International Journal of Organic Chemistry
Vol.4 No.1(2014), Article ID:43931,8 pages DOI:10.4236/ijoc.2014.41010
In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Some Novel 3-(Substituted Phenyl) Isocoumarins, 1(2H)-Isoquinolones and Isocoumarin-1-Thiones
Zaman Ashraf1*, Aamer Saeed2
1Department of Chemistry, Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad, Pakistan
2Department of Chemistry, Quaid-I-Azam University, Islamabad, Pakistan
Email: *mzchem@yahoo.com
Copyright © 2014 by authors and Scientific Research Publishing Inc.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/


Received 20 January 2014; revised 28 February 2014; accepted 10 March 2014
ABSTRACT
The work reports antibacterial and antifungal activity of some 3-(substituted phenyl) isocoumarins (1H-2-benzopyran-1-ones), isocarbostyrils 1(2H)-isoquinolones, the nitrogen analogues of isocoumarins and isocoumarin-1-thiones, the thio derivatives of isocoumarins. The antimicrobial activity was determined against ten different Gram positive and Gram negative bacterial strains and three fungal strains. The bacterial strains were Klebsiella pneumonae (ATCC 6633), Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 29213), Micrococcus luteus (ATCC 9341), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 33347), Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922), Salmonella typhi (ATCC 19430), Lactobacillus bulgaricus, (ATCC 25929), Pasteurella multocida A (ATCC 9150), Staphylococcus epidermidis (ATCC 29232) and Proteus vulgaris (ATCC 49565) and fungal strains were Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus nigar and Aspergillus pterus. Agar well diffusion method was followed for antibacterial activity and poison plate method was adopted for antifungal assay. Chloramphenicol and fluconazole used as standard drugs for antibacterial and antifungal activity respectively. In general, these compounds exhibited high antibacterial potential than antifungal. Comparative study reveals that the 1-thio derivatives are more active than parent isocoumarins but 1(2H)-isoquinolones, are less active. Most of these compounds showed poor activity but some of these compounds exhibited moderate to good activity against Staphylococcus epidermidis, Klebsiella pneumonae, Escherichia coli and Proteus vulgaris, compared with the standard drug.
Keywords:Antimicrobial Activity; Isocoumarins; Isocarbostyrils; 1-Thioisocoumarins

1. Introduction
Isocoumarins are the secondary metabolites of fungi, bacteria, plants and insect venoms and pheromones. A huge number of them have been isolated from fungi, lichens and bacteria. Some higher plants, insect and marine organisms are also the rich source of these secondary metabolites [1] [2] . They exhibit a broad range of pharmacological activities including antimalarial, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, cytotoxic, antiangiogenic and antiallergic [3] -[9] . Isocoumarins are also used as a lead compound for the identification of insecticides which selectively bind at the insect GABA receptor [10] .
3-Substituted isocoumarins also show anti HIV activity in vitro, diuretic, antihypertensive, antiarrythmics, β-sympatholytics, anticorrosive, laxatives, asthmolytic, phytotoxic, and are useful in the treatment of emphysema [11] . Isocoumarin derivatives are potently inhibits endothelial cell proliferation, migration, sprouting, tube formation in vitro, and tumor growth in vivo [12] .
1(2H)-isoquinolones are the nitrogen analogues of isocoumarins. 1(2H)-isoquinolone derivatives are found in several bioactive natural product such as thalifolin, doryphorine [13] , ruprechstyril [14] , narciclasine [15] , lycoricidine [16] and the alkaloids coryaldine and thalflavine. Substitutd isoquinolones exhibit antidepressant, antiinflamatory, analgesic, hypolipidimic, and analeptic activities have also been reported.
Though a number of new antibiotics have been produced in the last three decades, yet resistance to these drugs by microorganisms has developed. Some antibiotics have become almost obsolete because of drug resistance [17] . In general, bacteria have the genetic ability to transmit and acquire resistance to drugs utilized as therapeutic agents [18] . Consequently new drugs must be synthesized and assayed against these pathogenic resistant microorganisms for the sake of life.
The present study has been designed to determine the in vitro antibacterial and antifungal activity of 3-(substituted phenyl)isocoumarins, 1-thioisocoumarins and 1(2H)-isoquinolones against some pathogenic and nonpathogenic strains. A comparison of the efficacy of these classes of compounds and then establishes a structure activity relationship between differently substituted analogues of isocoumarins, 1-thioisocoumarins and isoquinolones is also discussed.
2. Materials and Method
In this in vitro antimicrobial assay, we used three series of the compounds i.e. 3-(substituted phenyl) isocoumarins (1H-2-benzopyran-1-ones) (1 - 10), (isocarbostyrils 1(2H)-isoquinolones, the nitrogen analogues of isocoumarins (1H-2-enzopyran-1-ones) (11 - 20) and 1-thioisocoumarins (1H-isochromenes-1-thiones) (21 - 30). Each series contains ten compounds having different functionality at position 3. All of the compounds used in this study have been synthesized, purified and characterized by the author [19] [20] . All chemical used are of analytical grade. The purified samples were dissolved in DMSO 5 mg/ml which is the negative control in this bioassay. The antibiotic chloramphenicol and fluconazole were used as standard drugs for antibacterial and antifungal activity respectively.
2.1. Antibacterial Activity
The antibacterial assay was performed by agar well diffusion method against ten different Gram positive and Gram negative bacterial strains [21] . The bacterial strains Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonae (ATCC 6633), Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 29213), Micrococcus luteus (ATCC 9341), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 33347), Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922), Salmonella typhi (ATCC 19430), Lactobacillus bulgaricus, (ATCC 25929), Pasteurella multocida A (ATCC 9150), Staphylococcus epidermidis (ATCC 29232) and Proteus vulgaris (ATCC 49565) were selected in this study. Micrococcus luteus, Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis are the Gram positive whilst the remaining seven are Gram negative bacteria. All of the tested microorganisms were maintained on nutrient agar at 4˚C and sub-cultured before use.
The bacteria studied are clinically important ones causing several infections and it is essential to overcome them through some active therapeutic agents. Each tested bacterium was sub-cultured in nutrient broth at 37˚C for 24 h. One hundred microliters of each bacterium was spread with the help of sterile spreader on to a sterile Muller-Hinton agar plate so as to achieve a confluent growth. The plates were allowed to dry and wells (6mm diameter) were punched in the agar with the help of cork borer. 0.1 mL of the each compound solution (5 mg/ mL) in DMSO was introduced in to the well and the plates were incubated overnight at 37˚C.
The antimicrobial spectrum of the compounds was determined for the bacterial species in terms of size of the zones around each well and results are presented in tables 1-3. The diameters of the zone of inhibition produced by the compounds were compared with those produced by the commercial antibiotic chloramphenicol (5 mg/mL). This is the common antibiotic used for the treatment of infections caused by gram positive and gram negative bacteria. The control activity was deducted from the test and the results obtained were plotted. The experiment was performed three times to minimize the error and the mean values are presented.
2.2. Antifungal Activity
Antifungal activity of these three series of compounds was determined by using three fungal strain; Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus nigar and Aspergillus pterus using poison plate method [22] . Potato dextrose agar (PDA) plates were equipped by using pour plate technique for each compound. A 2% concentration of the synthesized compounds in DMSO as a solvent was used. A 2% solution of fluconazole was used as standard. A drug free control was included and plates were observed for growth after 48 h of static incubation at 30˚C and results are presented in tables 4-6. All of the synthesized compounds showed poor antifungal activity against the selected fungal strains. The 1-thioisocoumarins showed good growth inhibition than the parent isocoumarins and isoquinolones. The Aspergillus niger is the most resistant strain against these isocoumarins derivatives.
3. Results and Discussion
The antibacterial activity of the 3-phenylsubstituted isocoumarins, 3-phenylsubstituted isoquinolin-1(2H)-ones and 3-phenylsubstituted 1H-isochromenes-1-thiones was determined against ten bacterial strains and reported in tables 1-3 respectively. The results of the antibacterial assay of these three series of compound reflect that the 3-phenyl substituted isocoumarins are more active as compared to their nitrogen analogues but less active as compared to their thio analogues. The structures of the compounds of these three series are shown in figure 1.
Table 1. In vitro Antibcterial activity of 3-substituted isocoumarins (1 - 10).
Table 2. In vitro Antibcterial activity of 3-substituted isoquinolones (11 - 20).
Table 3. In vitro Antibcterial activity of 3-substituted-1-thioisocoumarins (21 - 30).
*Activity of each sample is measured by subtracting the activity of DMSO, (-) No activity. Escherichia coli (E. c.), Klebsiella pneumonae (K. p.), Lactobacillus bulgaricus (L. b.), Micrococcus luteus (M. l.), Pasteurella multocida (P. m.), Proteus vulgaris (P. v.), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. a.), Salmonella typhi (S. t.), Staphylococcus aureus (S. a.) and Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. e.).
Table 4. In vitro Antifungal activity of 3-substituted isocoumarins (1 - 10).
Table 5. In vitro Antifungal activity of 3-substituted isoquinolones (11 - 20).
Table 6. In vitro Antifungal activity of 3-substituted-1-thioisocoumarins (21 - 30).
(-) No activity.
Among all the ten differently 3-phenylsubstituted isoquinolin-1(2H)-ones only the 3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)- 1(2H) isoquinolone (18) shows moderate to potent activity against these tested microorganisms. It shows potent activity against K. pneumonae and have moderate efficacy against L. bulgaricus and P. multocida. These results indicate that in case of 1(2H) isoquinolones presence of two electronegative halogen (chlorine) functionality is important in showing antibacterial activity. It is inactive against gram negative bacteria and all of the remaining 1(2H) isoquinolones are inactive against both selected gram positive and gram negative bacterial strains.
Most of the 3-phenylsubstituted isocoumarins are inactive against these tested gram positive and gram negative bacterial strains. The 3-(4-nitrophenyl) isocoumarin (7) exhibits moderate activity against all the selected gram positive and gram negative bacterial strains. The compound 3-(3-flourophenyl)isocoumarin (9) shows moderate activity against L. bulgaricus and P. auriginosa which are gram positive bacterial strains but is inactive against all the remaining gram positive and gram negative bacterial strains.
It was found that 3-phenylsubstituted 1H-isochromenes-1-thiones show potent activity against gram positive bacteria and three derivatives also exhibit activity against gram negative bacteria. 3-(3-Iodophenyl)-1H-isochromenes-1-thiones is most active against E. coli but inactive towards all other tested microorganisms. Similarly
Figure 1. Structures of the compounds.
3-pentadecyl-1H-isochromenes-1-thiones (21) and 3-(2-chloro-4-flourophenyl)-1H-isochromenes-1-thiones (30) shows activity against K. pneumonae and S. epidermidis but are inactive against all other bacterial strains. 3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-1H-isochromenes-1-thiones (28) has maximum potential in inhibiting the growth of K. pneumonae but possess moderate activity against the S. epidermidis. 3-(3-flourophenyl)-1H-isochromenes- 1-thiones (29) is the member of this series which shows maximum effectiveness against both gram positive (E. coli, L. bulgaricus, P. vulgaricus) and gram negative (M. luteus, S. epidermidis) bacteria. Some other members of this series also possess moderate activity against these studied microorganisms.
The antifungal activity results showed that most of the isaocoumarin analogues exhibited poor to moderate activity but some of the compounds displayed excellent growth inhibition. 3-(4-fluorophenyl)isocoumarin (5) and 3-(2-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)isocoumarin (10) showed good growth inhibition against Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus pterus but moderate activity against Aspergillus nigar. Most of the 3-substituted isoquinolones (11 - 20) depict poor or no antifungal activity against the selected fungal strains. 3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1(2H) isoquinolone (15) and 3-(2-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-1(2H)-isoquinolone (20) possess moderate activity against Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus pterus but are not effective against Aspergillus nigar.
Some of the isocoumarin-1-thiones portrayed good to excellent activity against tested fungal stains. 3-(3- flourophenyl)-1H-isochromenes-1-thiones (29) and 3-(2-chloro-4-flourophenyl)-1H-isochromenes-1-thiones (30) represented excellent growth inhibition against Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus pterus and good activity against Aspergillus nigar. 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1H-isochromenes-1-thiones (25) having good antifungal potential against tested fungal strains. The thio derivatives of isocoumarins possess greater antimicrobial activity than nitrogen analogues and parent isocoumarins figure 2. The comparison of the antifungal activity among the three classes also presented in figure 3.
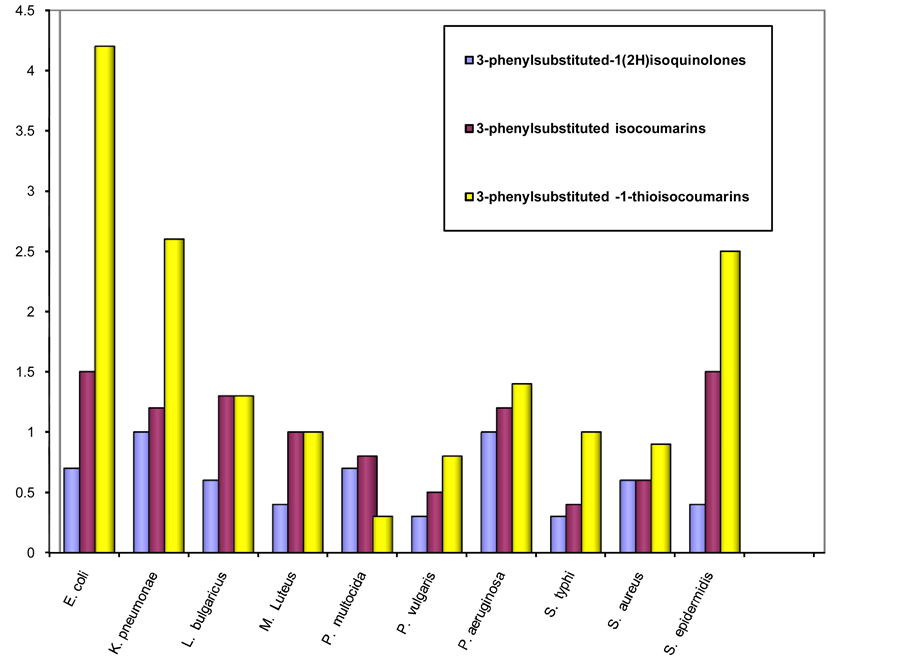
Figure 2. Comparison of the antibacterial activity of 3-phenylsubstituted isocoumarins (1 - 10), 3-phenylsubstituted isoquinolin-1(2H)-ones (11-20) and 3-phenylsubstituted 1H-isochromenes-1-thiones (21 - 30).
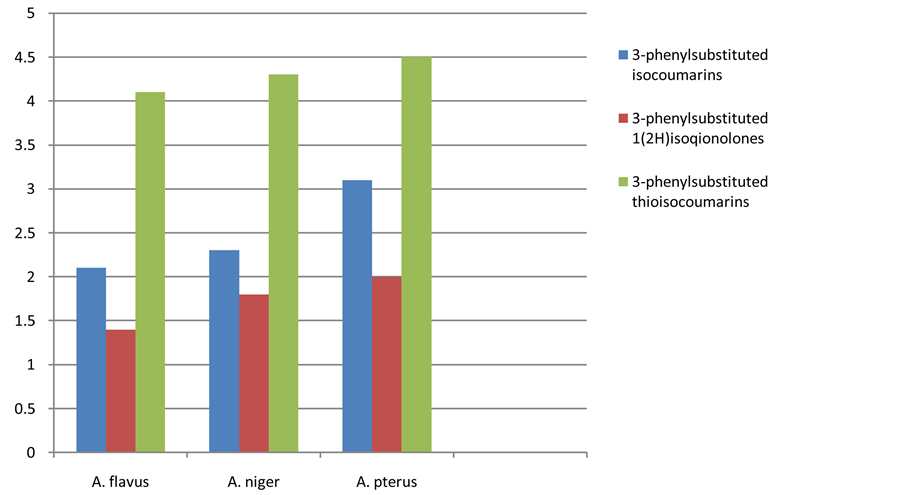
Figure 3. Comparison of the antifungal activity of 3-phenylsubstituted isocoumarins (1 - 10), 3- phenylsubstituted isoquinolin-1(2H)-ones (11 - 20) and 3-phenylsubstituted 1H-isochromenes-1-thiones (21 - 30).
4. Conclusion
We have concluded from this antibacterial assay that when the isocoumarins are converted into 1-thiones the biological activity of the resulting derivatives is increased and nitrogen analogues are less active as compared to parent isocoumarins. Most probably this is due to the high hydrophobicity of the sulphur analogues. In the nitrogen derivatives polarity is increased but hydrophobicity is decreased and as a result of decrease in the lipophilicity activity is decreased. Hydrophobic functionalities are the necessities for these compounds in exhibiting biological activity. The electronegativity of the substituents present at 3-phenyl ring also play an important role in biological activity. The fluorine and chlorine substituted derivatives are more active than the bromine and iodine ones.
References
- Napolitano, E. (1997) The Synthesis of Isocoumarins over the Last Decade. Organic Preparations and Procedures International, 29, 631-634. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00304949709355245
- Sankawa, U. (1999) Comprehensive Natural Products Chemistry. Elsevier Science Publishers Ltd., Amsterdam.
- Hisashi, M., Hiroshi, S. and Masayuki, Y. (1999) Structure-Requirement of Isocoumarins, Phthalides and Stilbenes from Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium for Inhibitory Activity on Histamine Release from Rat Peritoneal Mast Cells. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 7, 1445-1450. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0896(99)00058-9
- Masayuki, Y., Emiko, H., Yoshikazu, N., Kimiyo, I., Hisashi, M., Hiroshi, S., Johji, Y. and Nobutoshi, M. (1994) Development of Bioactive Functions in Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium. III. On the Antiallergic and Antimicrobial Principles of Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium (1). Thunberginol A, B, and F. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 42, 2225-2230. http://dx.doi.org/10.1248/cpb.42.2225
- (a) Hisashi, M., Hiroshi, S., Johji, Y. and Masayuki, Y. (1998) Immunomodulatory Activity of Thunberginol A and Related Compounds Isolated from Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium on Splenocyte Proliferation Activated by Mitogens. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 8, 215-220. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0960-894X(97)10221-9
- Authrine, C.W., James, B.G., James, A.S. and David, M. (1996) Cercophorins A-C: Novel Anti Fungal and Cytotoxic Metabolites from the Coprophilous Fungus Cercophora Areolata. Journal of Natural Products, 59, 765-769. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/np9603232
- Koohei, N., Mikikio, Y., Yoshiko, T., Kenichi, K. and Shoichi, N. (1981) Antifungal Activity of Oosponol, Oospolactone, Phylloducin, Hydrangenol, and Some Other Related Compounds. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 29, 2689-2691. http://dx.doi.org/10.1248/cpb.29.2689
- Takuya, F., Yoshiyasu, F. and Yoshinori, A. (1986) Polygonolide, an Isocumarin from Polygonum Hydropiper Possessing Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Phytochemistry, 25, 517-520. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(00)85513-2
- Jeong, H.L., Yun, J.P., Hang, S.K., Young, S.H., Kyu-Won, K. and Jung, J.L. (2001) Anti-Angiogenic Activities of Novel Isocoumarins, AGI-7 and Sescandelin. The Journal of Antibiotics, 54, 463-466. http://dx.doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.54.463
- Ozoe, Y., Kuriyama, T., Tachibana, Y., Harimaya, K., Takahashi, N., Yaguchi, T., Suzuki, E., Imamura, K. and Oyama, K. (2004) Isocumarin Derivatives as a Novel GABA Receptor Ligand from Neosartorya Quadricincta. Journal of Pest Science, 29, 328-331. http://dx.doi.org/10.1584/jpestics.29.328
- Hudson, J.B., Graham, E.A., Harris, L. and Ashwood-Smith, M.J. (1993) The Unusual UVA-Dependent Antiviral Properties of the Furoisocoumarin, Coriandrin. Phytochemistry and Photobiology, 57, 491-496.
- Corinne, L.R., Naoki, A., Jennifer, G.T., Michael, B., William, M.D., George, D.K., Susan, L.R., Michael, M., Robert, F., Raghu, K., Donald, K. and Surender, K. (2002) Antineoplastic Effects of Chemotherapeutic Agents Are Potentiated by NM-3, an Inhibitor of Angiogenesis. Cancer Research, 62, 789-795.
- Chen, C.Y., Chang, F.R. and Teng, C.M. (1999) Cheritamina, a New N-Fatty Acyl Tryptamine and Other Constituents from the Stem of Annona Cherimola. Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 46, 77-86.
- Pettit, G.R., Meng, Y.H., Herald, D.L., Graham, K.A.N., Pettit, R.K. and Doubek, D.L. (2003) Isolation and Structure of Ruprechstyril from Ruprechtia tangarana. Journal of Natural Products, 66, 1065-1069. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/np0300986
- David, G., Theodore, M. and Tomas, H. (1999) A Short Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of (+)-Narciclasine. Tetrahedron Letters, 40, 3077-3283.
- Richard, C.T. and James, K. (1990) An Annulative, Carbohydrate-Based Approach to Pancratistatin and StructurallyRelated Phenanthridone Alkaloids. Synthesis of (+)-Tetrabenzyllycoricidine. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 55, 6076-6078. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jo00312a007
- Ekpendu, T.O., Akshomeju, A.A. and Okogun, J.I. (1994) Antiinflamatory, Antimicrobial Activity. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 30, 379-384.
- Cohen, M.L. (1992) Epidemiology of Drug Resistance, Implications for a Post-Antimicrobial Era. Science, 257, 1050- 1057. http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.257.5073.1050
- Aamer, S. and Zaman, A. (2008) Synthesis of Some 3-Aryl-1H-Isochromene-1-Thiones. Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry, 45, 679-682. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jhet.5570450307
- Aamer, S. and Zaman, A. (2008) An Efficient Synthesis of Some 3-Aryl-Isoquinolin-1(2H)-Ones; Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds, 8, 1203-1208.
- Zaman, A., Aun, M., Muhammad, I. and Ahmed, H. (2011) In Vitro Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Methanol, Chloroform and Aqueous Extracts of Origanum vulgare and Their Comparative Analysis. International Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1, 257-261. http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijoc.2011.14037
NOTES

*Corresponding author.


