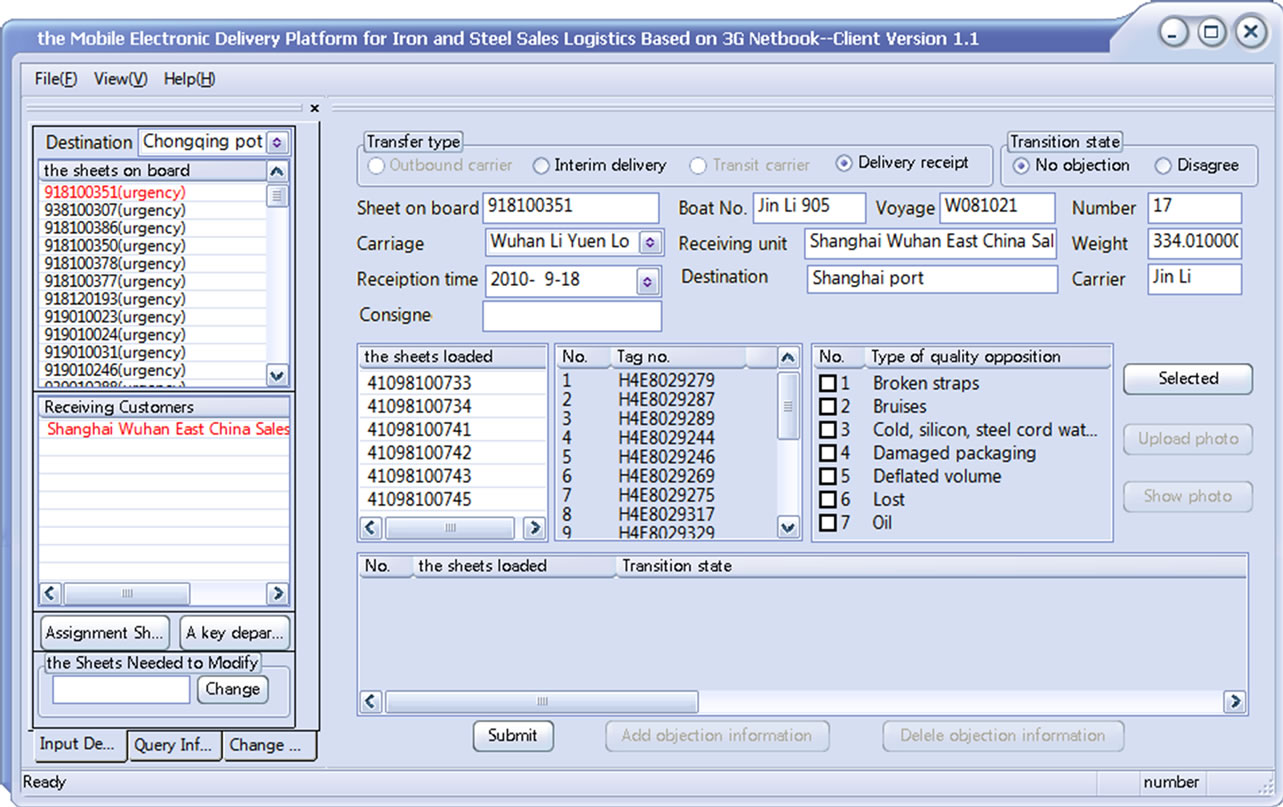
Figure 5. The main interface of the client.
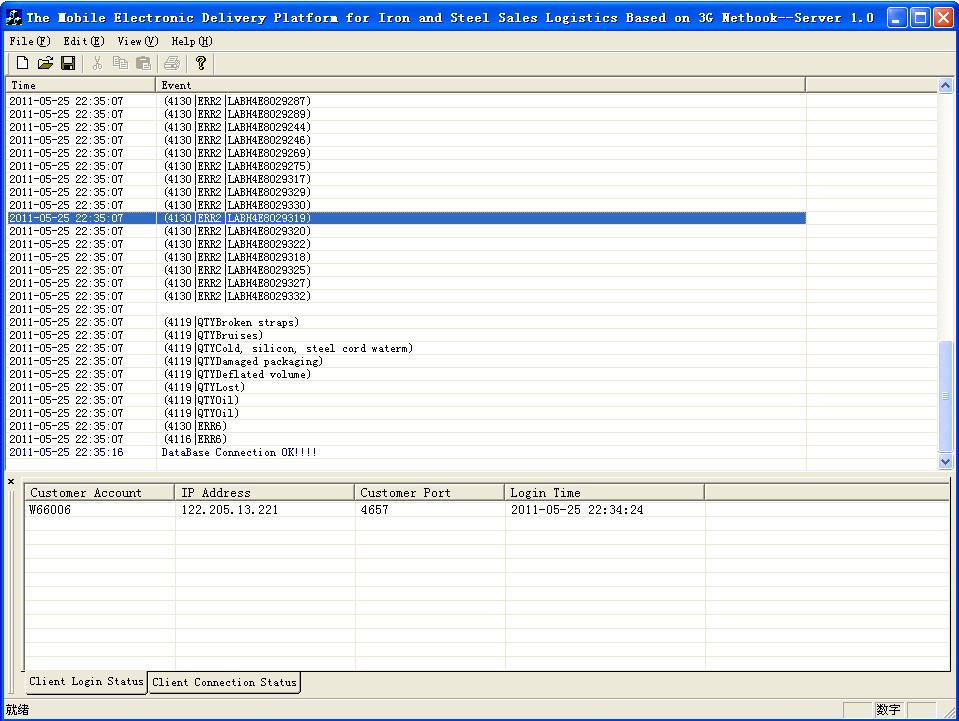
Figure 6. The main interface of the application server.
Or its customers will be listed if this assignment sheet has more than one receiving customers. The corresponding basic information will be displayed in the right interface following. Then the delivery information can be submitted easily.
The main interface of application server is shown in Figure 6. The events window and the output window are included. The occurred time and content of all operations in the application server are displayed in the events window. The output window is composed of the tab page that recording the status of the client login and the tab page which is used to record the client connection. The details as user account, IP address, port and logon time about all current users logged to the application server is displayed in the first tab page. All events of the client connection such as login successful, password error, exiting, etc are recorded in the next tab page.
6. Summary
The delivery information can be submitted at any time everywhere on the mobile electronic delivery platform based on 3G netbook for iron and steel sales logistics. Then the whole process of transportation and delivery can be monitored. More comprehensive information of quality opposition can be provided to distinct responsibility for compensation. The logistics risk can be reduced. The logistics management can be improved. The speed of reflecting and processing quality objection should be accelerated. Customer satisfaction will be improved and the image of iron and steel enterprises will be enhanced. And it can help carriers improve their transportation quality. The economic efficiency of enterprises will be improved as well.
It is an innovation of e-commerce in logistics field to develop the mobile electronic delivery platform for iron and steel sales logistics based on 3G technology with WAP protocol. It plays an important role of enhancing its management and reducing its logistics costs of the iron and steel enterprises.
7. Acknowledgements
The project was done with the Logistics Management Company of Wuhan Iron and Steel (Group) Corporation.
This research was also supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 60804038), and key scientific and technical research project of Ministry of Education of China (Grant No. 109104). This support is acknowledged gratefully.
REFERENCES
- X. Q. Zhang, “The Delivery of Goods Carrying under Bill of Lading,” Master’s Dissertation, Shanghai Maritime University, Shanghai, 2007.
- M. K. Sun, Z. J. Wang and J. Zhang, “The Design of the Moving, Inquiring, Monitoring and Navigating System Based on PDA—GPRS/GPS/GIS,” Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, Vol. 28, No. 5, 2005, pp. 70-73.
- R. M. Qian and Y. L. Hu, “The Design of Flood Control Application System Based on PDA of Jiangxi Province,” Jiangxi Hydraulic Science & Technology, Vol. 32, No. 4, 2006, pp. 191-194.
- B. A. Clark and J. D’Onofrio, “System for Communication with an Electronic Delivery System that Integrates Global Financial Services,” US Patent No. 5890140, 1999.
- G. Ghiani, F. Guerriero, G. Laporte and R. Musmanno, “Real-Time Vehicle Routing: Solution Concepts, Algorithms and Parallel Computing Strategies,” European Journal of Operational Reaserch, Vol. 22, No. 2, 2003, pp. 340-349.
- G. M. Giaglis, I. Mimis, A. Tatarakis and V. Zeimpekis, “Minimizing logistics Risk through Real-Time Vehicle Routing and Mobile Technologies,” International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, Vol. 34, No. 9, 2004, pp. 749-764.
- K. Xie, “Study on the Frontier Port Logistics System of Yunnan,” Logistics Technology, No. 230-231, 2010, pp. 11-14.
- X. H. Jiang and Y. Z. Lu, “Discuss the Application and Development of Electronic Payment in the Tourism,” Modern Business, No. 2, 2011, pp. 168-169.
- W. C. Li, “Research and Design the Atchitecture and Key Technologies of SDP,” Master’s Dissertation, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing, 2007.
- S. R. Mei, X. C. Huang and J. J. Hu, “Research on the Development of Sales Logistics Management and Control Systems for Iron and Steel Enterprises,” Computer Engineering & Science, Vol. 33, No. 1, 2011, pp. 176-180.

